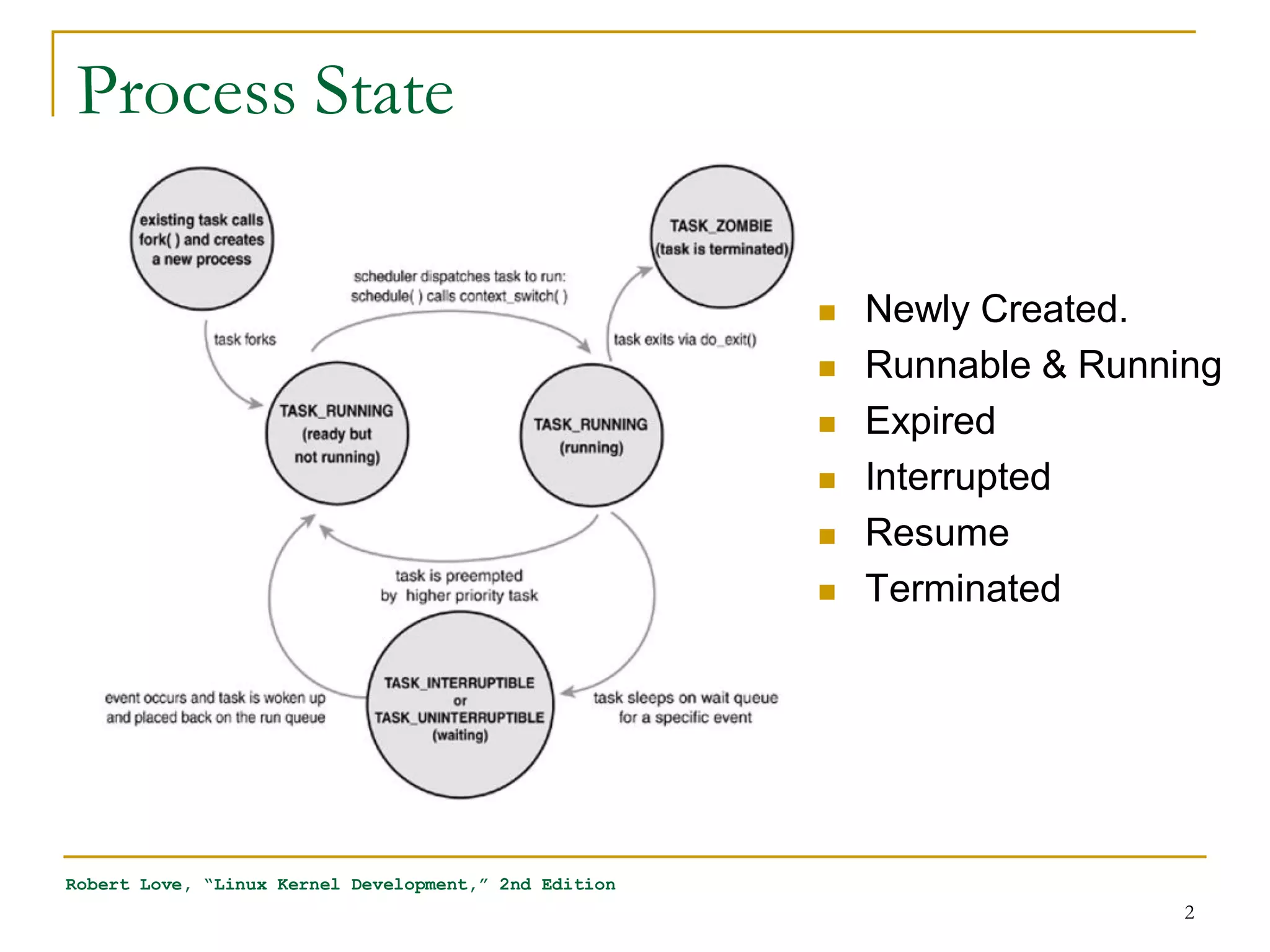
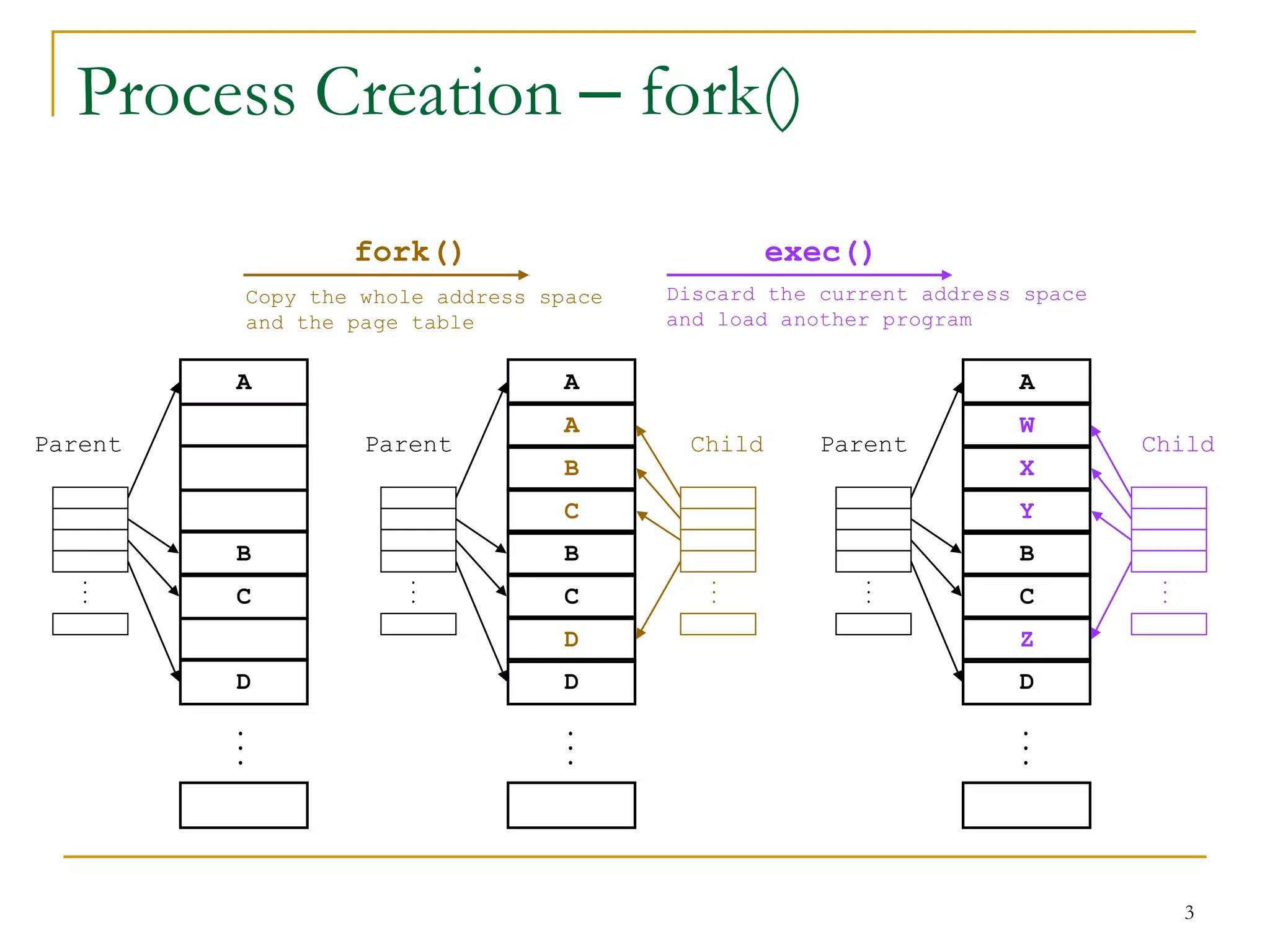
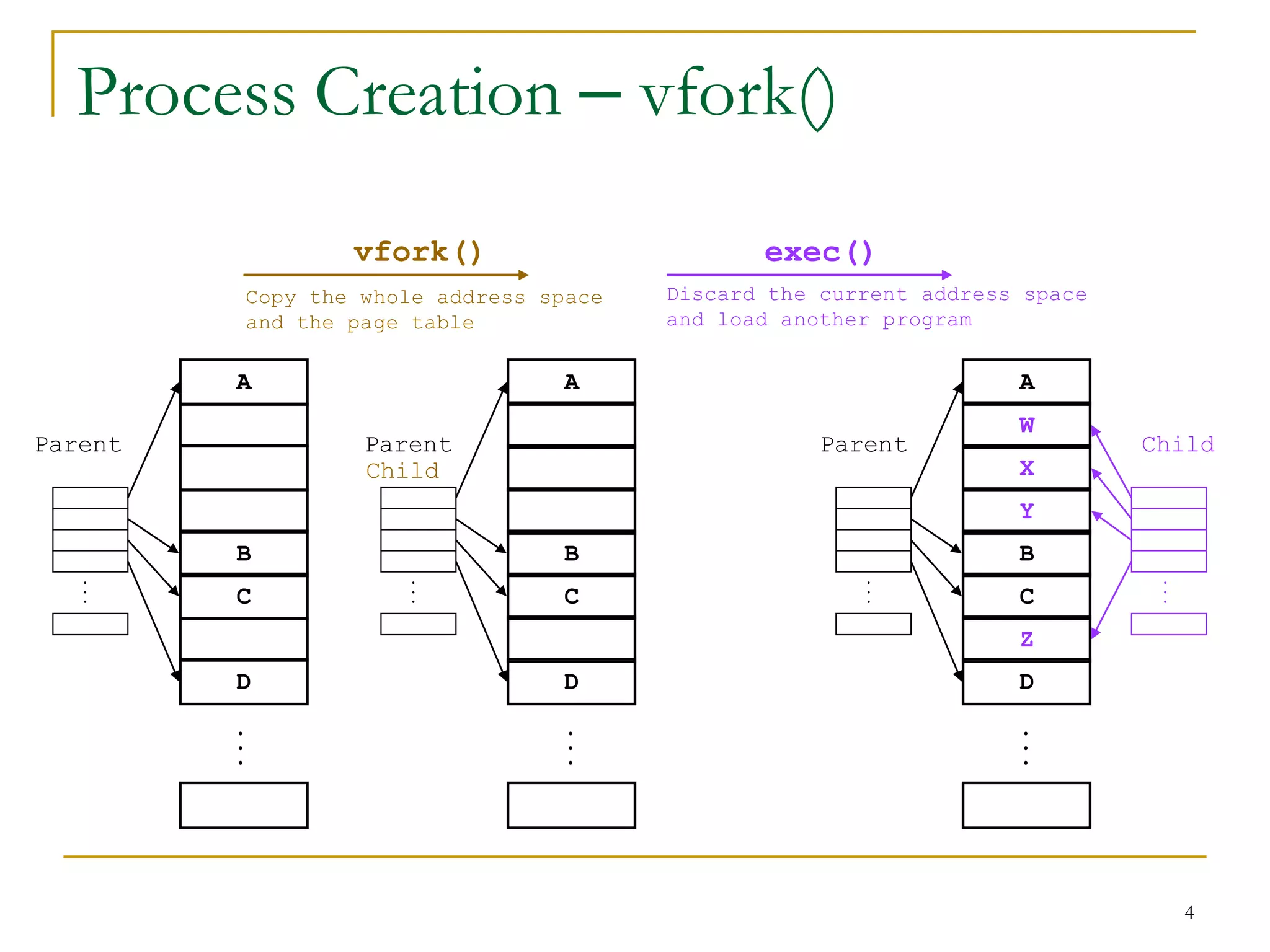
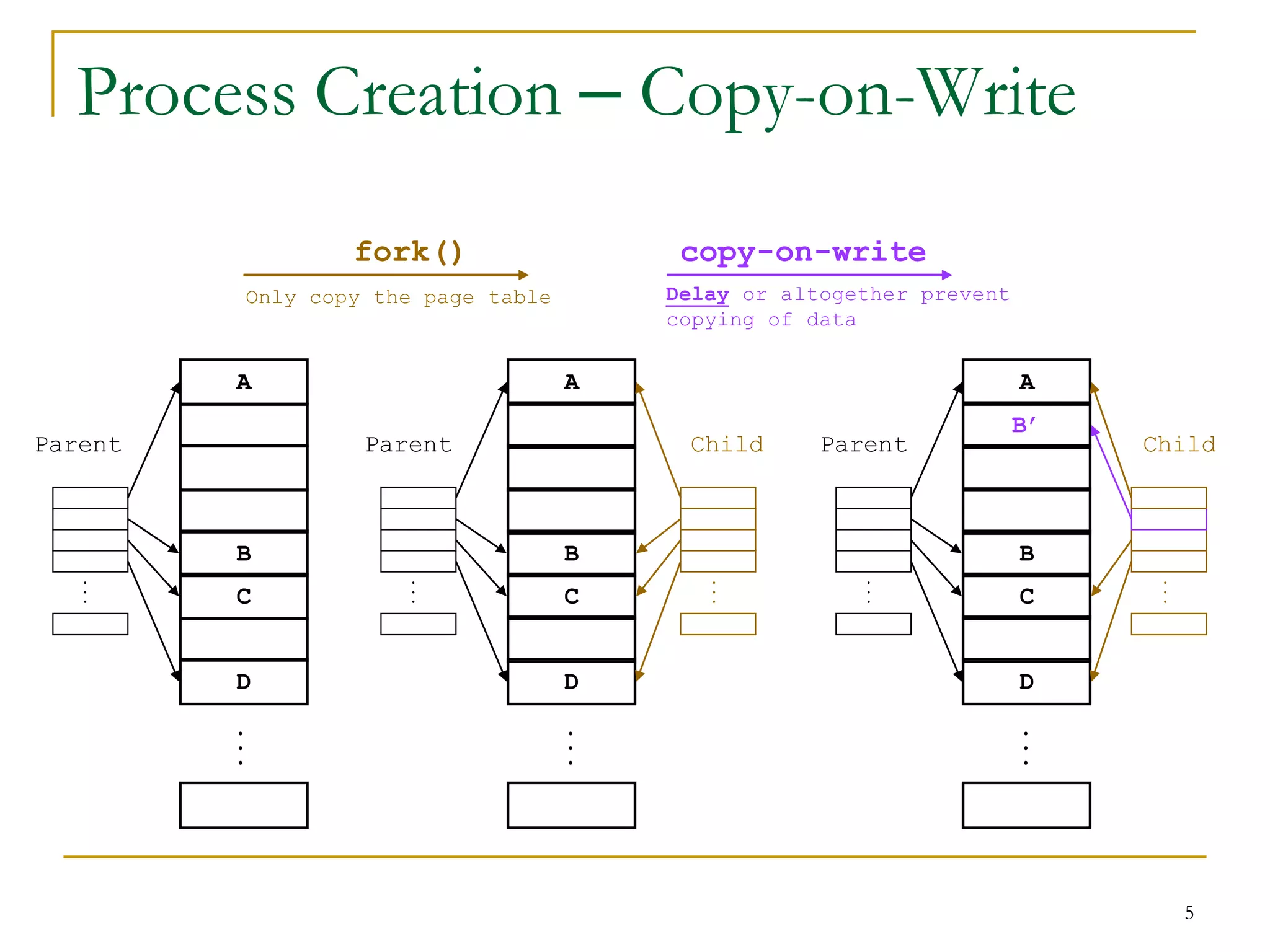
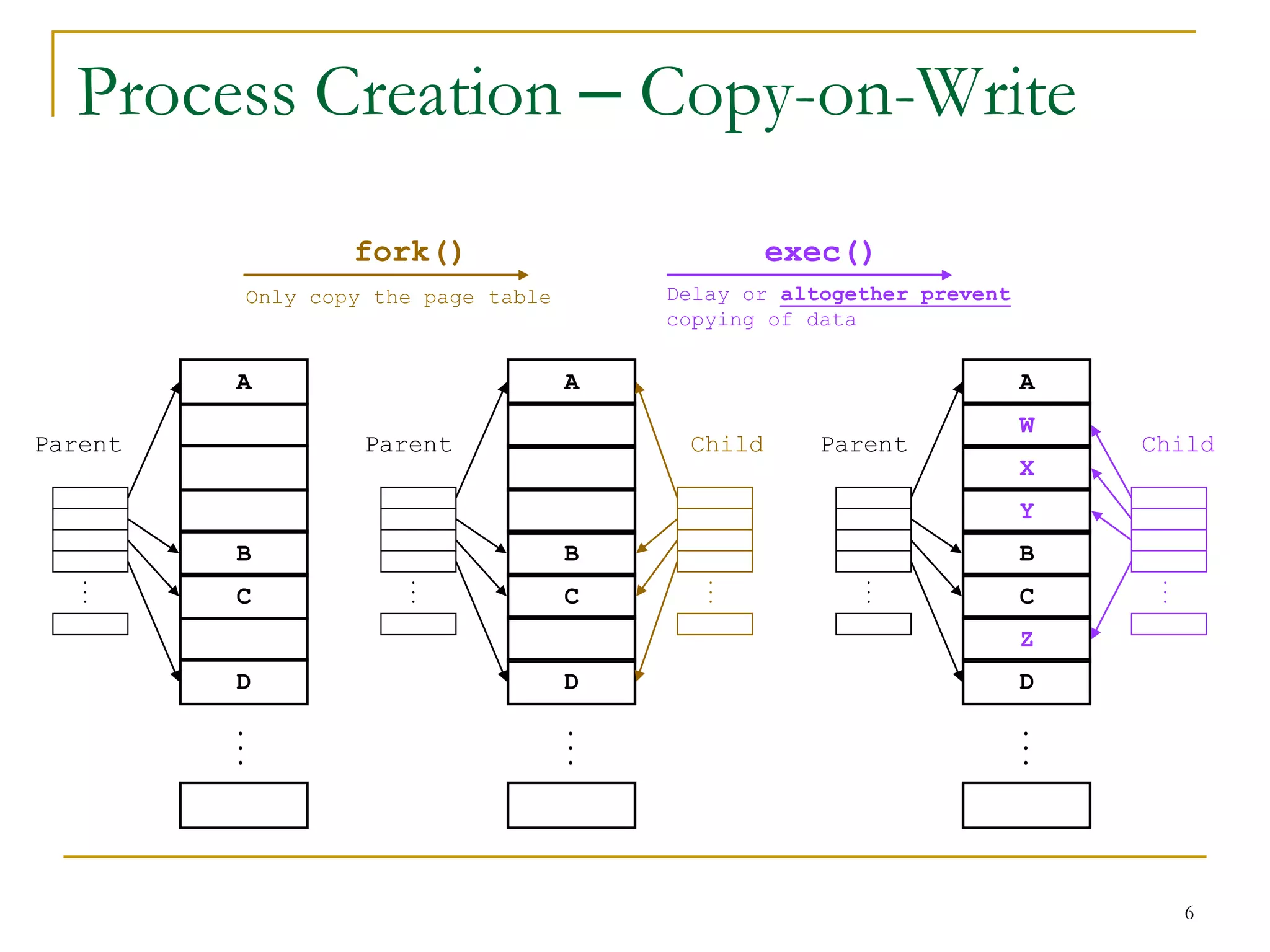
