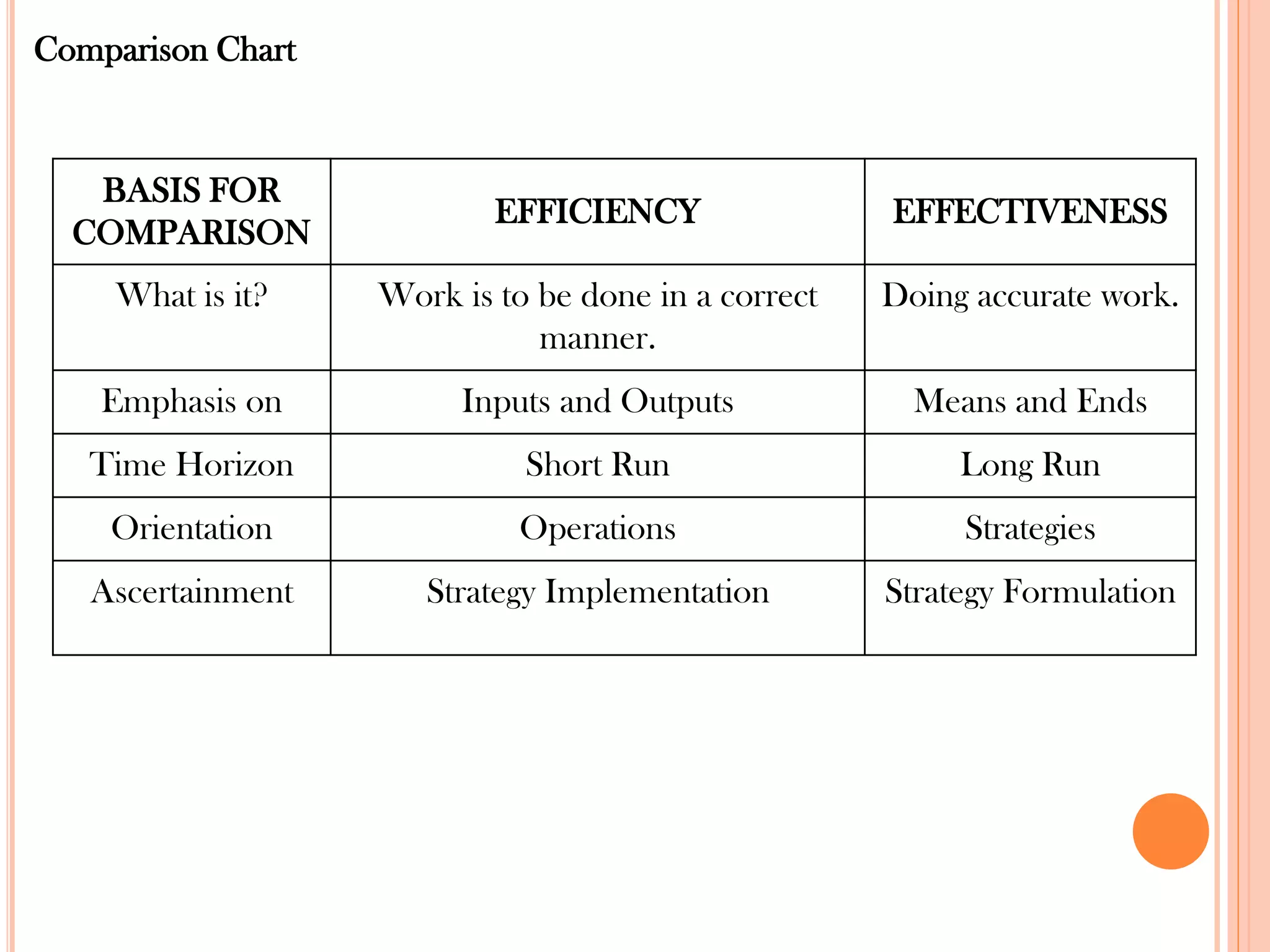
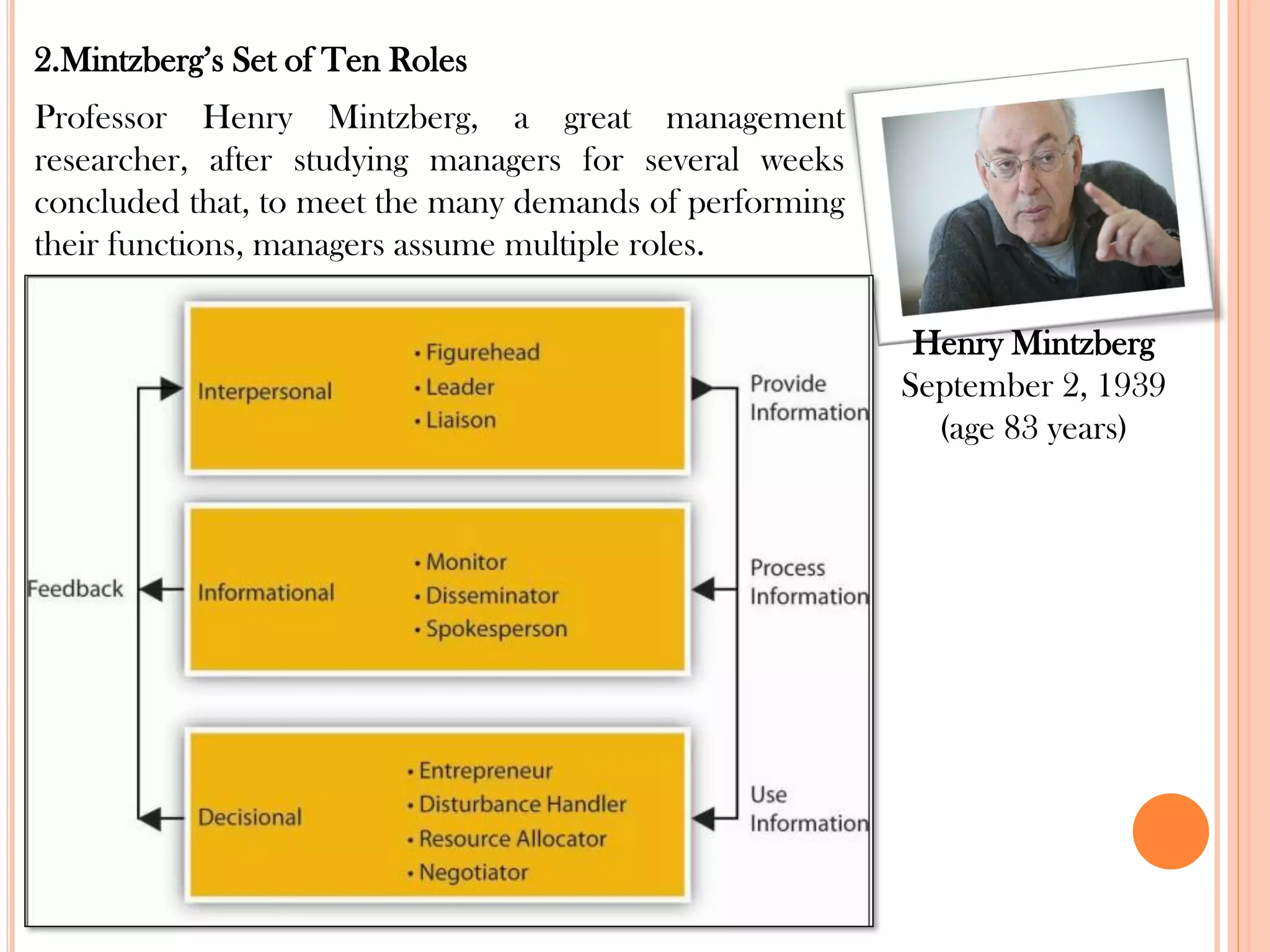
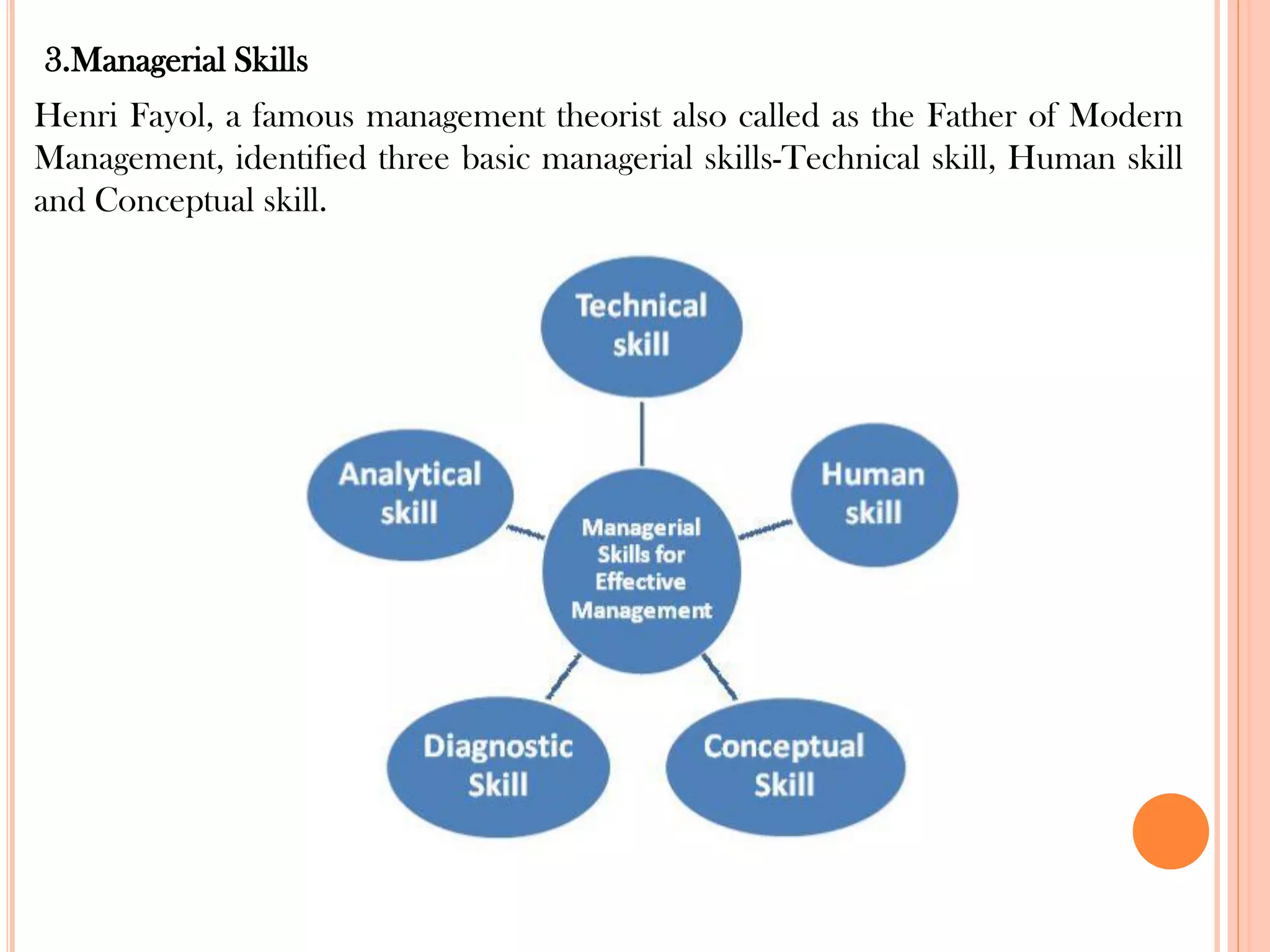
