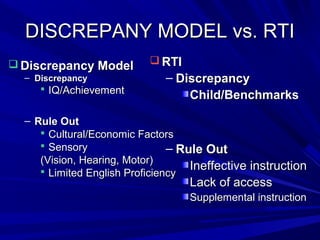
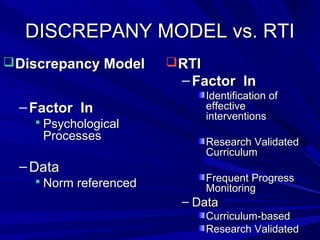
The presentation compared the discrepancy model and response to intervention (RTI) approaches for identifying learning disabilities. The discrepancy model focuses on identifying a disability through IQ-achievement discrepancies, while RTI uses data-driven interventions and progress monitoring. RTI aims to intervene early through research-based practices and determine if core instruction or supplemental support is needed. A multi-disciplinary team collaborates within the RTI process to problem-solve effective interventions based on frequent progress monitoring. The principal's role is to support RTI implementation through resource allocation, priority setting, and program evaluation.