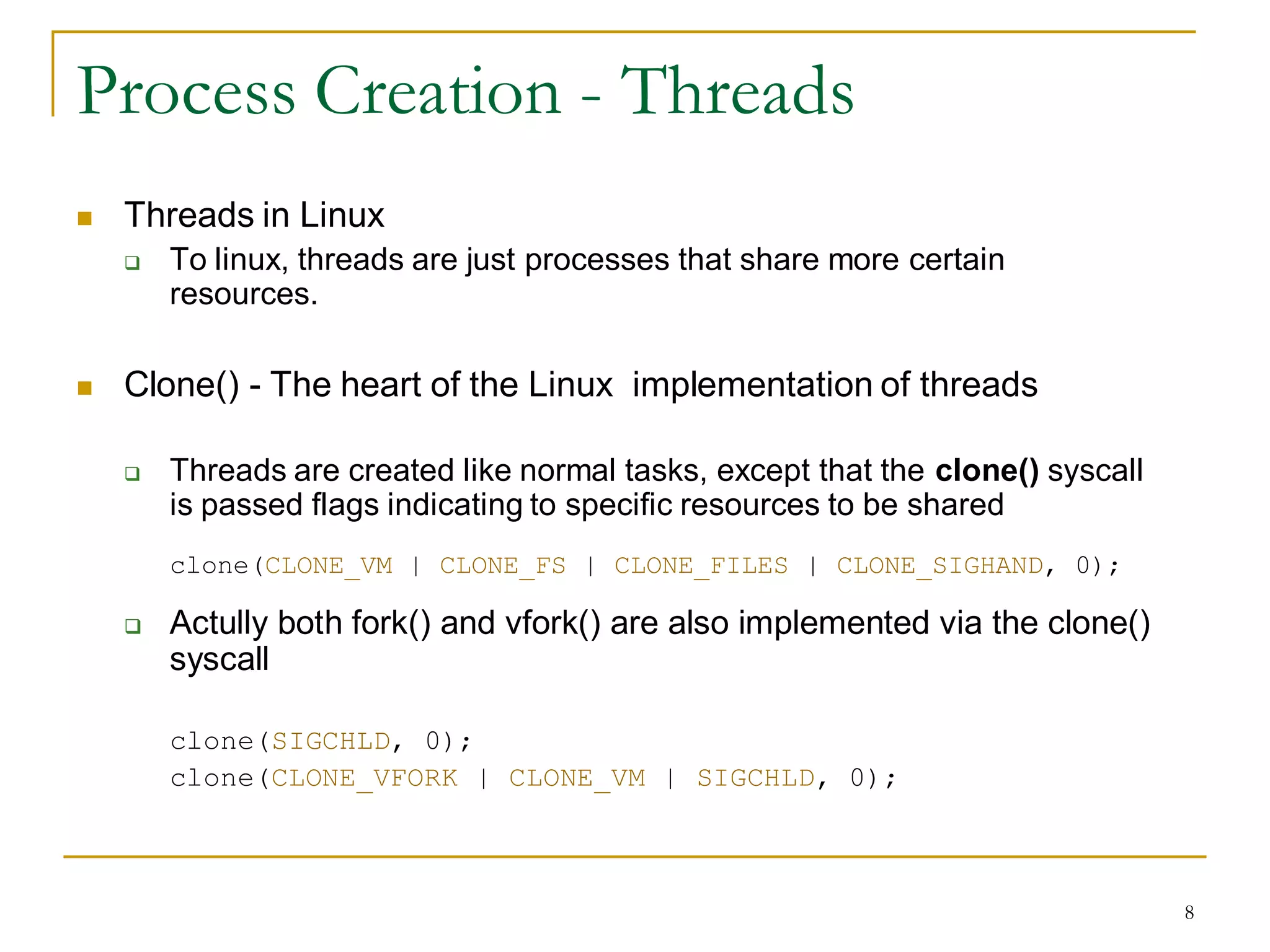
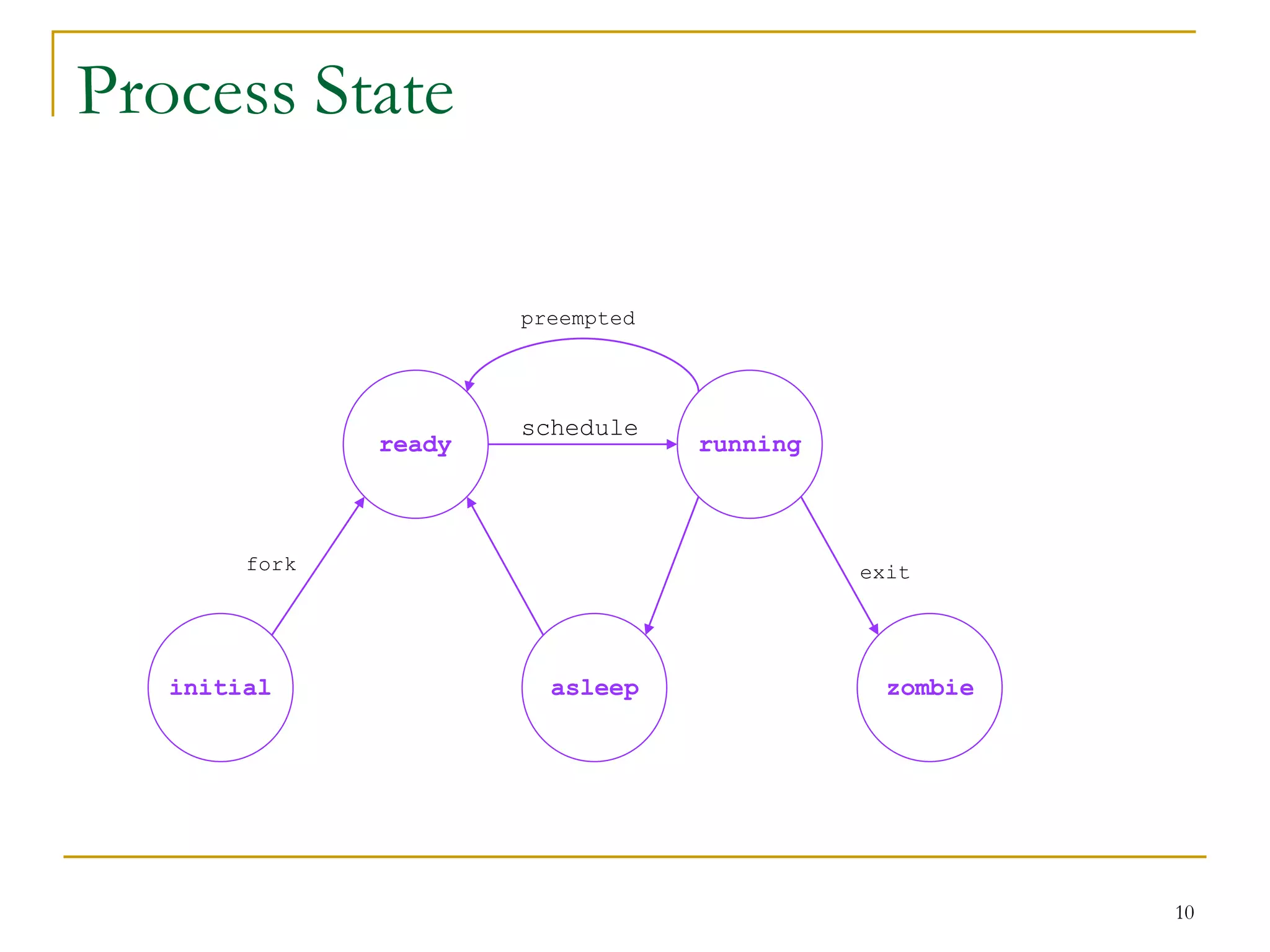
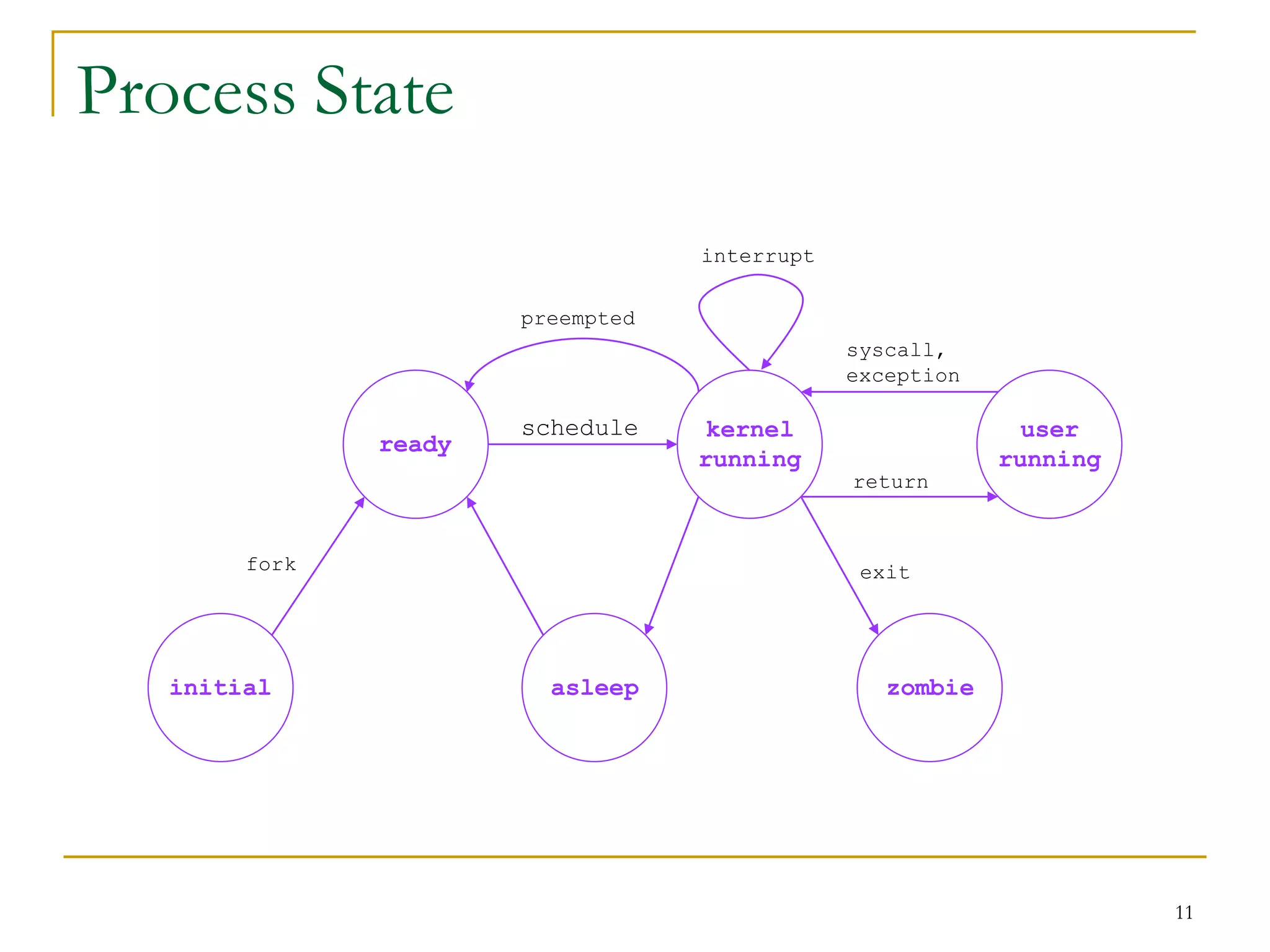
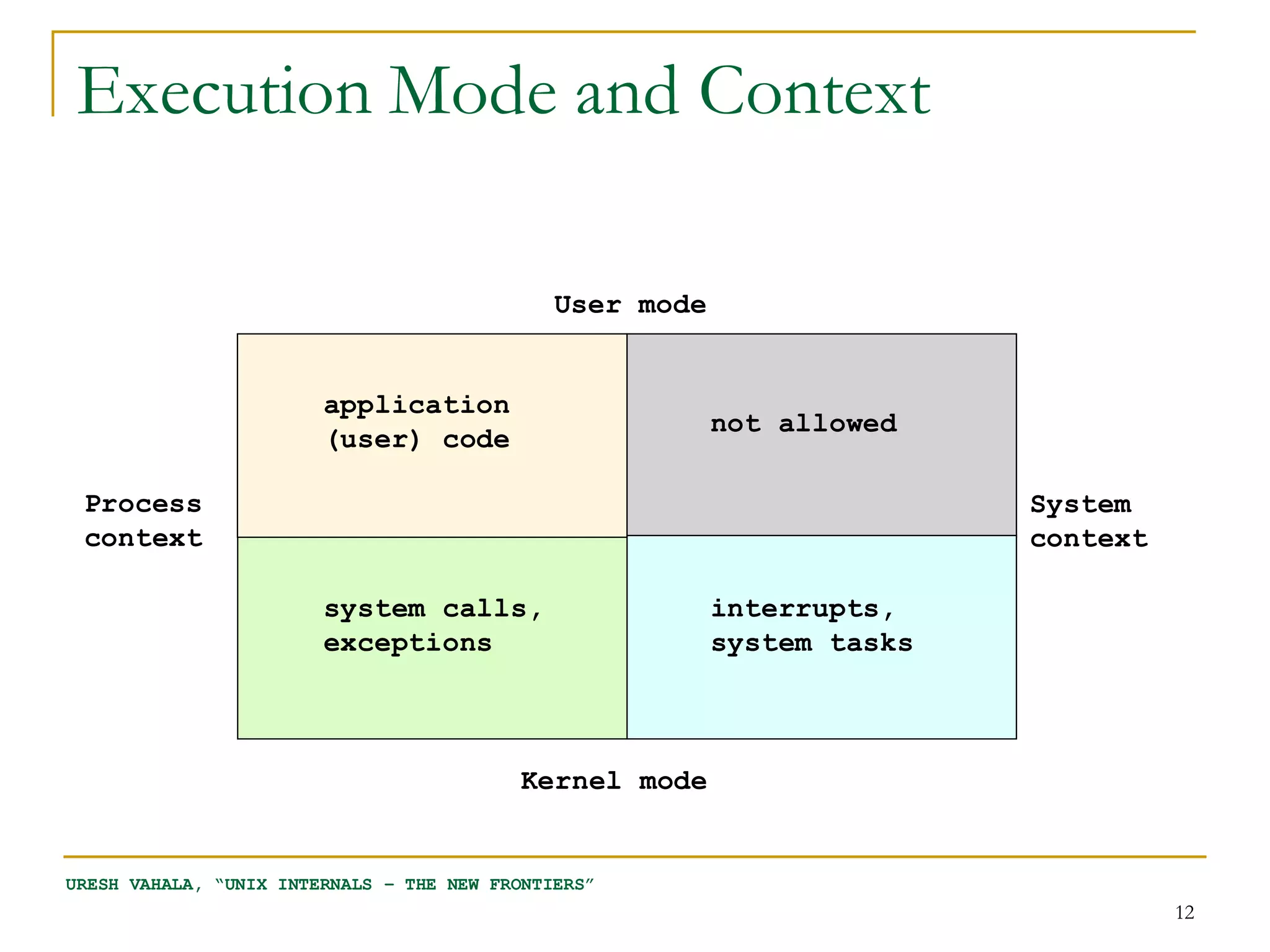
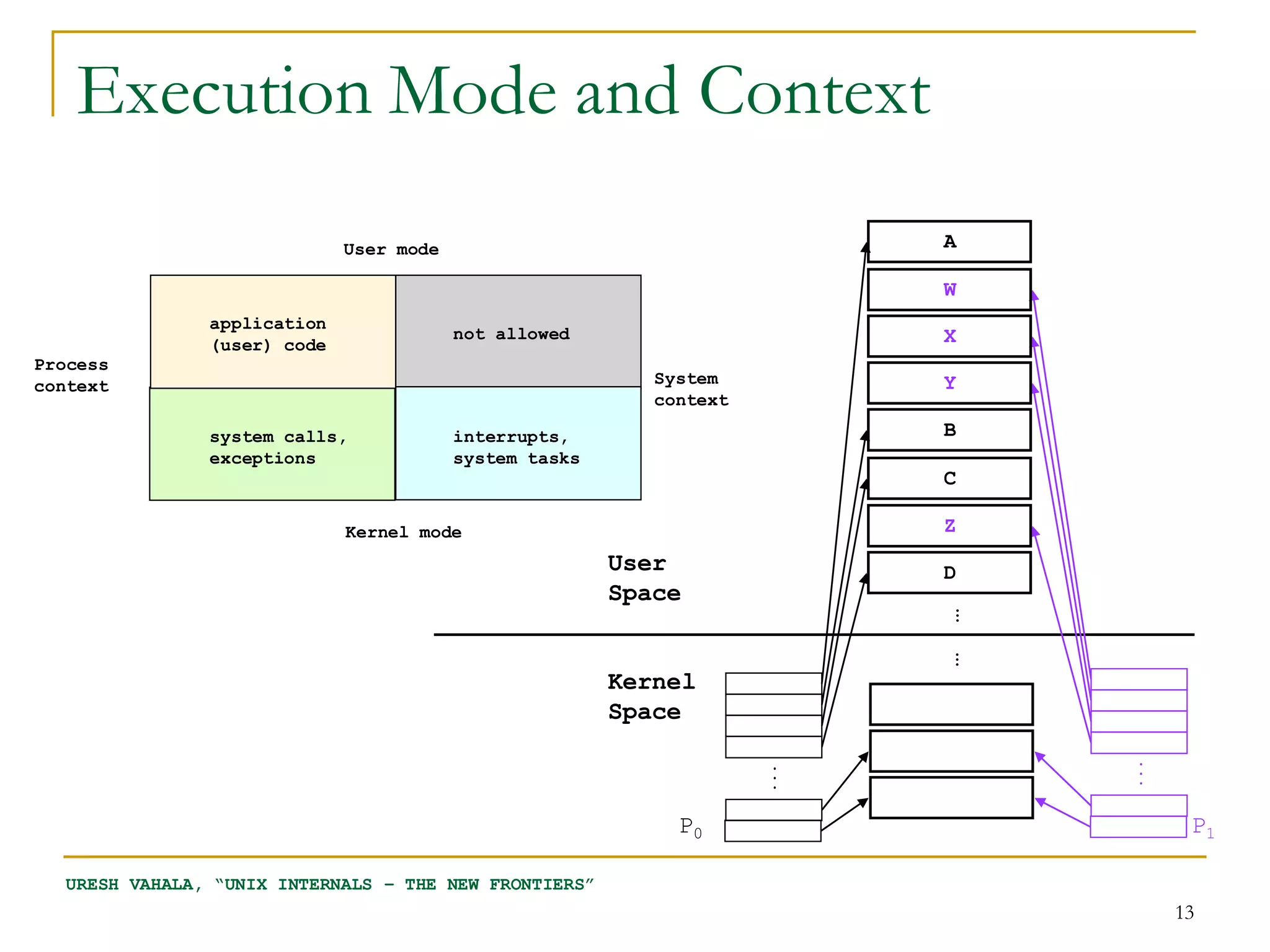
