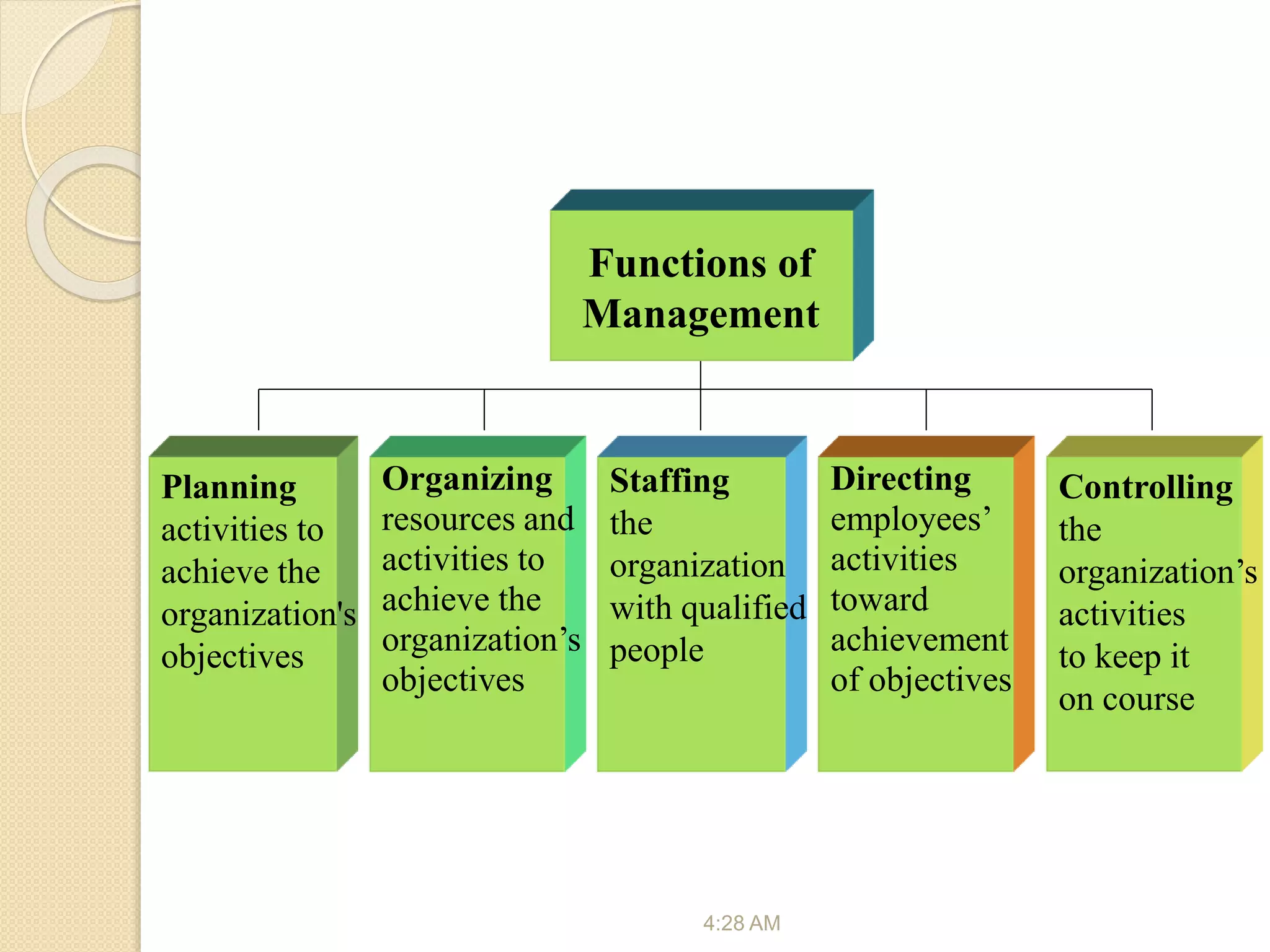
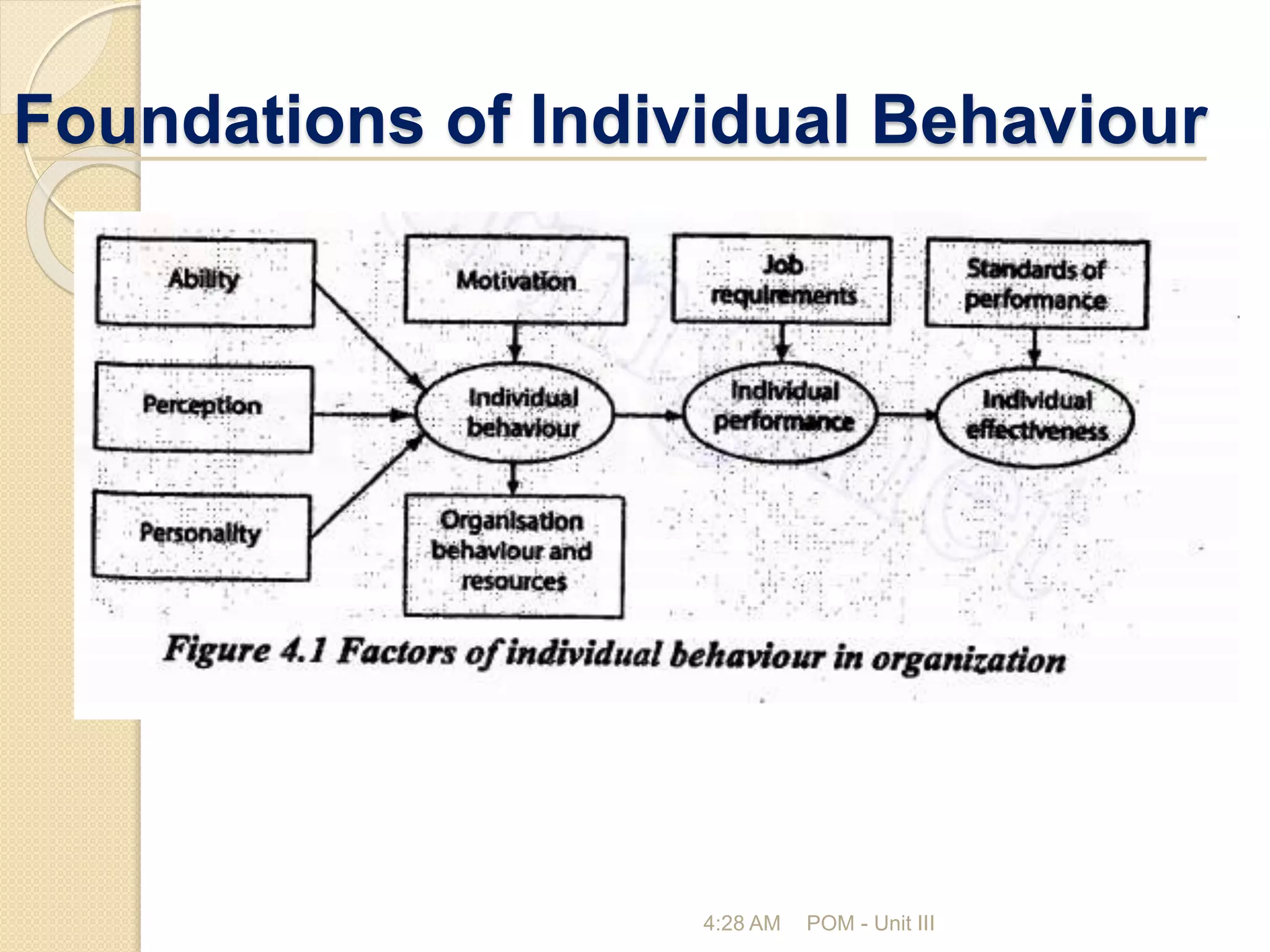
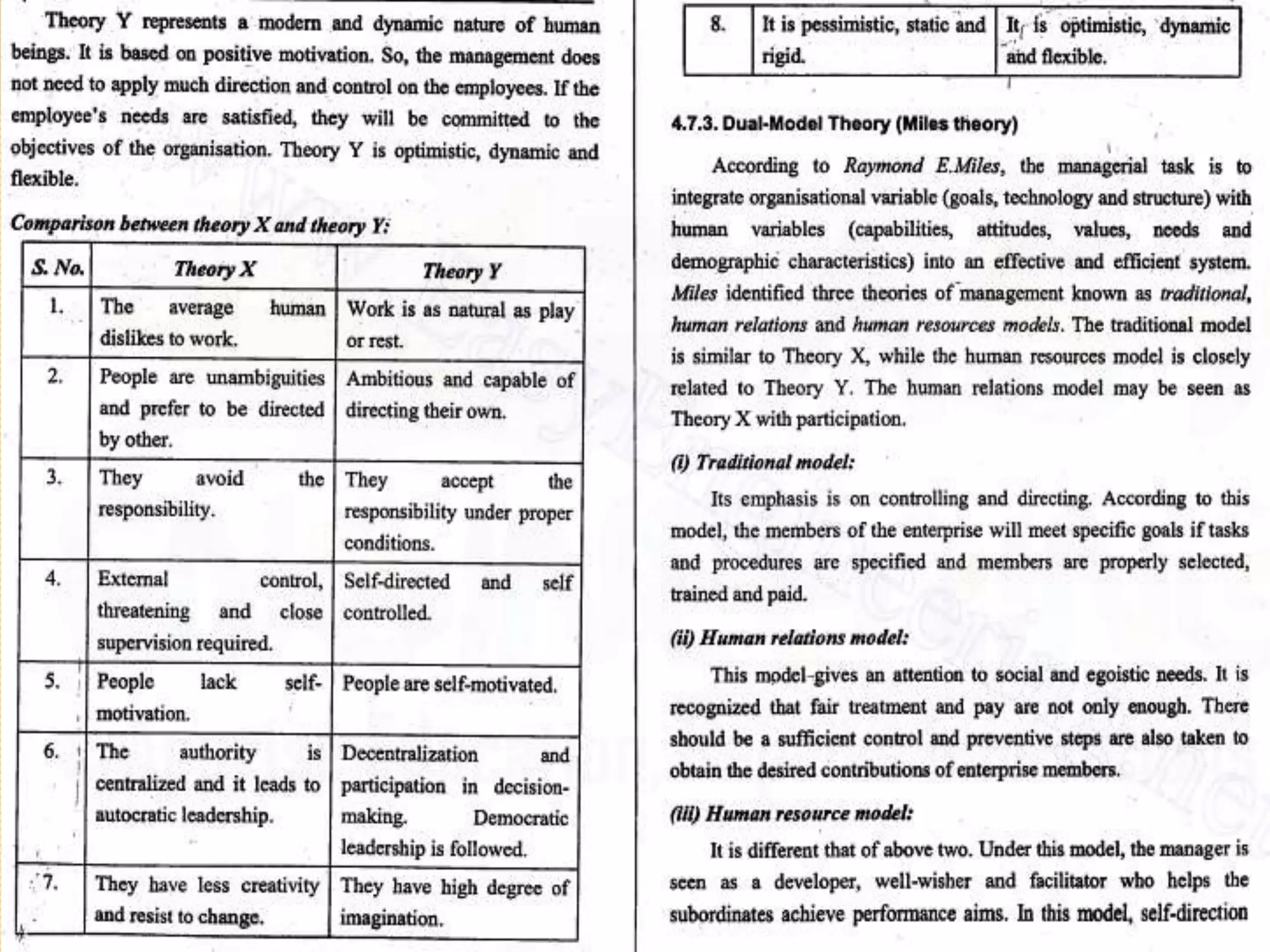
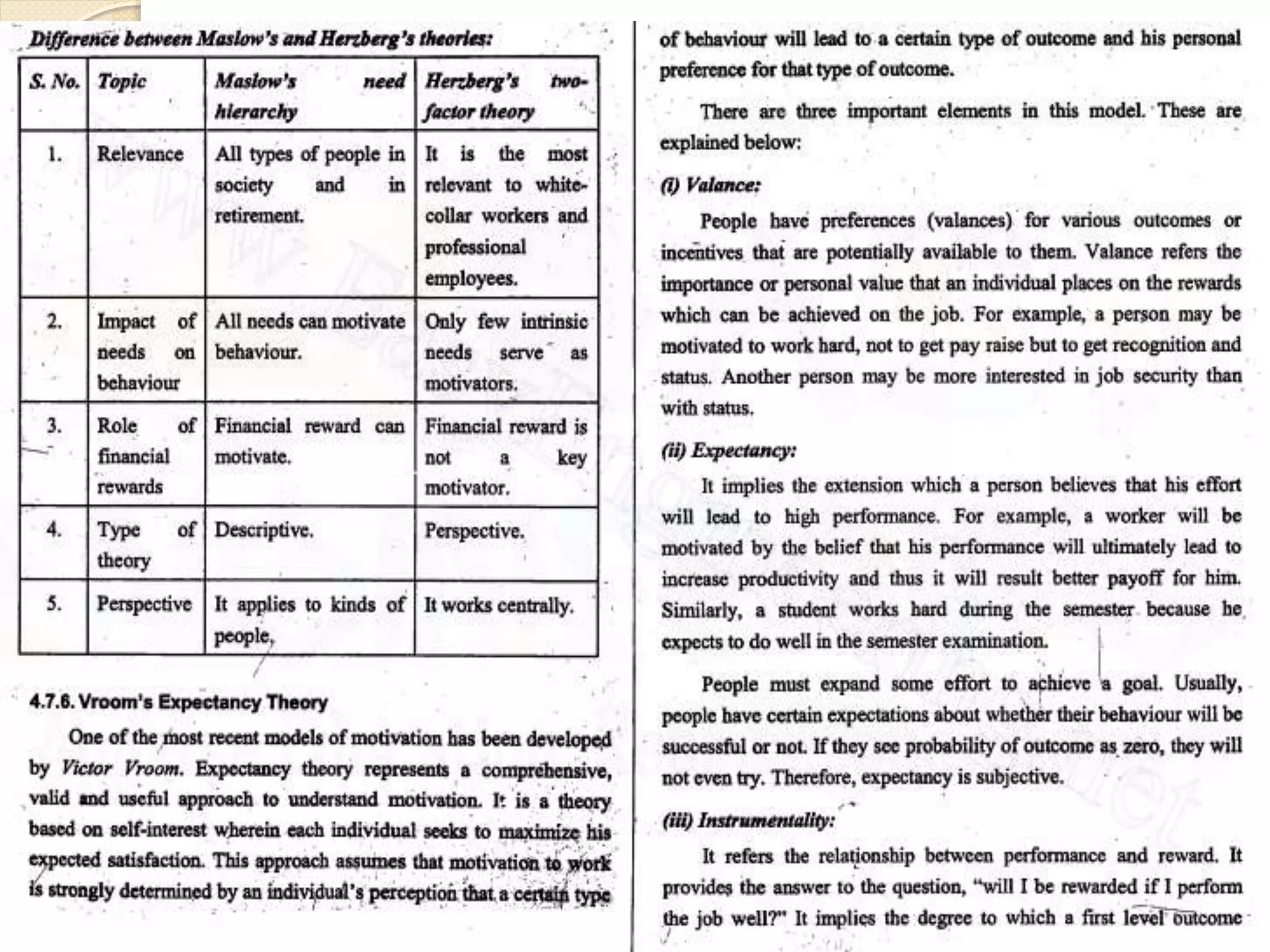
