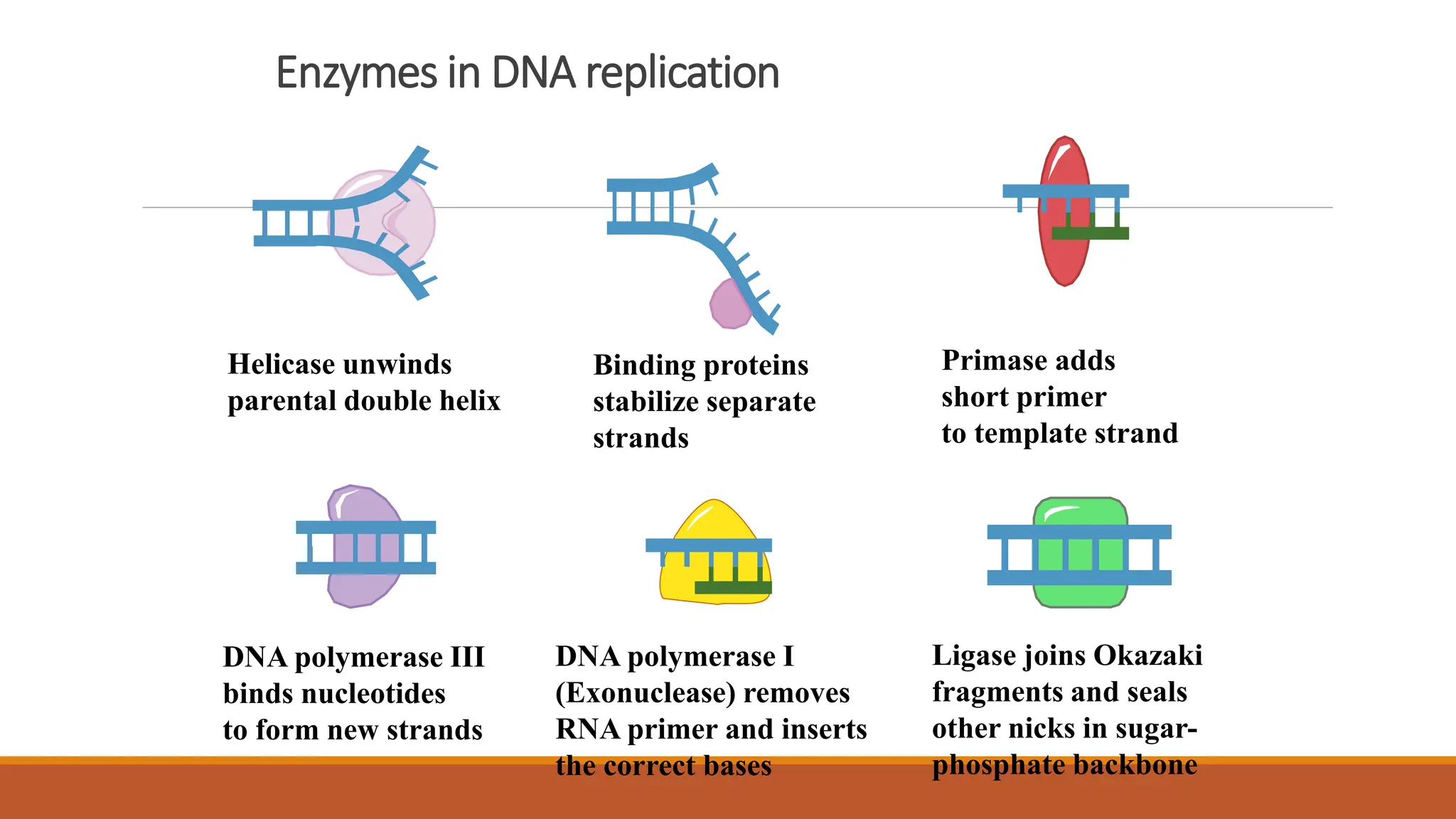
DNA replication involves unwinding the double helix and using each parental strand as a template to synthesize complementary daughter strands, facilitated by various enzymes. Transcription, on the other hand, creates messenger RNA (mRNA) from a DNA template through initiation, elongation, and termination phases, wherein RNA polymerase helps synthesize the RNA molecule. The resulting mRNA is then transported to the cytoplasm for translation.