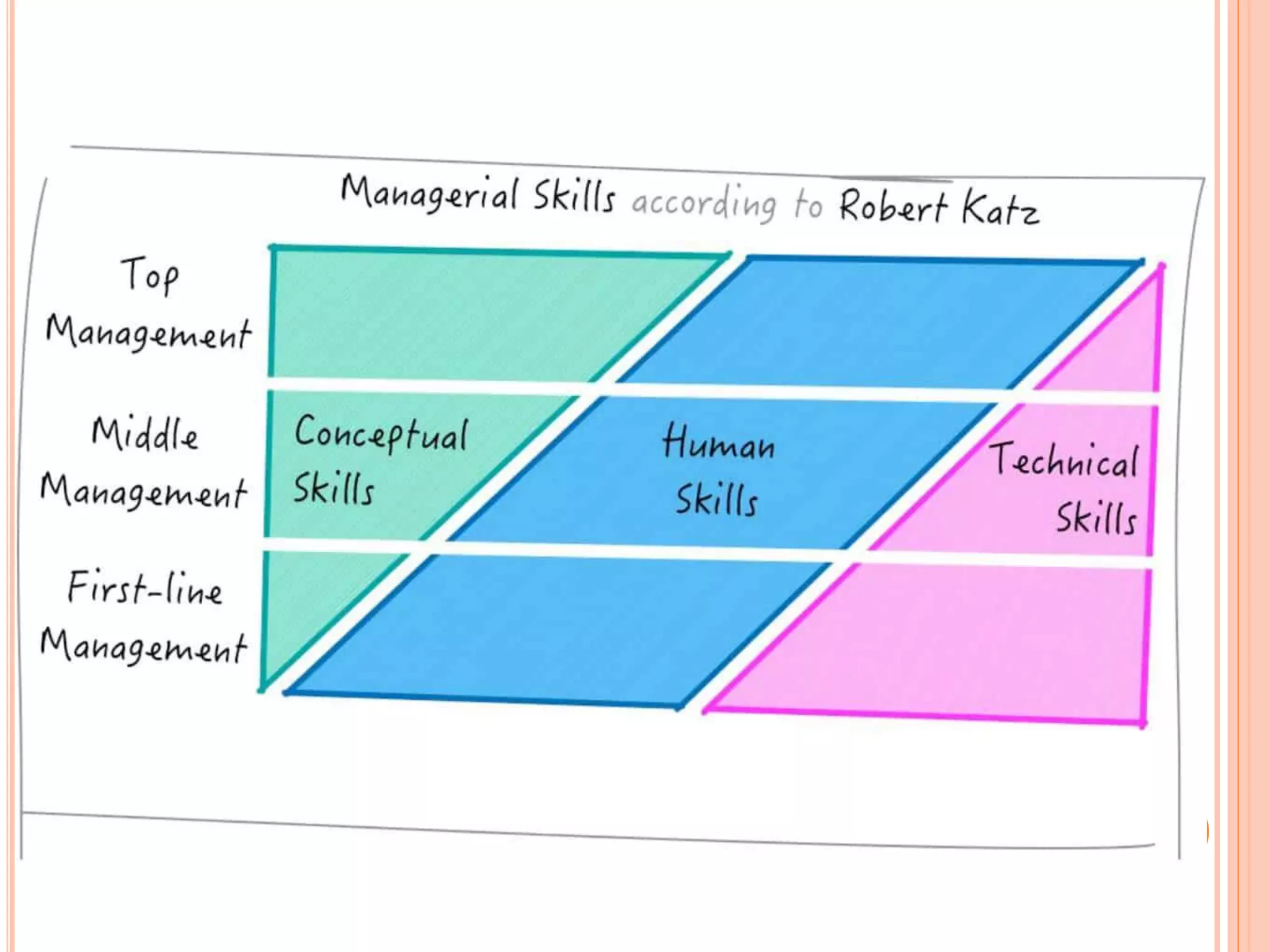
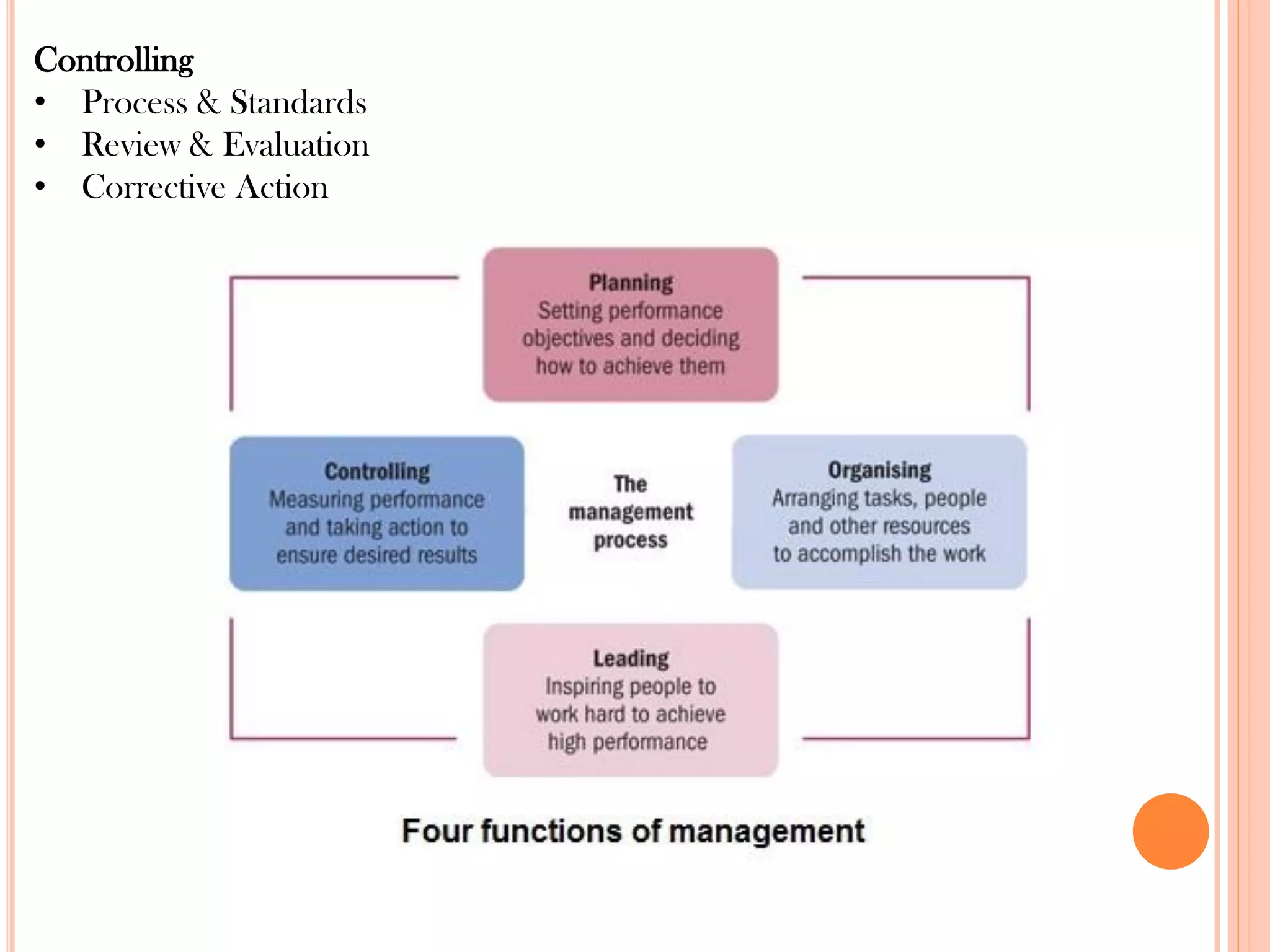
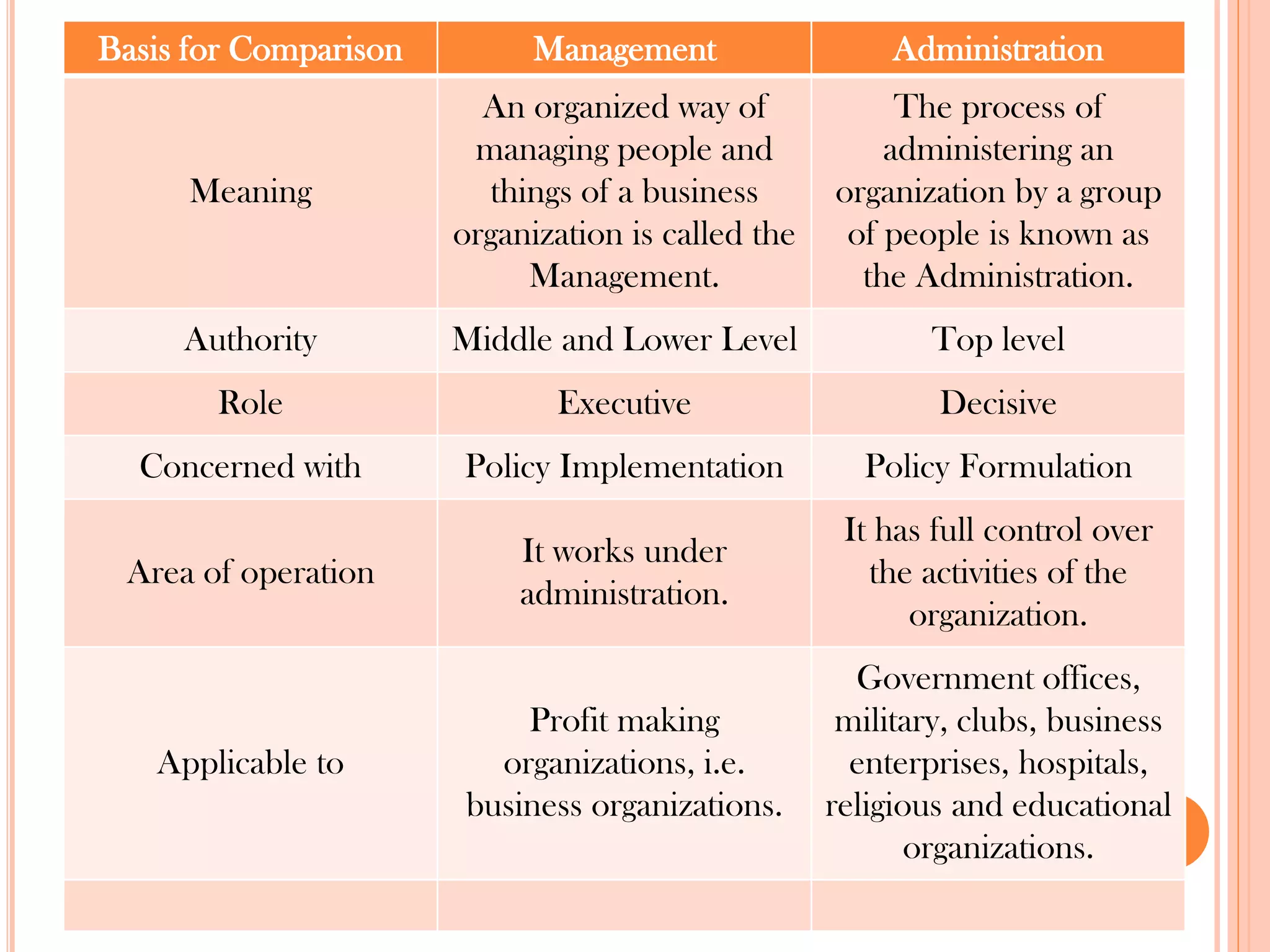
