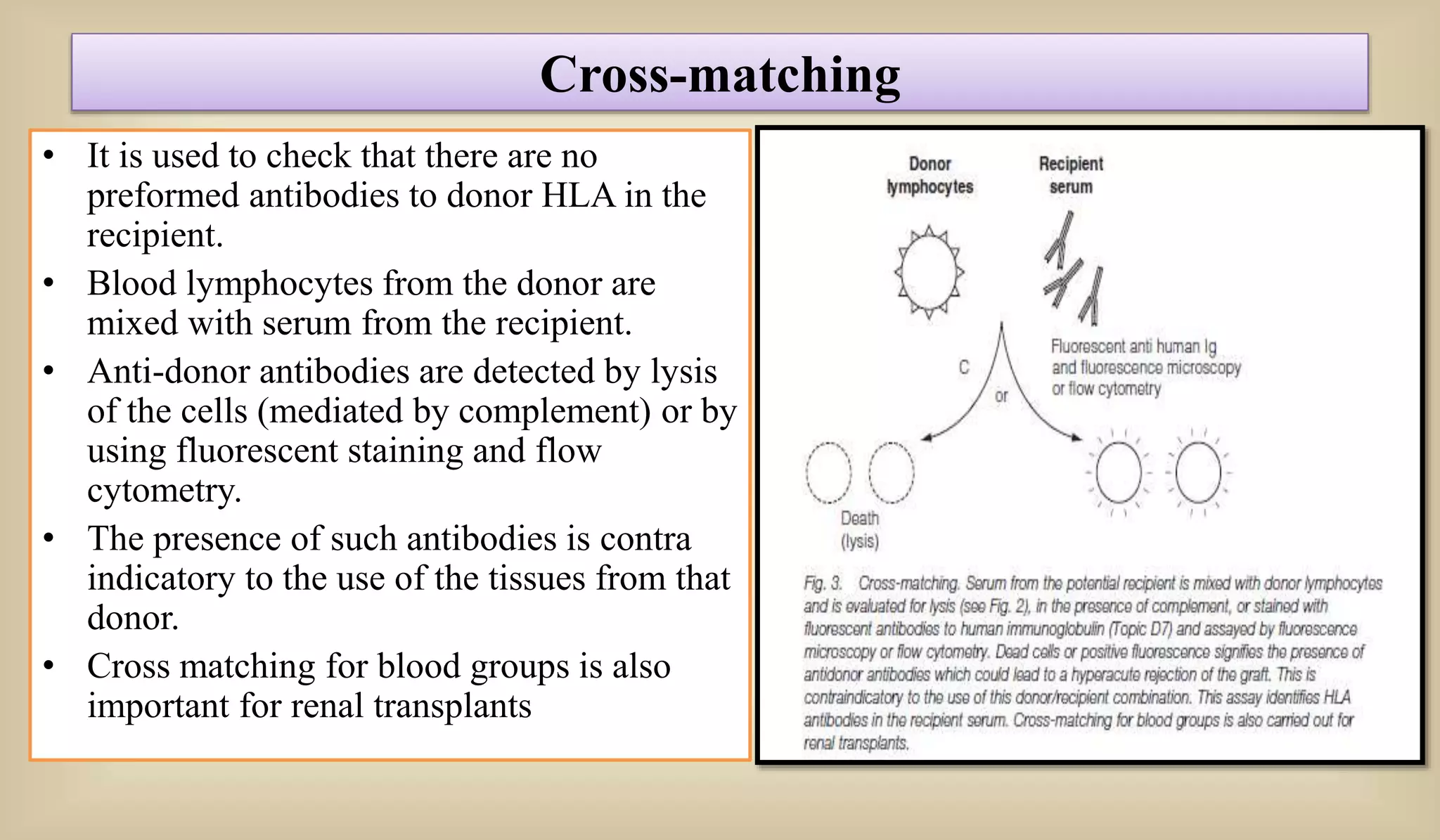
This document discusses various methods for preventing graft rejection in transplantation. It describes familial grafting which reduces HLA mismatches, tissue typing to determine allele matches between donor and recipient, and cross-matching to check for preexisting antibodies. It also discusses immunosuppression drugs like corticosteroids and cyclosporine A that are used when some mismatches are present. A special case of fetal transplantation is mentioned where the fetus carries HLA alleles from both parents.