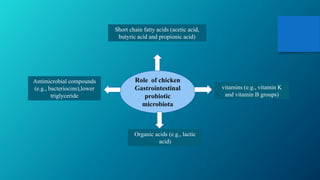
The document introduces probiotic microbiota from the gastrointestinal tract of commercial poultry, emphasizing the definition and characteristics of probiotics, particularly beneficial strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. It discusses the role of probiotics in enhancing chicken health and performance, including various metabolic functions of the gut microbiota. Additionally, it highlights the economic importance of probiotics as feed supplements in the poultry industry.