Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


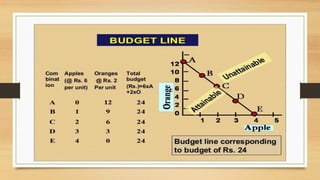
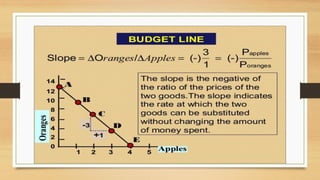


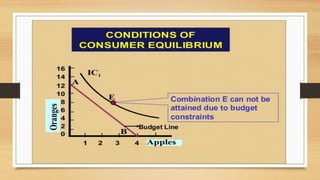
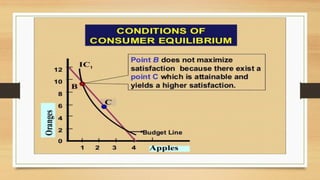
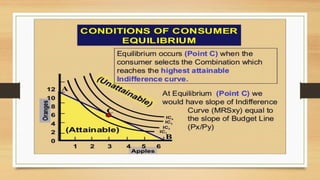



The document discusses budget constraints and consumer equilibrium. It explains that a budget line shows all combinations of two goods a consumer can buy given their budget and the goods' prices. A consumer will choose the combination on the budget line that maximizes their satisfaction. This optimal combination must be located on the budget line and give the consumer their most preferred basket of goods. For a consumer to be in equilibrium, their highest indifference curve must be tangent to their budget line. Indifference curve analysis is useful for understanding consumer behavior and concepts like consumer surplus.










