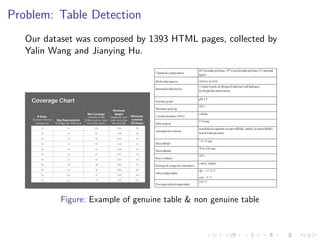
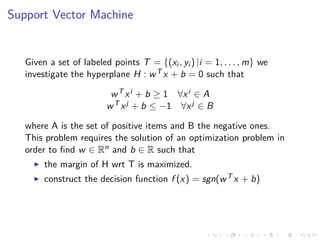
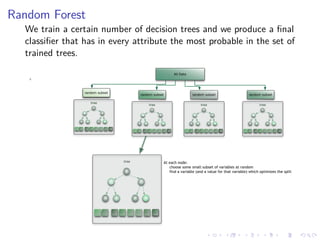
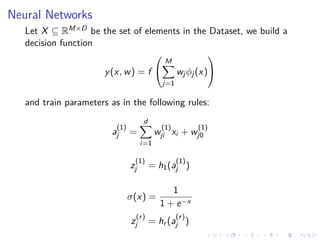
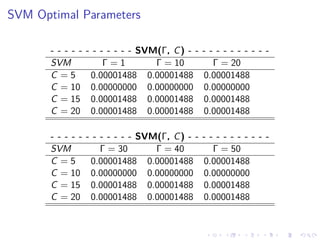
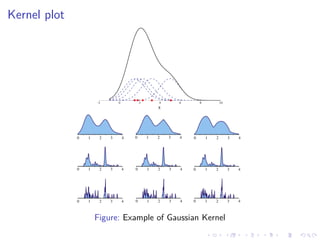
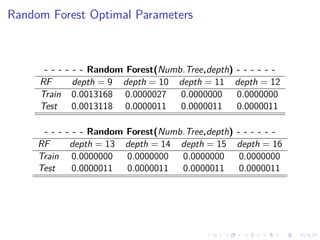
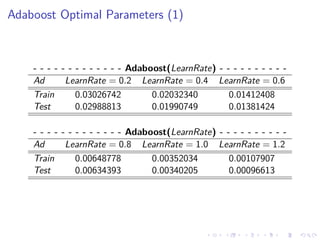
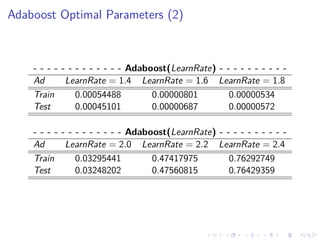
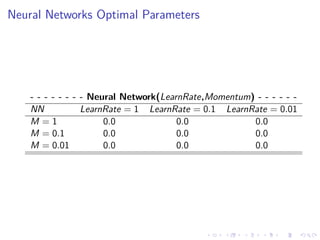
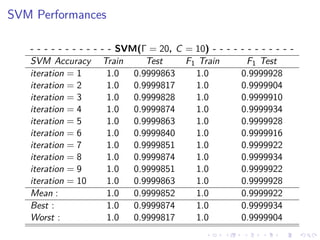
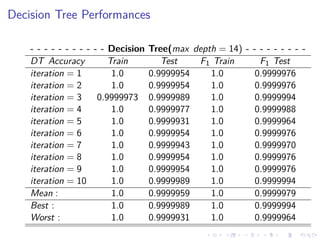
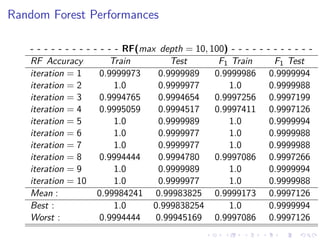
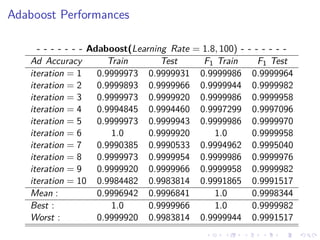
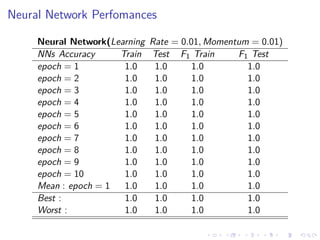
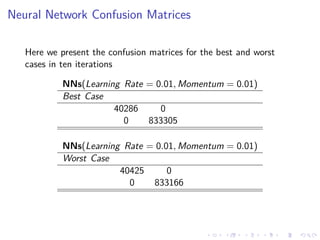
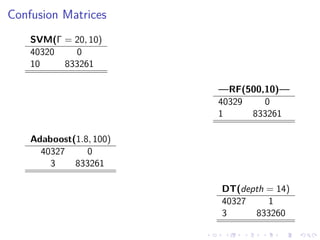
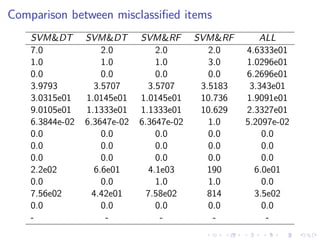
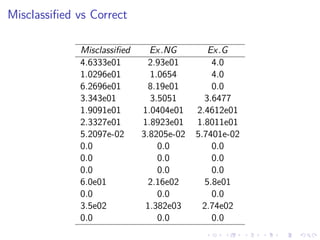
This document summarizes the results of a study on classifying tables in HTML documents as genuine or non-genuine tables. It describes the dataset, features considered for the classification including layout, content type and word group features. It discusses various machine learning models tested - SVM, Decision Tree, Random Forest, Adaboost and Neural Networks. It provides the optimal parameters determined for each model and compares their performance on the table classification task based on accuracy, F1 score and confusion matrices.