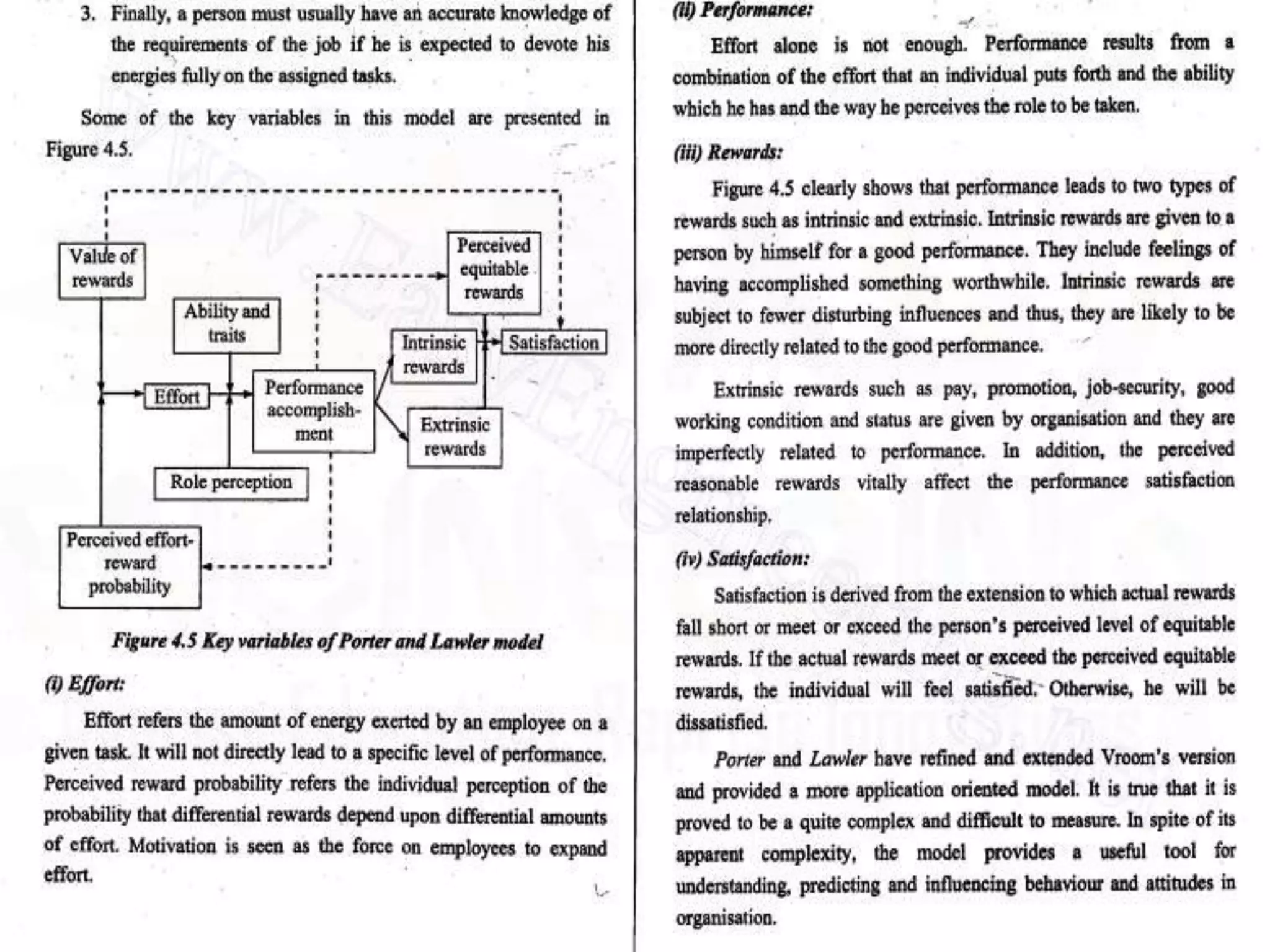
The document discusses the key functions and concepts of management including planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling. It specifically focuses on the directing function and covers topics like the nature and purpose of directing, foundations of individual and group behavior, motivation theories like Maslow's hierarchy and Herzberg's theory, techniques to improve motivation like incentives and job enrichment, leadership, communication, and ensuring job satisfaction. The document is about the principles of management with a focus on the directing function and how to guide and inspire human resources to achieve organizational goals.