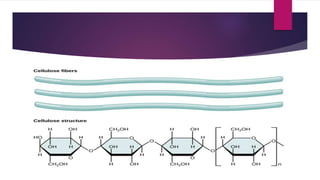
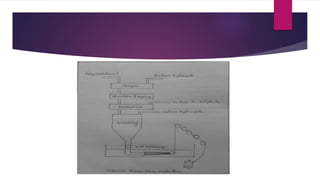
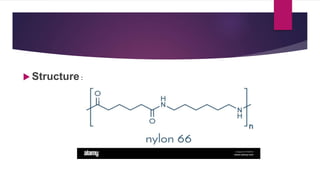
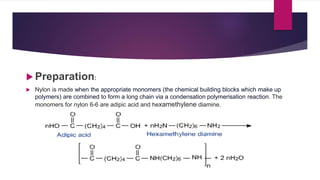
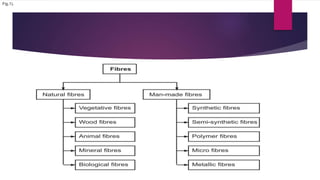
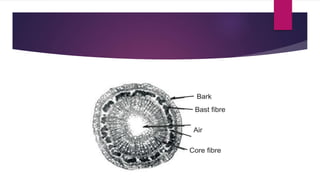
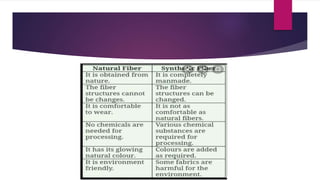
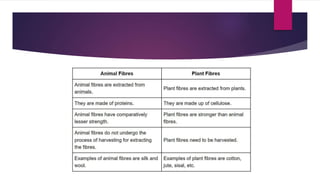
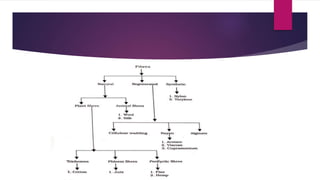
Cellulose is a polysaccharide composed of glucose units linked together by beta-1,4-glycosidic bonds. It is the main component of plant cell walls and is produced by plants and some bacteria through biosynthesis. In plants, cellulose synthesis occurs on plasma membrane-bound rosette terminal complexes that polymerize glucose residues from UDP-glucose to form cellulose chains. These chains then assemble into crystalline microfibrils in the cell wall. Cellulose is widely used to produce derivatives like cellulose esters and rayon. Rayon is a regenerated cellulose fiber produced through a chemical process involving wood pulp. It has the same molecular structure as cellulose. Catgut is prepared from the natural