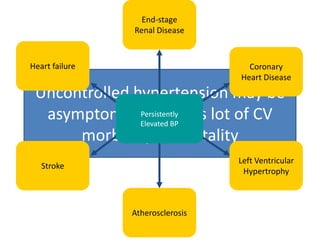
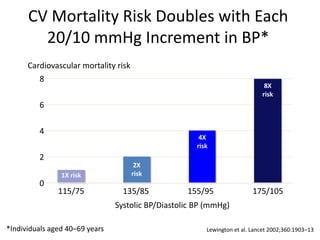
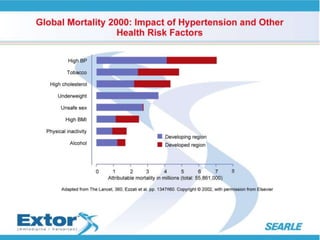
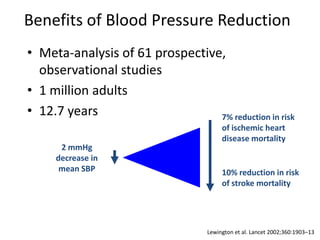
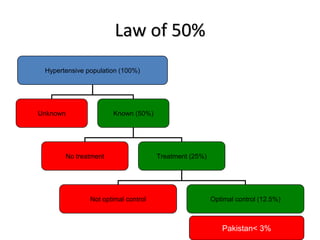
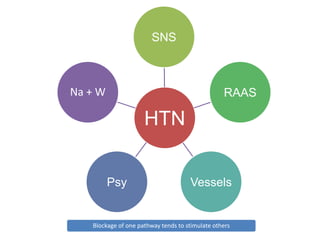
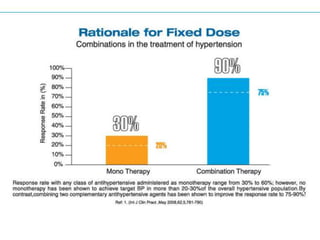
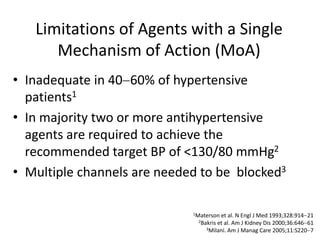
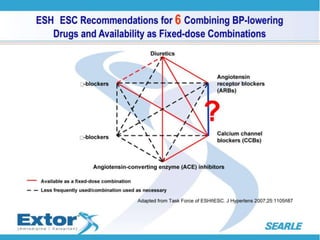
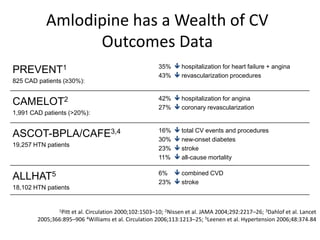
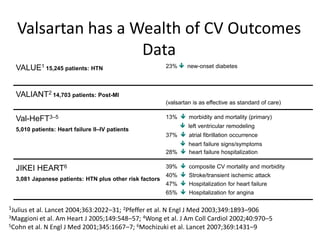
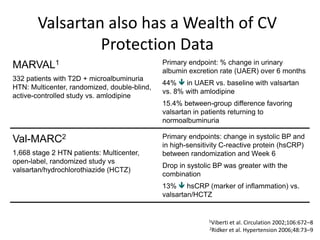
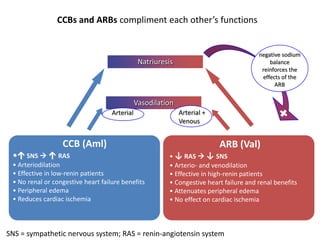
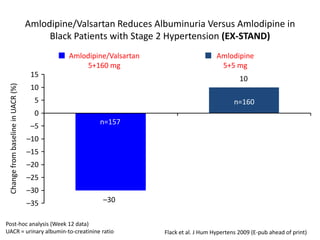
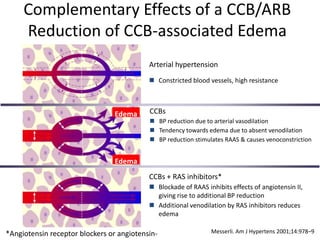
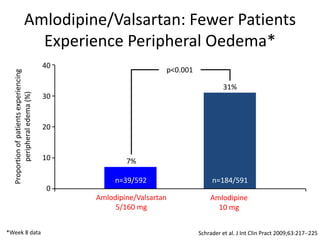
The document discusses hypertension and the benefits of combination therapy using amlodipine and valsartan. It summarizes that:
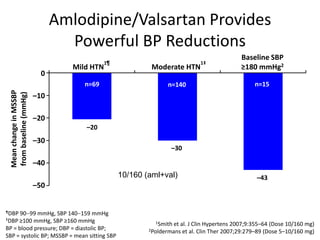
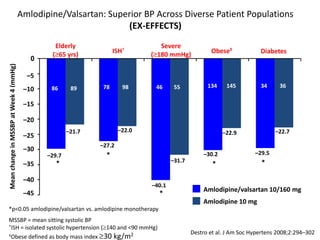
1) Amlodipine/valsartan provides powerful blood pressure reductions of up to 43 mmHg in systolic blood pressure across different hypertension severities and patient types, including the elderly, those with isolated systolic hypertension, obesity, and diabetes.
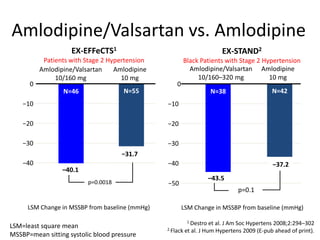
2) In patients uncontrolled on monotherapy, amlodipine/valsartan reduces blood pressure by around 21 mmHg on average.
3) Fewer patients experience peripheral edema with amlodipine/valsartan compared to amlodipine monotherapy.