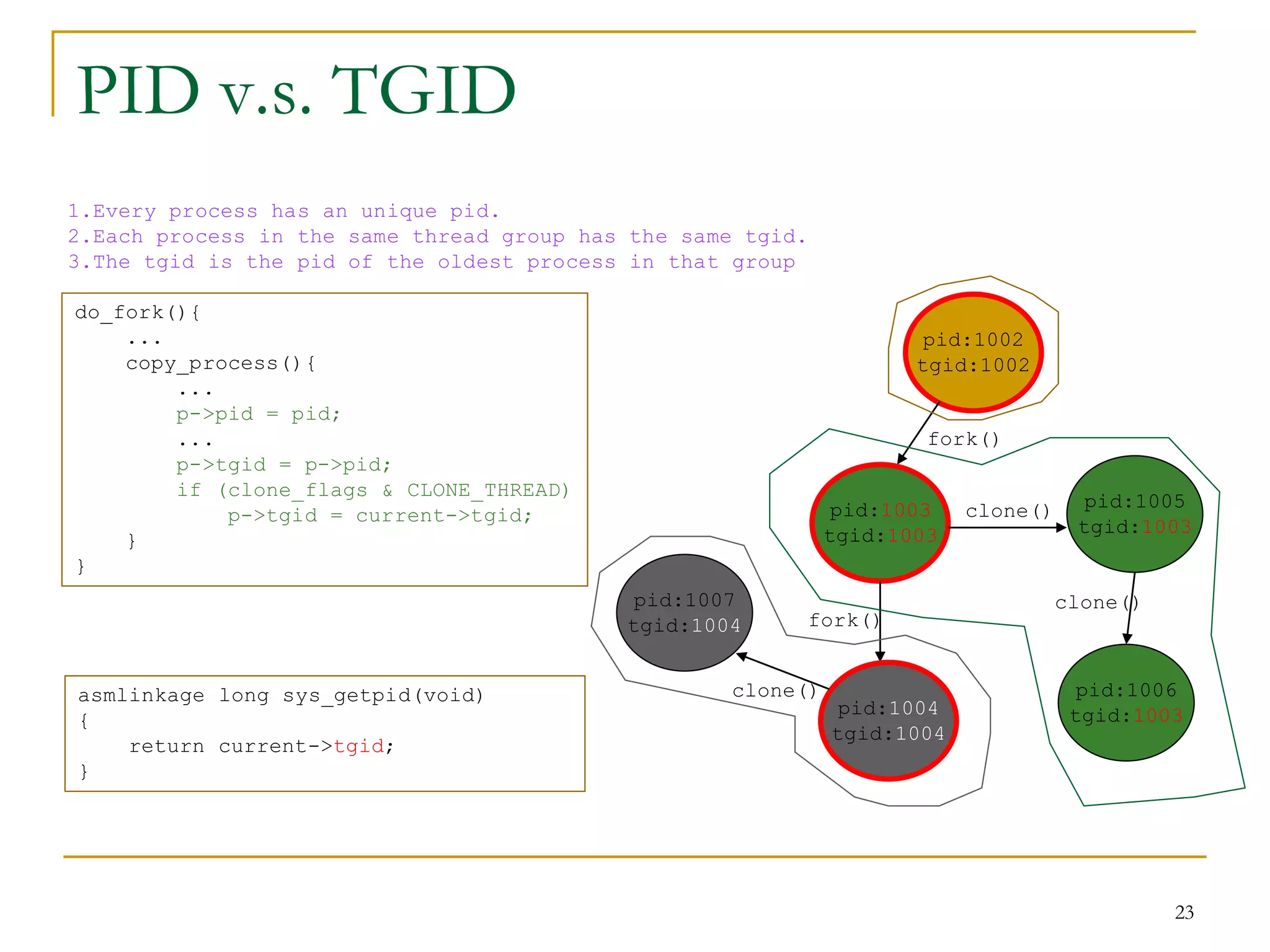
The document discusses process management in Linux operating systems. It describes process states like running, ready, terminated. It explains process creation using fork(), vfork(), and clone() system calls. fork() copies the whole address space while vfork() and clone() can share resources using flags. Copy-on-write is used to delay copying data pages until a process writes to them. A thread is like a process but shares more resources, created via clone(). Process context switches between user mode for applications and kernel mode for system calls.

