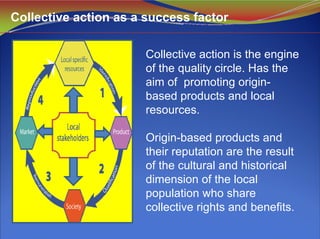
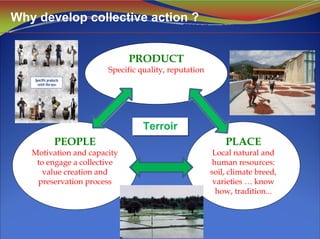
1) Collective action by local producers is important for developing and promoting origin-based products and preserving local cultural heritage and resources.
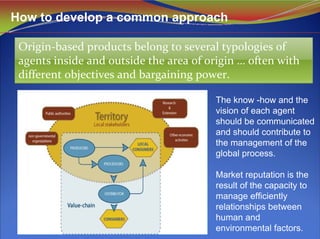
2) Successful collective action requires coordination among local producers, processors, certifiers and other stakeholders to establish common rules around production, quality standards, and marketing/branding of origin products.
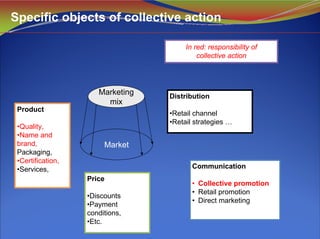
3) Defining a code of practice that specifies rules for all aspects of an origin product from production to marketing helps ensure economic returns for producers while protecting the reputation of the product over the long term.