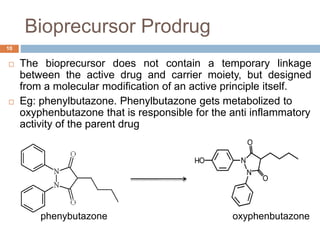
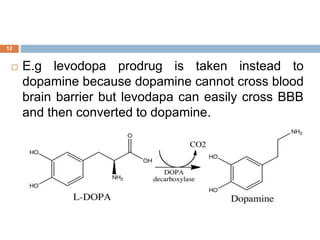
This document discusses prodrugs, which are medications that are metabolized in the body into an active drug. Prodrugs can improve how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted. Prodrugs are classified based on their structure and include carrier-linked bipartite, tripartite, and mutual prodrugs as well as bioprecursor prodrugs. The objectives of prodrugs are to improve solubility, stability, bioavailability, and therapeutic effects while decreasing toxicity. Examples are given of prodrugs that increase stability, such as levodopa, and those that increase bioavailability, such as ampicillin esters.