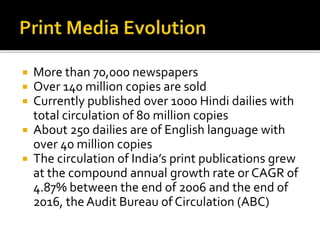
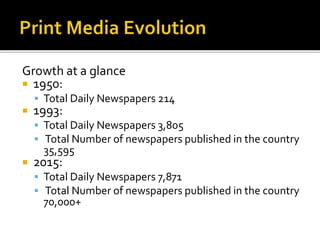
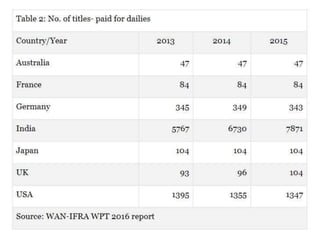
The document outlines the evolution of print media advertising, highlighting key styles and significant historical milestones in India from the 18th century to the present. It discusses the shift in advertising techniques, showing a transition from text-heavy ads to visually focused designs, and details the growth of newspaper and magazine publications across various languages in India. Additionally, it evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of newspapers and magazines as advertising mediums, emphasizing their roles in local and national markets.