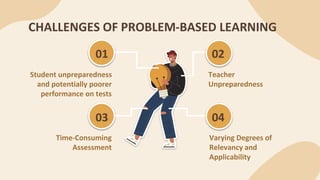
The document discusses problem-based and project-based learning (PBL) in social studies, emphasizing their student-centered approach and benefits such as improved collaboration, engagement, and transferable skills. It also highlights challenges educators face, including time constraints, teacher preparedness, and adapting to non-traditional roles. Real-world applications of PBL are illustrated through various examples, promoting critical thinking and problem-solving abilities among students.















![REFERENCES:
● 5 Advantages and Disadvantages of Problem-Based Learning [+ Activity Design Steps]. (2016,
December 14). Prodigy. https://www.prodigygame.com/main-en/blog/advantages-disadvantages-
problem-based-learning/
● Azzano, T. (2020, December 7). Getting Started With PBL in Social Studies. GEORGE LUCAS
EDUCATIONAL FOUNDATION. https://www.edutopia.org/article/getting-started-pbl-social-
studies#:~:text=When%20I%20became%20a%20teacher,broader%20audience%20than%20their%2
0teacher
● Bogler, M. (2016, August 18). Implementing Project-Based Learning: Challenges and Solutions.
ProjectPals. https://www.projectpals.com/project-based-learning-blog/implementing-project-
based-learning-challenges-and-solutions
● Dave, S. (2022, February 23). Project Based Learning: Benefits and Techniques of PBL. Practera.
https://practera.com/project-based-learning-benefits-and-techniques/
● Nilson, L. B. (2010). Teaching at its best: A research-based resource for college instructors (2nd ed.).
San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
● What is Problem-Based Learning (PBL) | Hun School of Princeton. (2020). The Hun School of
Princeton. https://www.hunschool.org/resources/problem-based-learning](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/problem-projectbasedlearninginsocialstudies-220309060324/85/Problem-Project-Based-Learning-in-Social-Studies-18-320.jpg)
