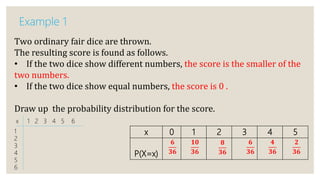
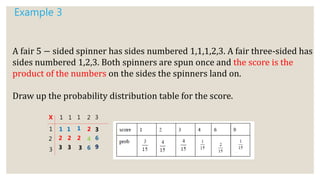
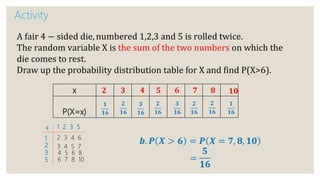
This document discusses probability distributions of discrete random variables. It defines a discrete random variable as one that can take only certain values that occur by chance. Examples are provided to show how to construct probability distribution tables for discrete random variables by listing the possible values and their probabilities based on the experiment or problem. Key points are that the sum of the probabilities must equal 1 and probabilities are always positive. Examples include tossing coins, selecting roses, spinning spinners, and rolling dice.