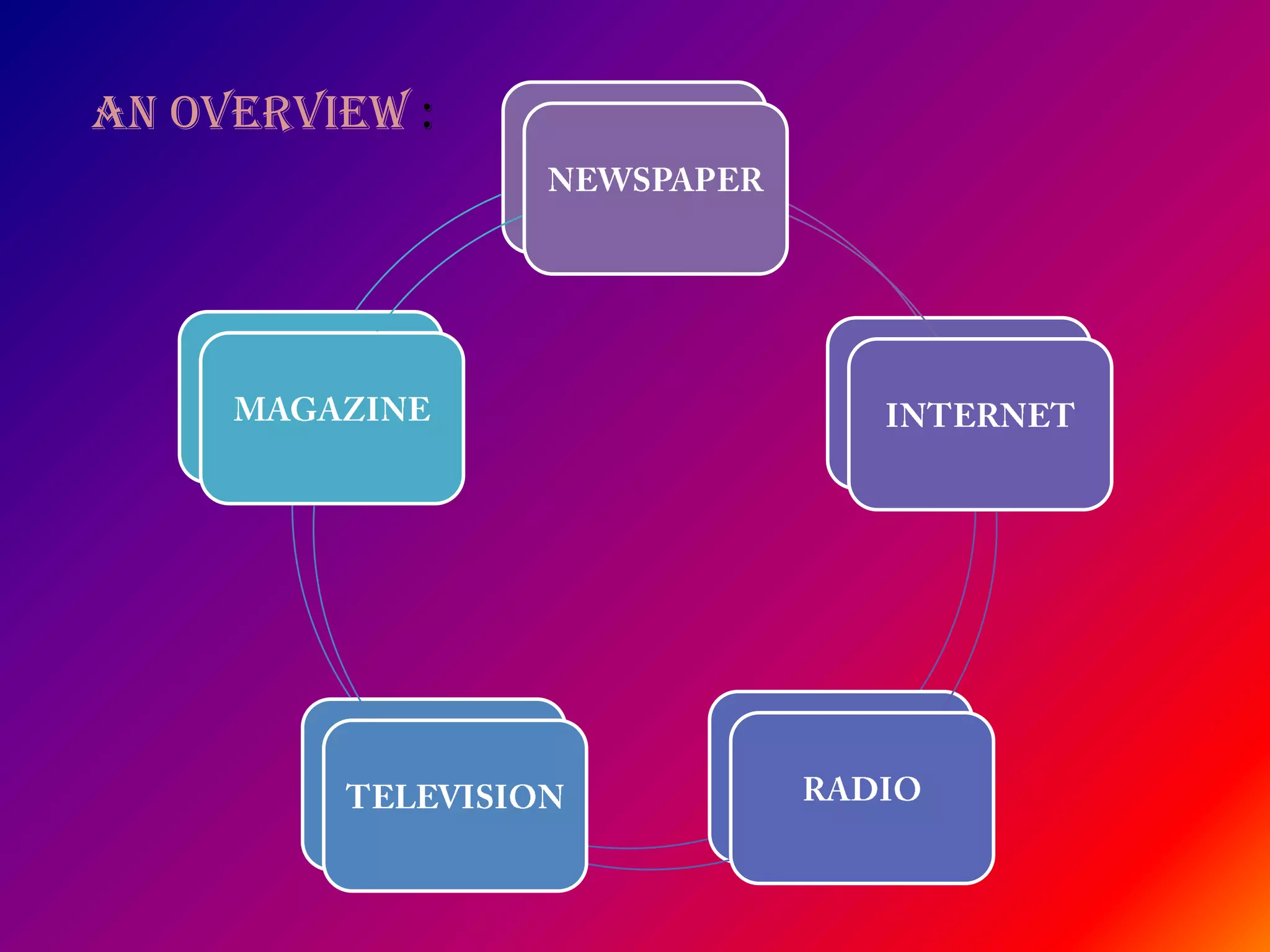
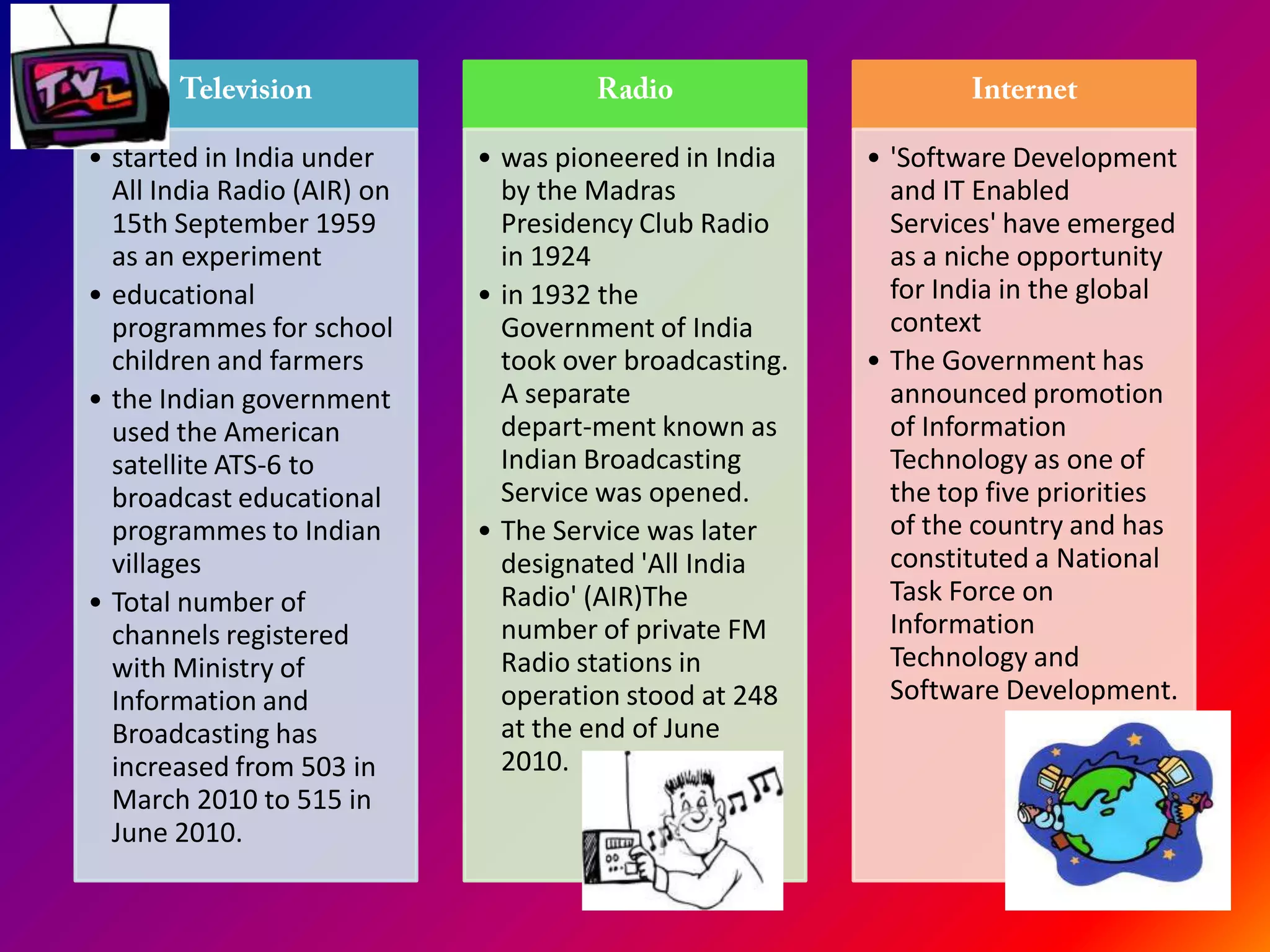
The document discusses the history and development of mass media in India, highlighting the impact of print media and the emergence of online platforms. It details the evolution of newspapers, magazines, and radio broadcasting, as well as their role in education and nation-building. Despite advancements in technology, print media remains significant for its in-depth reporting and long-lasting influence on readers.