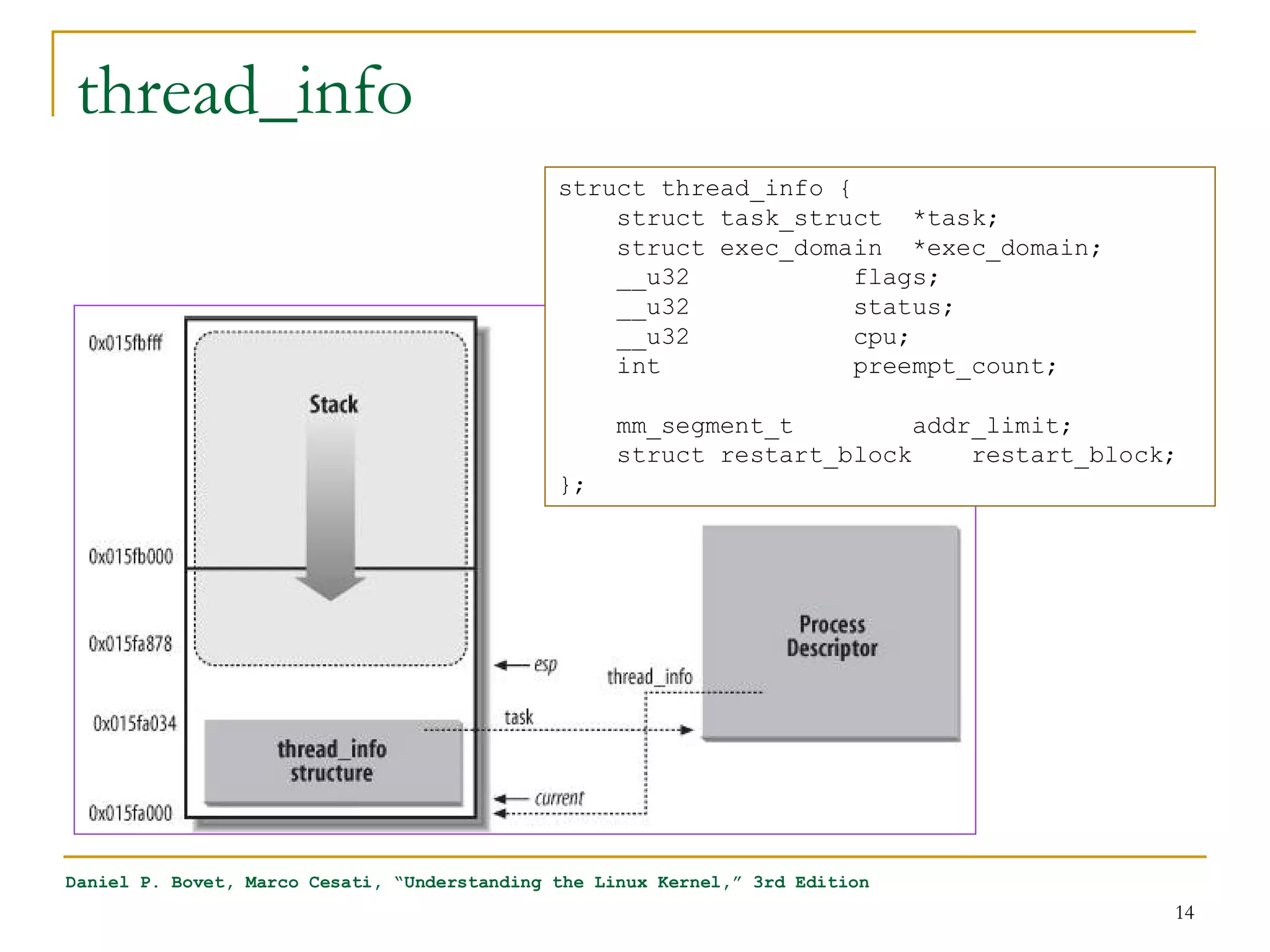
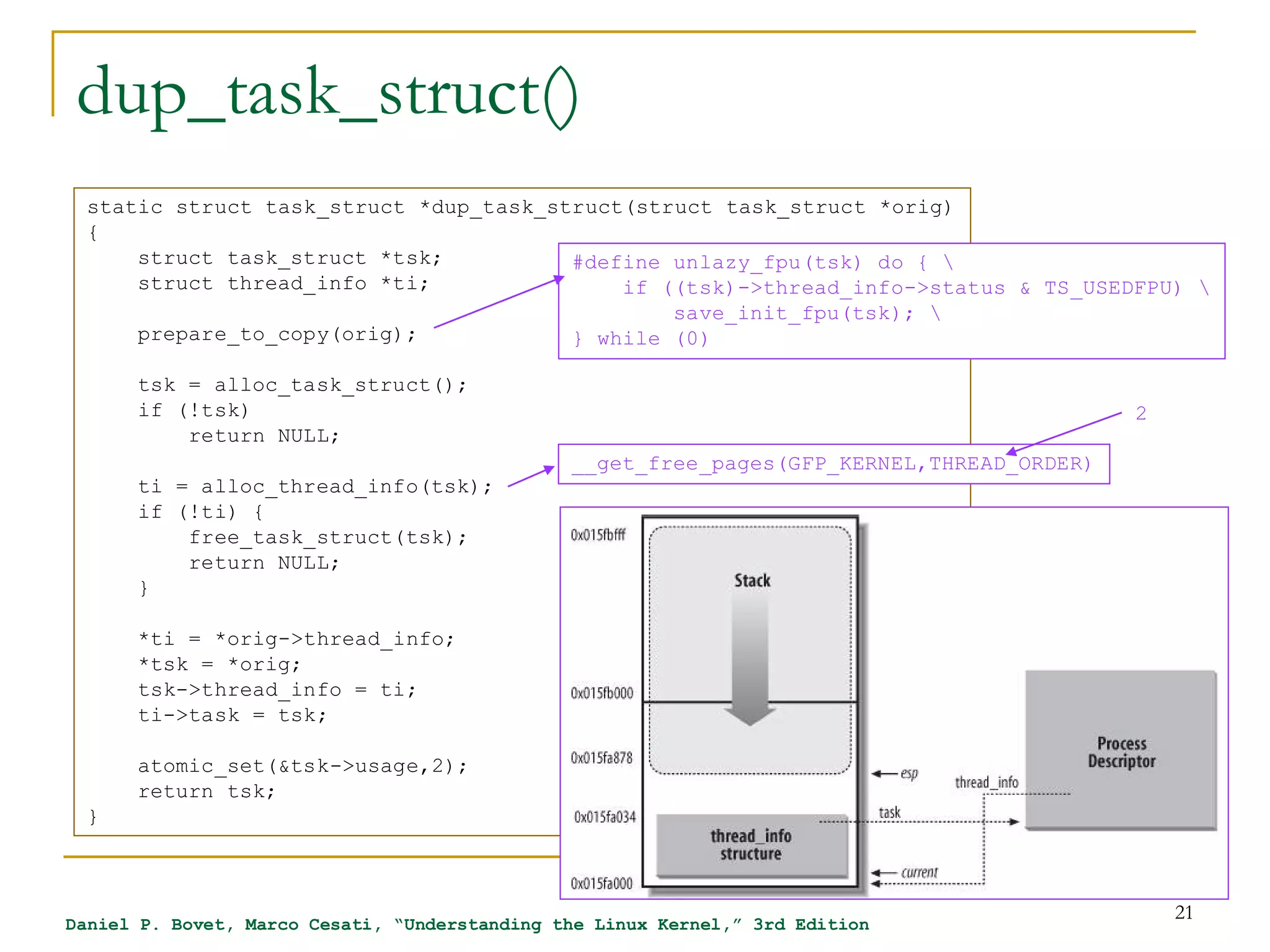
![task_struct
[include/linux/sched.h]
Robert Love, “Linux Kernel Development,” 2nd Edition
Daniel P. Bovet, Marco Cesati, “Understanding the Linux Kernel,” 3rd Edition 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/process-110320013227-phpapp01/75/Process-Management-7-2048.jpg)
![Process Creation Flow
User space
sys_fork() sys_vfork() sys_clone()
Kernel space
[kernel/process.c]
[kernel/fork.c]
do_fork() [kernel/sched.c]
alloc_pidmap()
duplicate the task_struct, initialize it
copy_process()
and setup according to the specified clone_flags
success?
