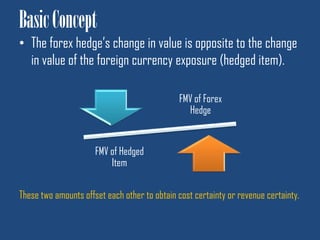
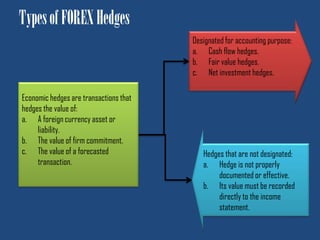
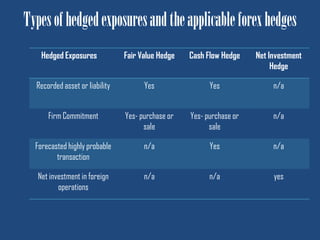
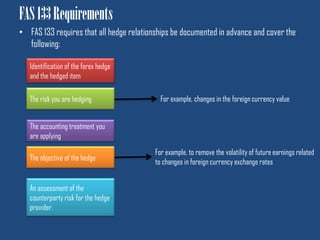
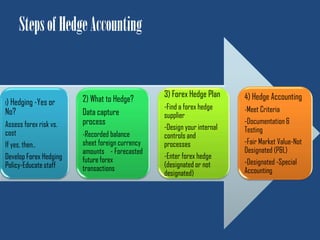
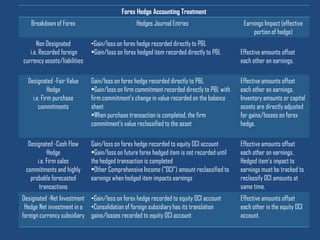
This document discusses forex hedge accounting and provides an overview of key concepts. It describes the basic idea that a forex hedge's value changes opposite to the hedged foreign currency exposure to provide cost or revenue certainty. It outlines the main types of hedges including cash flow, fair value, and net investment hedges. The document also discusses hedge accounting standards like IAS 39 and FAS 133, which require documentation of hedge relationships in advance. Finally, it notes some common causes of hedge ineffectiveness like mismatches in currencies, maturities, or underlying risks between the hedged item and hedging instrument.