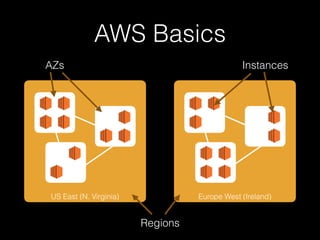
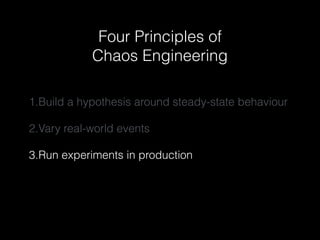
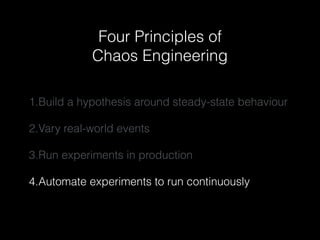
The document discusses chaos engineering as a systematic approach to improving system reliability by conducting experiments to understand how systems behave under unexpected conditions. It explores the evolution of chaos testing, the significance of resilience through redundancy, and highlights various tools like Chaos Monkey and its variants used for testing. Additionally, it outlines four principles of chaos engineering focused on understanding steady-state behavior, varying real-world events, conducting experiments in production, and automating these experiments.