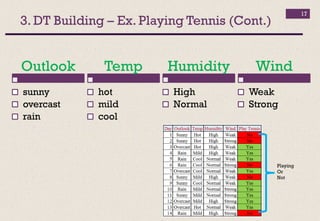
The document outlines the process of building decision trees for machine learning. It discusses key concepts like decision tree structure with root, internal and leaf nodes. It also explains entropy and information gain, which are measures of impurity/purity used to select the best attributes to split nodes on. The example of building a decision tree to predict playing tennis is used throughout to demonstrate these concepts in a step-by-step manner.