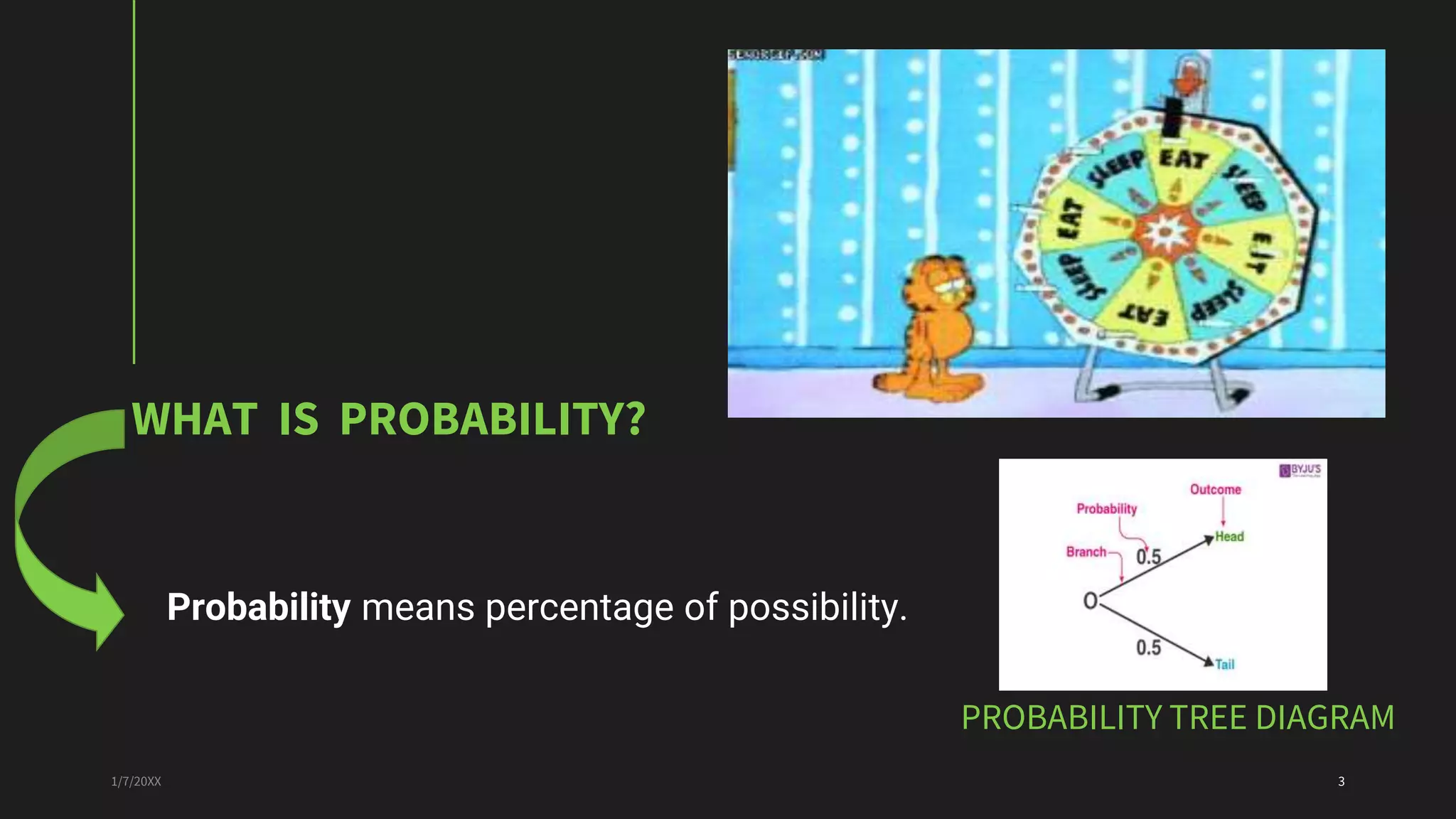
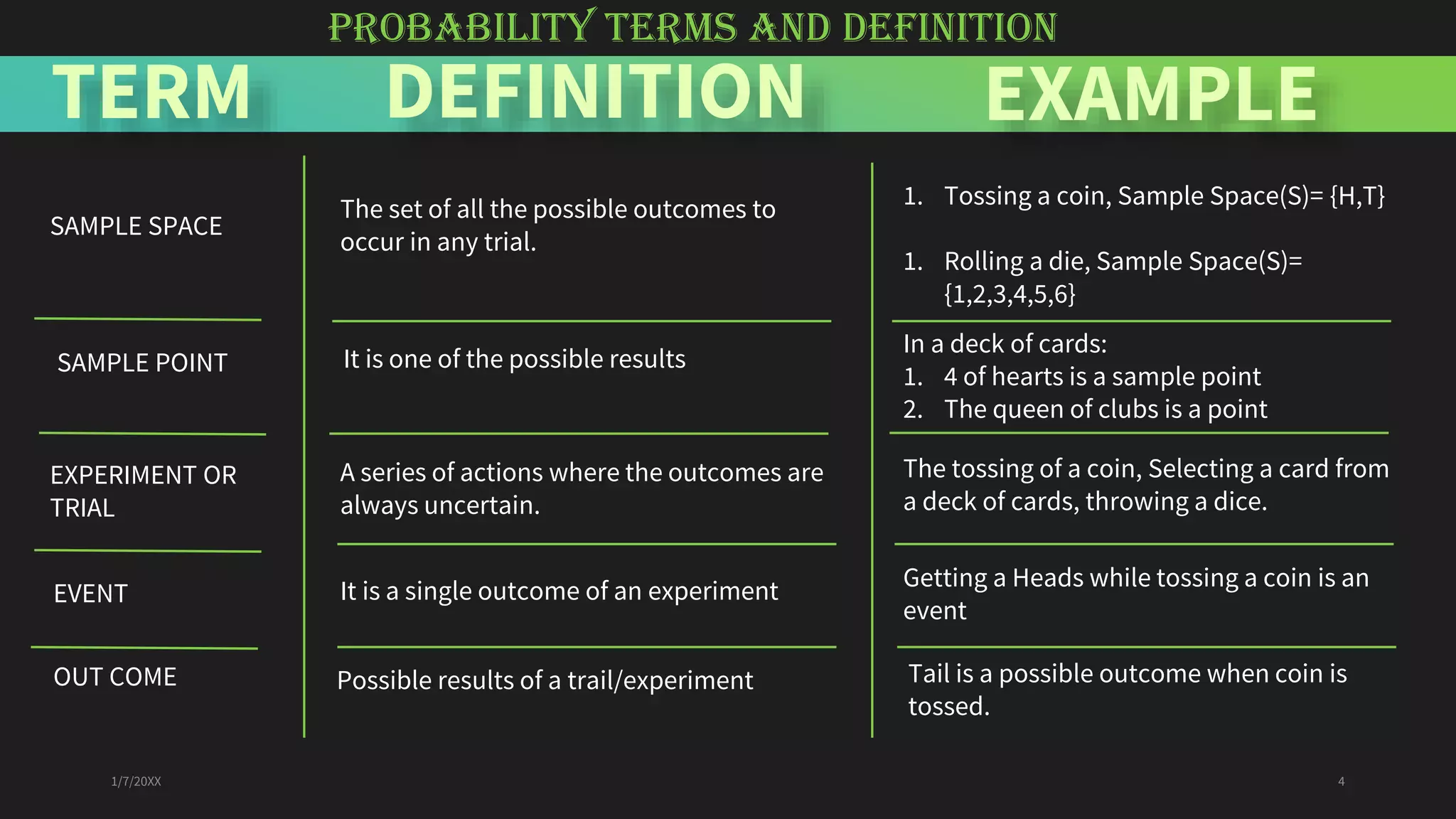
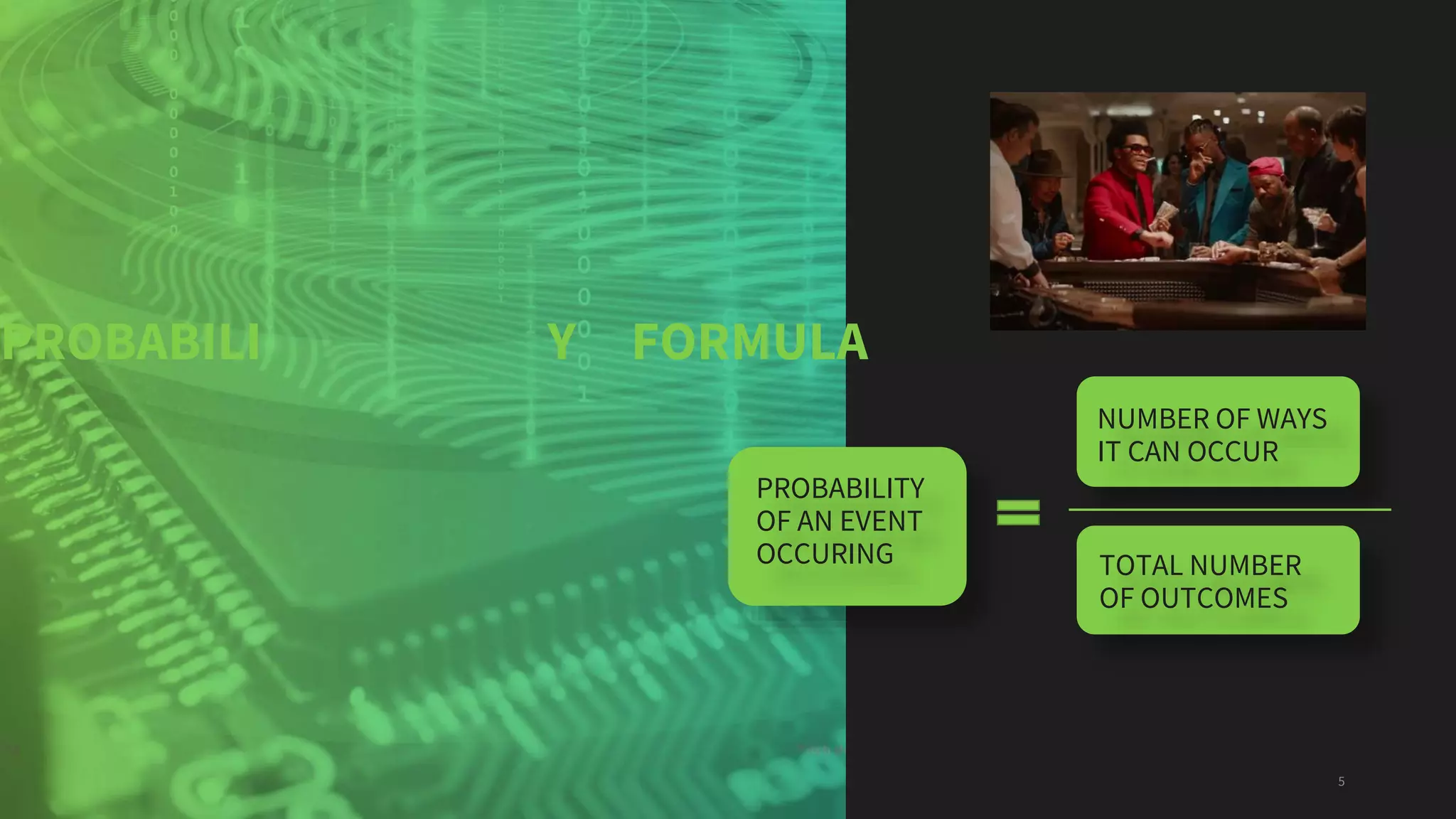
This document discusses probability and the Python programming language. It defines probability as the percentage of possibility and describes probability terms like sample space, sample point, experiment, outcome, and event. It presents the probability formula and explains theoretical, experimental, and axiomatic probabilities. Examples of calculating probabilities are shown. The document also lists some applications of probability and defines Python as an interpreted, object-oriented programming language. It describes advantages of Python like being high-level, having built-in data structures, supporting modules and packages, using dynamic typing and binding, and being easy to use. Finally, it provides an example Python program to simulate coin tosses.