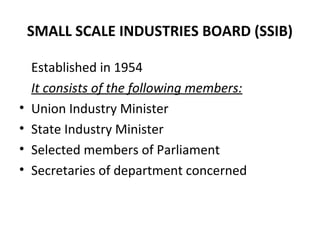
The document outlines the institutional support systems for micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in India, detailing three stages of enterprise development: inception, management, and expansion. It identifies key government organizations such as the Small Industries Development Organization (SIDO) and the National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC), alongside their roles and services in promoting and supporting MSMEs. Additionally, it highlights the importance of state and non-government entities in providing financial assistance, training, and resource allocation to enhance entrepreneurship and industrial growth.