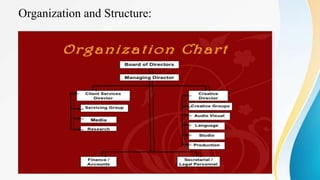
This document provides an overview of print media, including its history and various types. It discusses how print media has evolved from handwritten manuscripts to digital technologies. It then describes different forms of print media like newspapers, magazines, newsletters, books, and posters. Newspapers are highlighted as one of the most important print media, providing information, education, and other services to communities. The functions and types of newspapers, magazines, and other materials are outlined. Finally, various terminology used in print media are defined.