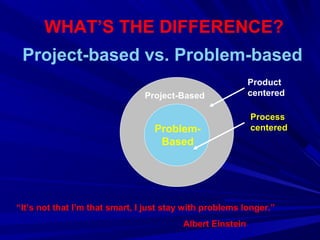
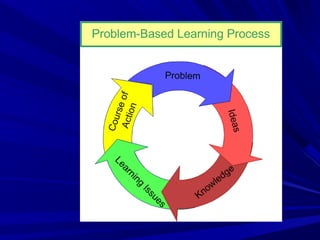
This document discusses how problem-based learning (PBL) connects to the Common Core standards. PBL engages students by designing real-world problems that stimulate meaningful experiences through problem-solving, collaboration, and resource sharing. An effective problem for PBL is student-centered, well-prepared, cognizant, and meaningful. PBL supports Common Core by using problems to drive skills acquisition and encourage exploration, with the process building real-world connections and content synthesis demonstrated through products. Collaboration and technology integration are key aspects of how PBL facilitates deeper learning aligned with Common Core.