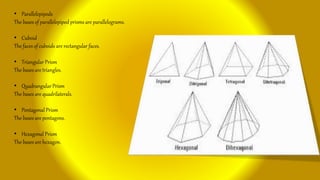
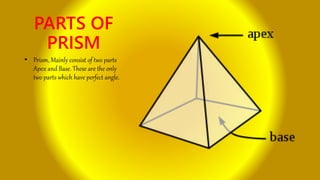
This document provides an introduction to prisms, including their basic structure and types. It discusses the different types of prisms such as regular, irregular, right, oblique and parallelepipeds. It also outlines some common uses of prisms for internal reflection and describes the main parts of a prism as the apex and base. Finally, it provides a brief explanation of how prisms work by refracting light as it passes from one medium to another due to changes in light speed.