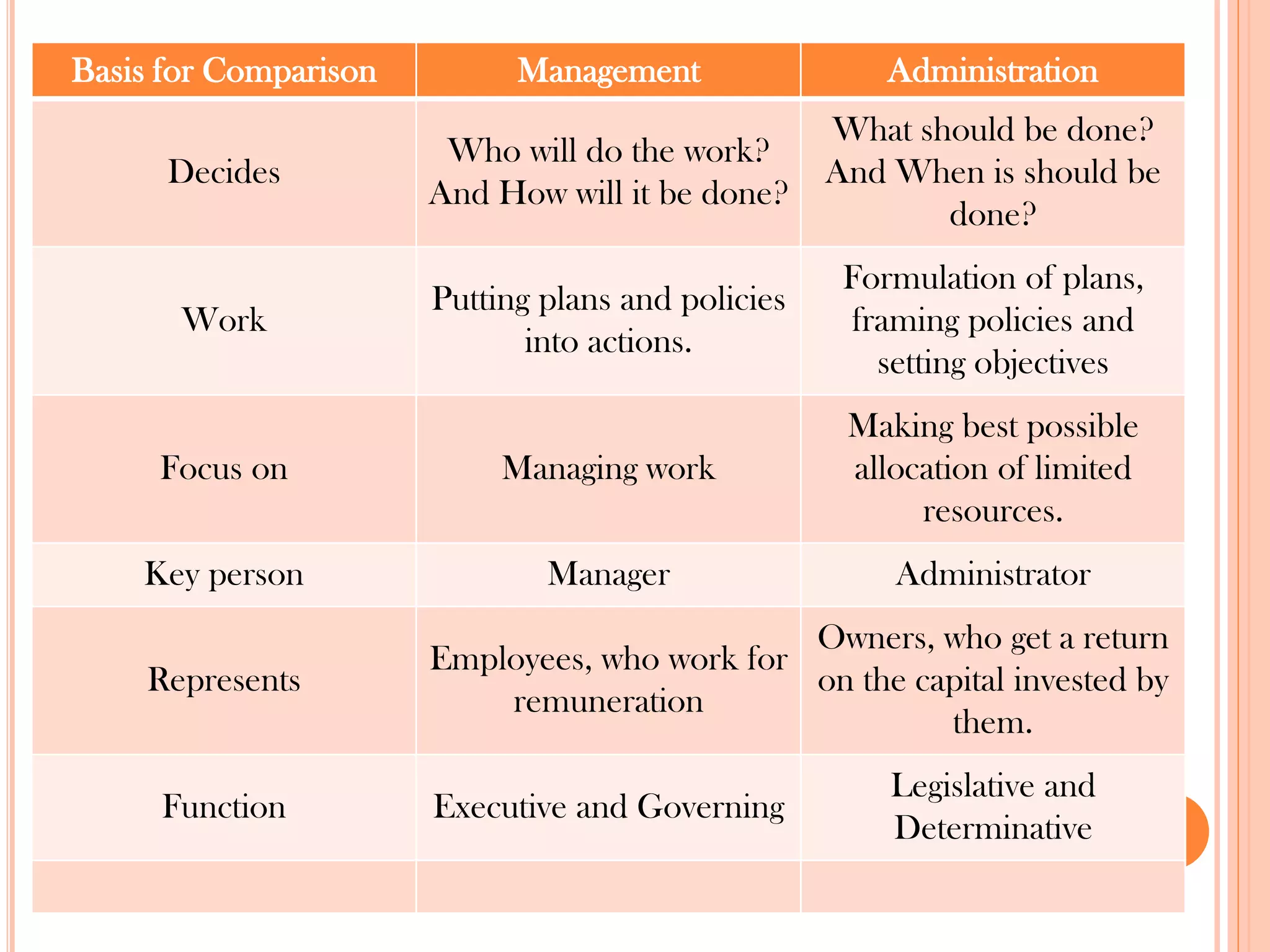
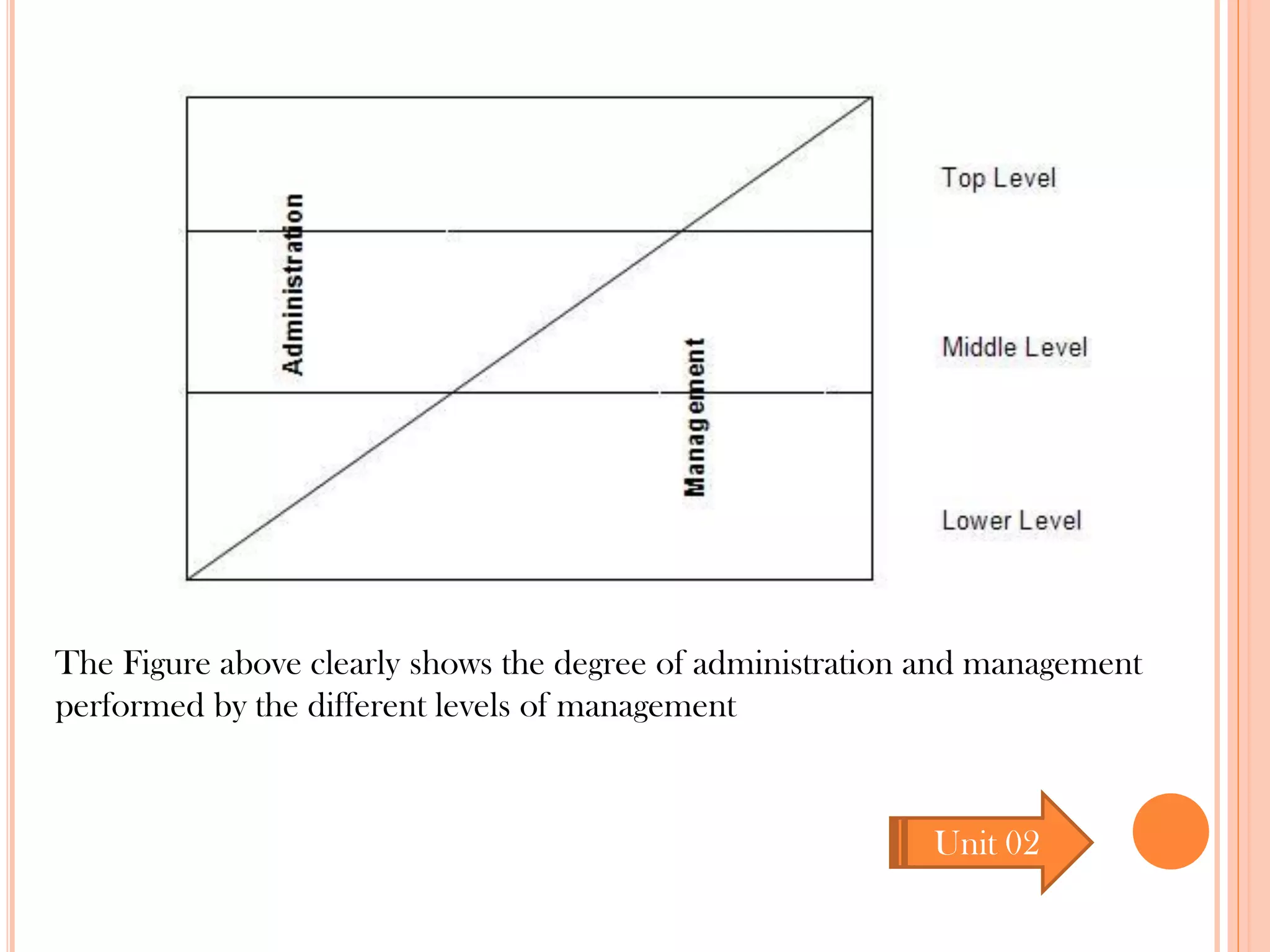
This document provides an overview of key principles of management. It discusses what management is, definitions of management, whether it is an art or science, the roles and skills of managers, and the P-O-L-C framework for the four main functions of management: planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Planning involves setting goals and strategies. Organizing is creating the organizational structure and allocating resources. Leading provides direction, motivation, and coordination. Controlling involves setting standards, reviewing performance, and taking corrective action.