Embed presentation











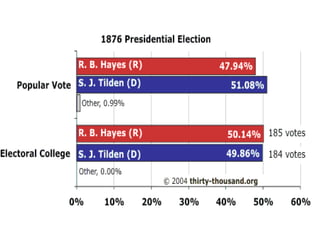
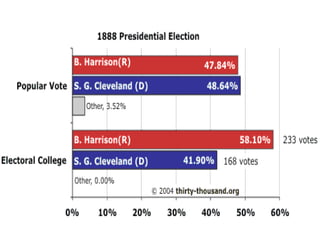
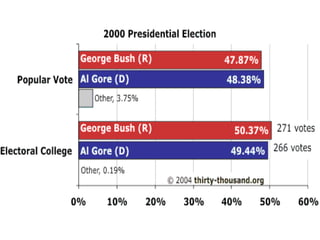
The document discusses the process for electing the US president as outlined in the Constitution. It notes the basic qualifications to be president, that the election occurs through the Electoral College rather than a popular vote, and how electoral votes are allocated to each state based on representation in Congress. It also describes amendments that modified the process, such as separating the ballots for president and vice president. The document then outlines the steps of how citizens vote for electors who then cast votes for president following the election. It discusses methods of selecting electors and issues like faithless electors. Finally, it covers edge cases if no candidate receives a majority of electoral votes and debates around the Electoral College system.