yes
wake_up_new_task() put the child into runqueue
no
free_pidmap() vfork? wait_for_completion()
yes
when the child terminates,
no it wakes up the parent sleeping in the wait queue
return pid
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/process-110320013227-phpapp01/75/Process-Management-9-2048.jpg)
![do_fork() (1/4)
[kernel/fork.c]
1. long pid = alloc_pidmap();
2. if (pid < 0)
3. return -EAGAIN;
4. …
5. p = copy_process(clone_flags, stack_start, regs, stack_size, parent_tidptr, child_tidptr, pid);
6. if (!IS_ERR(p)) {
7. struct completion vfork;
8. if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK) {
9. p->vfork_done = &vfork;
10. init_completion(&vfork);
11. }
12. …
13. if (!(clone_flags & CLONE_STOPPED))
14. wake_up_new_task(p, clone_flags);
15. else
16. p->state = TASK_STOPPED;
17. …
18. if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK) {
19. wait_for_completion(&vfork);
20. if (unlikely (current->ptrace & PT_TRACE_VFORK_DONE))
21. ptrace_notify ((PTRACE_EVENT_VFORK_DONE << 8) | SIGTRAP);
22. }
23. } else {
24. free_pidmap(pid);
25. pid = PTR_ERR(p);
26. }
27. return pid;
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/process-110320013227-phpapp01/75/Process-Management-15-2048.jpg)
![do_fork() (2/4)
[kernel/fork.c]
1. long pid = alloc_pidmap();
2. if (pid < 0)
3. return -EAGAIN;
4. …
5. p = copy_process(clone_flags, stack_start, regs, stack_size, parent_tidptr, child_tidptr, pid);
6. if (!IS_ERR(p)) {
7. struct completion vfork;
8. if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK) {
9. p->vfork_done = &vfork;
10. init_completion(&vfork);
11. }
12. …
13. if (!(clone_flags & CLONE_STOPPED))
14. wake_up_new_task(p, clone_flags);
15. else
16. p->state = TASK_STOPPED;
17. …
18. if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK) {
19. wait_for_completion(&vfork);
20. if (unlikely (current->ptrace & PT_TRACE_VFORK_DONE))
21. ptrace_notify ((PTRACE_EVENT_VFORK_DONE << 8) | SIGTRAP);
22. }
23. } else {
24. free_pidmap(pid);
25. pid = PTR_ERR(p);
26. }
27. return pid;
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/process-110320013227-phpapp01/75/Process-Management-16-2048.jpg)
![do_fork() (3/4)
[kernel/fork.c]
1. long pid = alloc_pidmap();
2. if (pid < 0)
3. return -EAGAIN;
4. …
5. p = copy_process(clone_flags, stack_start, regs, stack_size, parent_tidptr, child_tidptr, pid);
6. if (!IS_ERR(p)) {
7. struct completion vfork;
8. if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK) {
9. p->vfork_done = &vfork;
10. init_completion(&vfork);
11. }
12. …
13. if (!(clone_flags & CLONE_STOPPED))
14. wake_up_new_task(p, clone_flags);
15. else
16. p->state = TASK_STOPPED;
17. …
18. if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK) {
19. wait_for_completion(&vfork);
20. if (unlikely (current->ptrace & PT_TRACE_VFORK_DONE))
21. ptrace_notify ((PTRACE_EVENT_VFORK_DONE << 8) | SIGTRAP);
22. }
23. } else {
24. free_pidmap(pid);
25. pid = PTR_ERR(p);
26. }
27. return pid;
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/process-110320013227-phpapp01/75/Process-Management-17-2048.jpg)
![do_fork() (4/4)
[kernel/fork.c]
1. long pid = alloc_pidmap();
2. if (pid < 0)
3. return -EAGAIN;
4. …
5. p = copy_process(clone_flags, stack_start, regs, stack_size, parent_tidptr, child_tidptr, pid);
6. if (!IS_ERR(p)) {
7. struct completion vfork;
8. if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK) {
9. p->vfork_done = &vfork;
10. init_completion(&vfork);
11. }
12. …
13. if (!(clone_flags & CLONE_STOPPED))
14. wake_up_new_task(p, clone_flags);
15. else
16. p->state = TASK_STOPPED;
17. …
18. if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK) {
19. wait_for_completion(&vfork);
20. if (unlikely (current->ptrace & PT_TRACE_VFORK_DONE))
21. ptrace_notify ((PTRACE_EVENT_VFORK_DONE << 8) | SIGTRAP);
22. }
23. } else {
24. free_pidmap(pid);
25. pid = PTR_ERR(p);
26. }
27. return pid;
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/process-110320013227-phpapp01/75/Process-Management-18-2048.jpg)
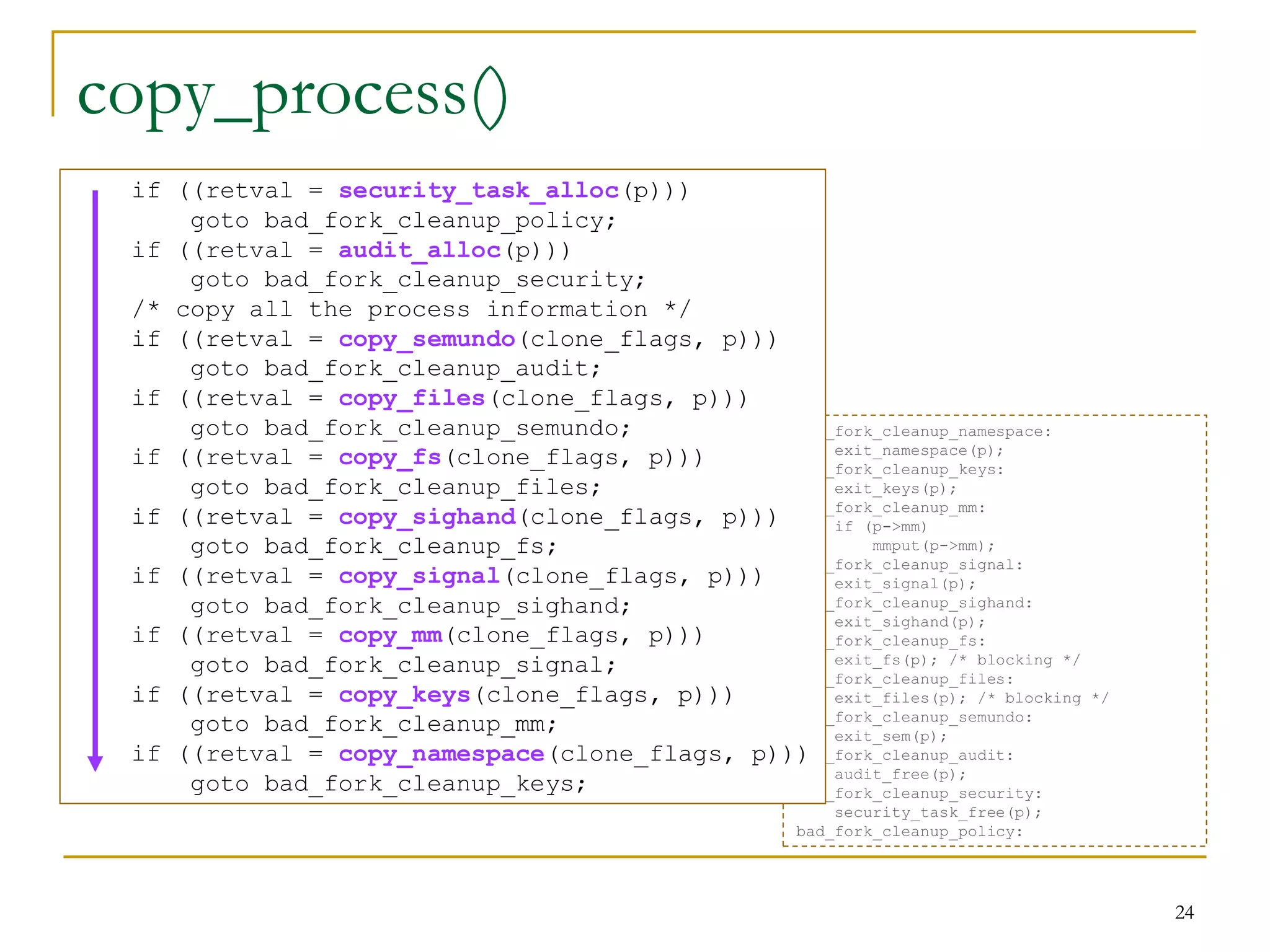
![copy_process() [kernel/fork.c]
int retval;
struct task_struct *p = NULL;
if ((clone_flags & (CLONE_NEWNS|CLONE_FS)) == (CLONE_NEWNS|CLONE_FS))
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
/*
* Thread groups must share signals as well, and detached threads
* can only be started up within the thread group.
