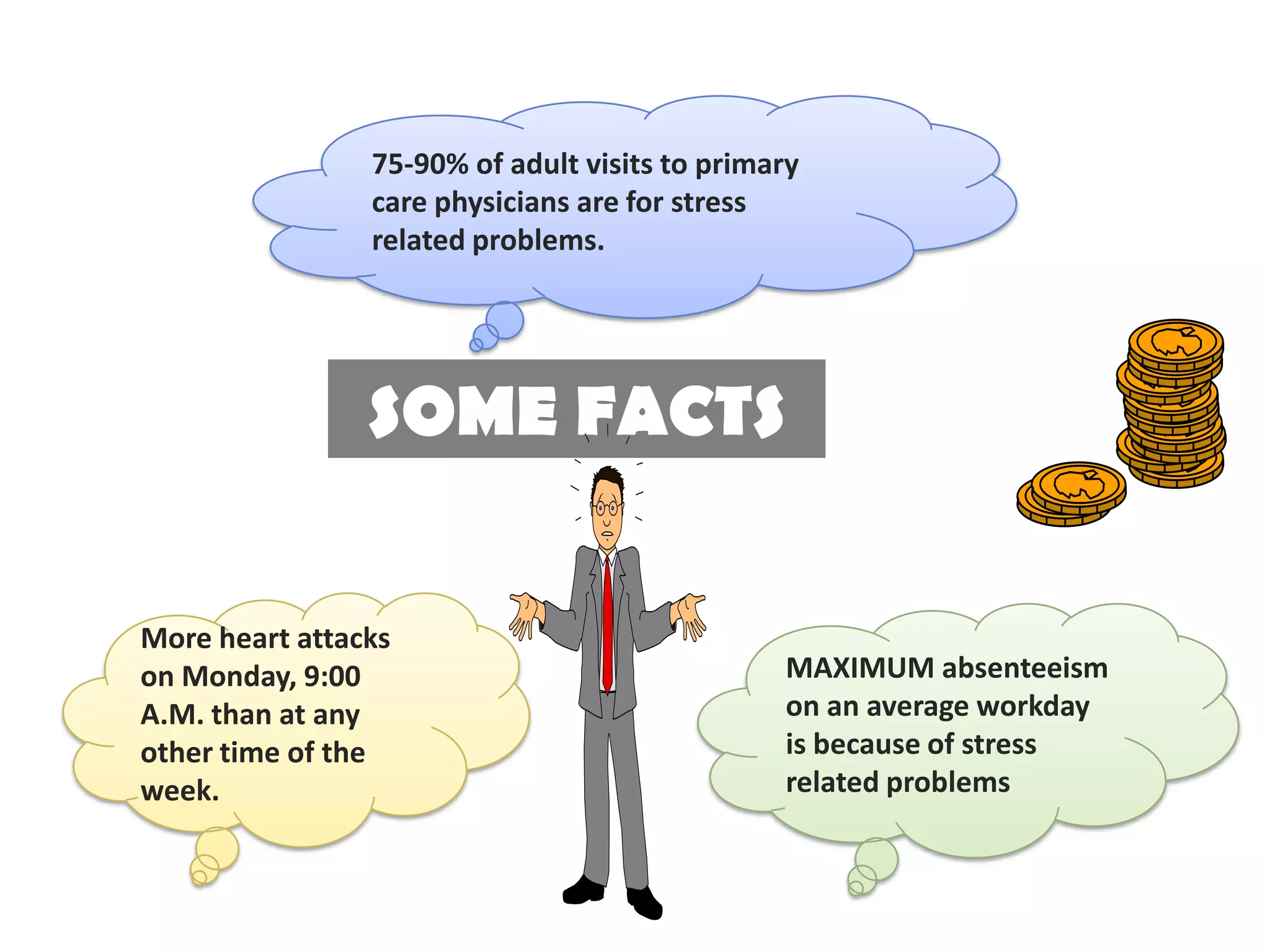
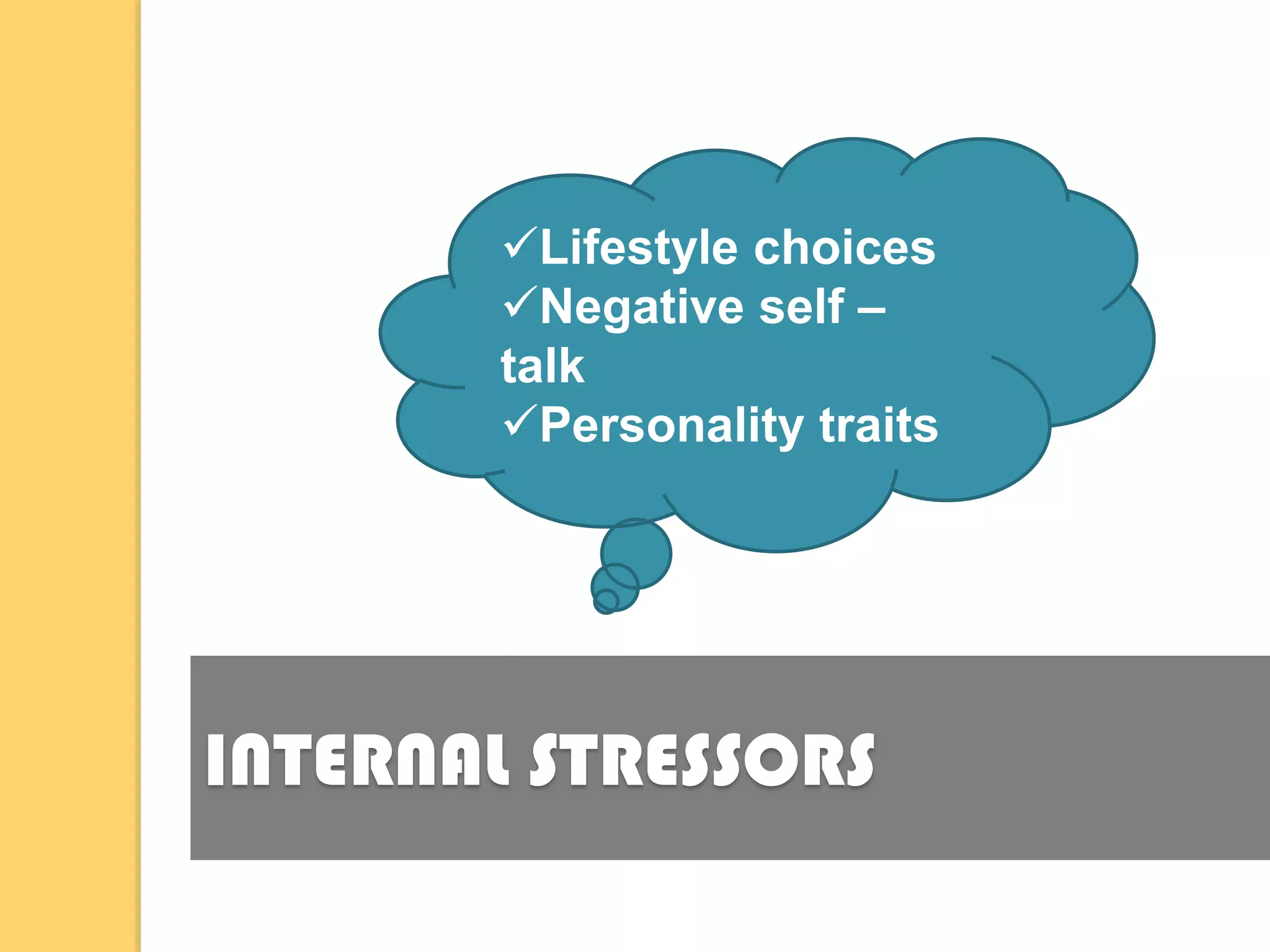
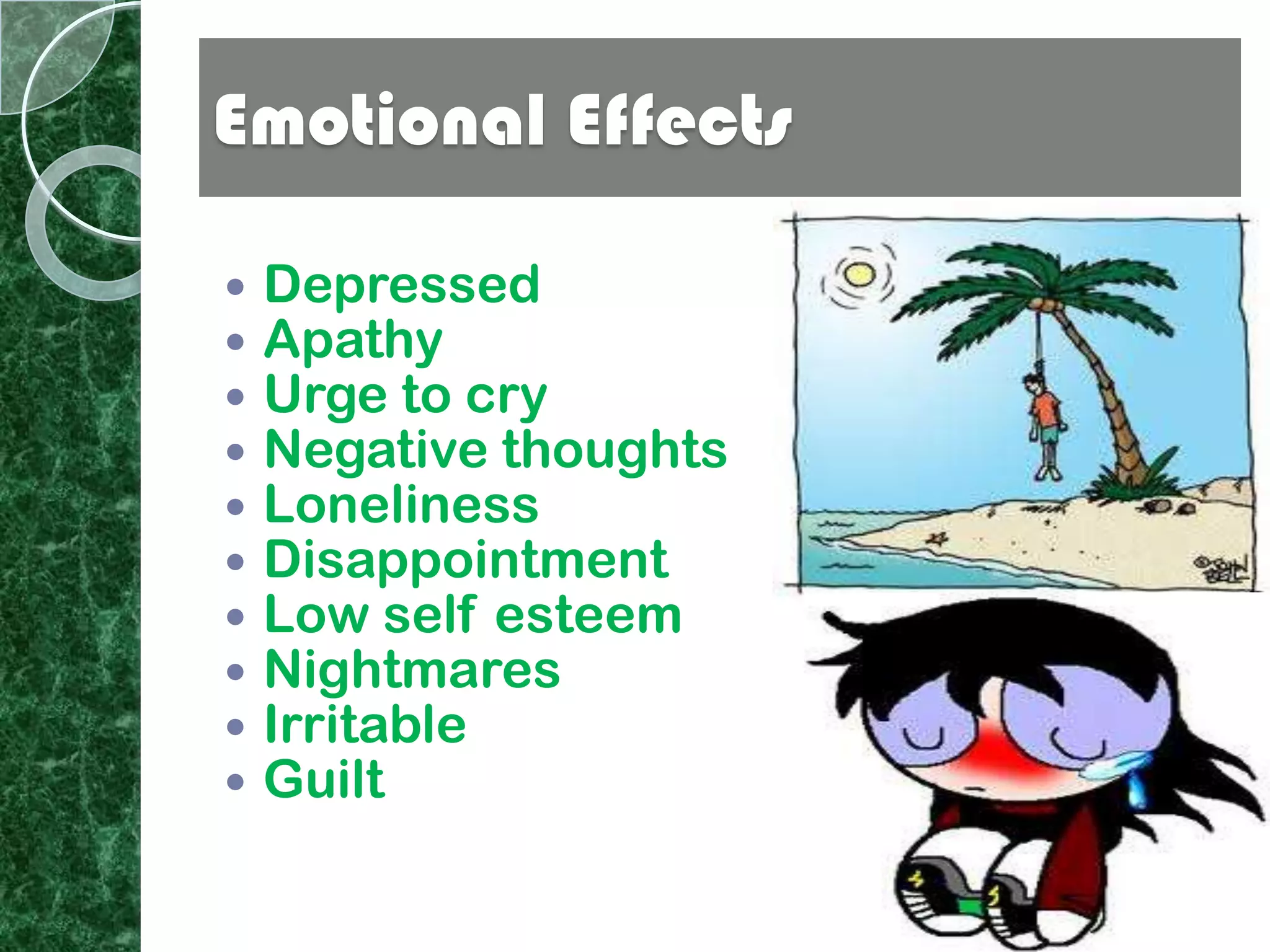
This document discusses stress, its causes and effects. It defines stress and identifies common stressors like noise, rules and deadlines. It describes the three stages of the general adaptation syndrome: alarm reaction, resistance and exhaustion. The document outlines the physical, mental, behavioral and emotional symptoms of stress. It discusses workplace stress and provides strategies for managing stress like positive thinking, humor and time management. Finally, it addresses study stress and exam stress and gives tips for relieving stress like preparation, visualization and limiting drugs.