*/
if ((clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD) && !(clone_flags & CLONE_SIGHAND))
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
/*
* Shared signal handlers imply shared VM. By way of the above,
* thread groups also imply shared VM. Blocking this case allows
* for various simplifications in other code.
*/
if ((clone_flags & CLONE_SIGHAND) && !(clone_flags & CLONE_VM))
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/process-110320013227-phpapp01/75/Process-Management-19-2048.jpg)
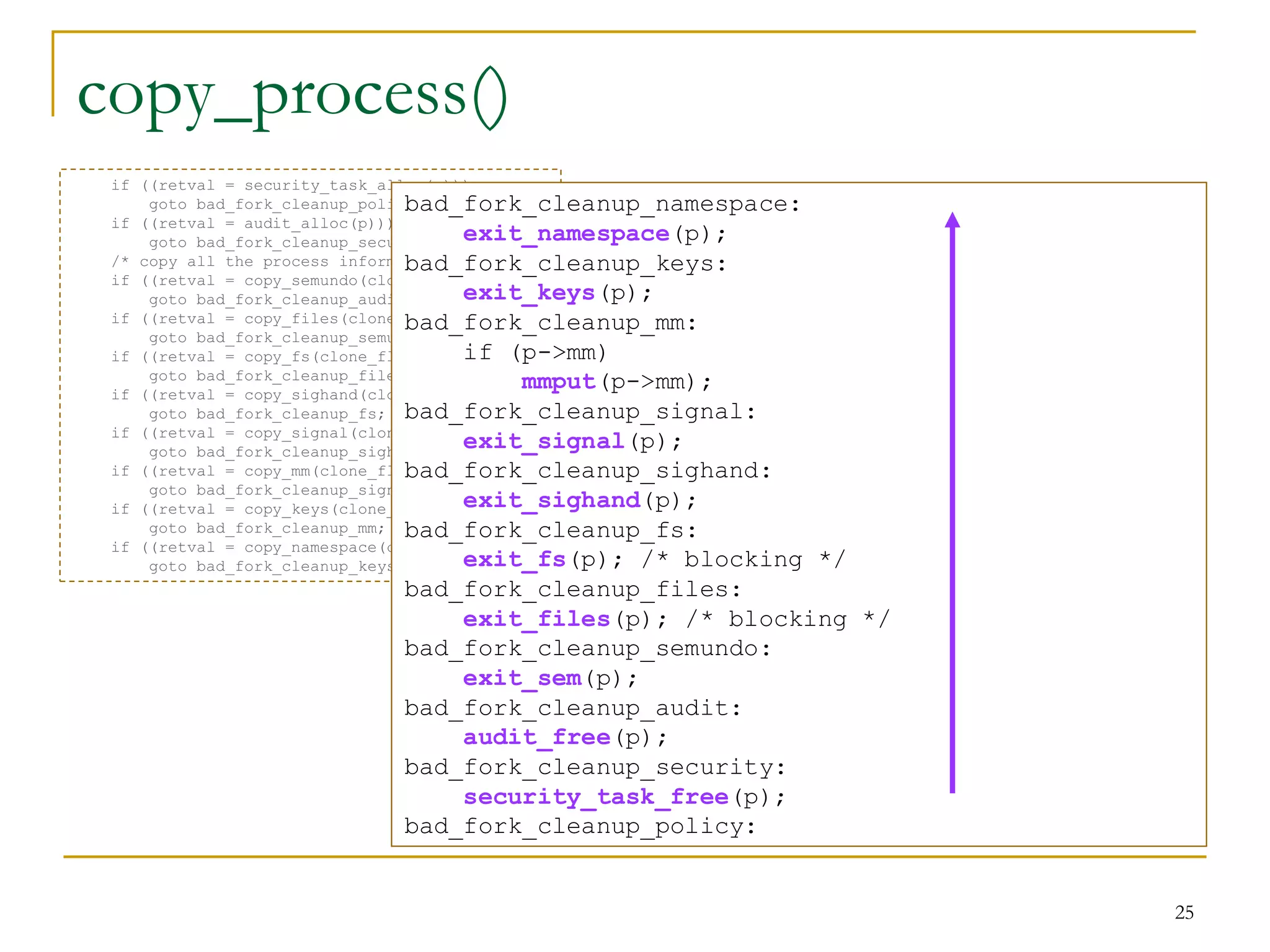
![copy_process()
retval = security_task_create(clone_flags);
if (retval)
goto fork_out;
retval = -ENOMEM;
p = dup_task_struct(current);
if (!p)
goto fork_out;
retval = -EAGAIN;
if (atomic_read(&p->user->processes) >=
p->signal->rlim[RLIMIT_NPROC].rlim_cur) {
if (!capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN) && !capable(CAP_SYS_RESOURCE) &&
p->user != &root_user)
goto bad_fork_free;
}
atomic_inc(&p->user->__count);
atomic_inc(&p->user->processes);
get_group_info(p->group_info);
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/process-110320013227-phpapp01/75/Process-Management-20-2048.jpg)

![context_swtich()
[kernel/sched.c]
1. static inline
2. task_t * context_switch(runqueue_t *rq, task_t *prev, task_t *next)
3. {
4. struct mm_struct *mm = next->mm;
5. struct mm_struct *oldmm = prev->active_mm;
6. if (unlikely(!mm)) {
7. next->active_mm = oldmm;
8. atomic_inc(&oldmm->mm_count);
9. enter_lazy_tlb(oldmm, next);
10. } else
11. switch_mm(oldmm, mm, next);
12. if (unlikely(!prev->mm)) {
13. prev->active_mm = NULL;
14. WARN_ON(rq->prev_mm);
15. rq->prev_mm = oldmm;
16. }
17. /* Here we just switch the register state and the stack. */
18. switch_to(prev, next, prev);
19. return prev;
20. }
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/process-110320013227-phpapp01/75/Process-Management-26-2048.jpg)