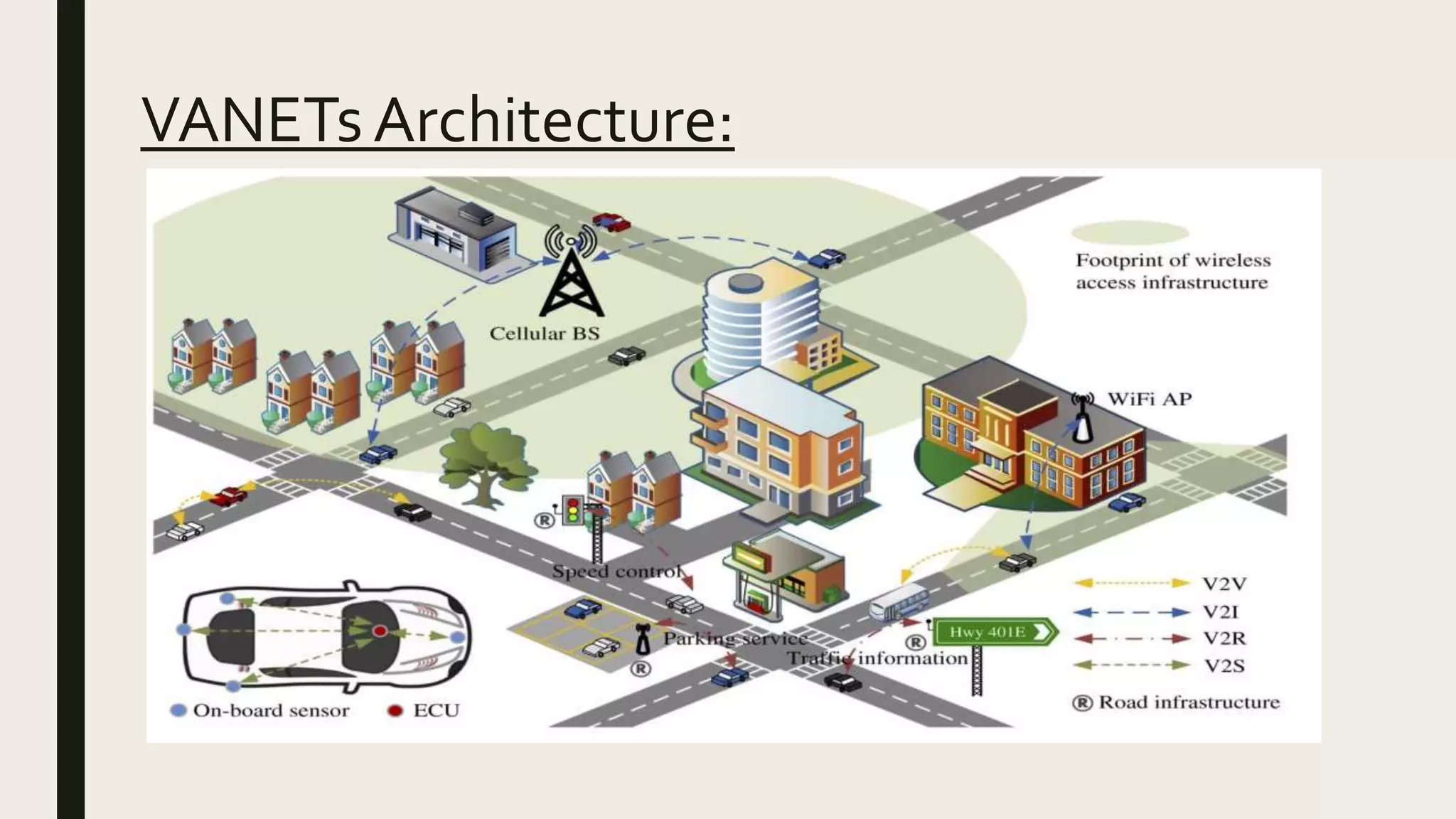
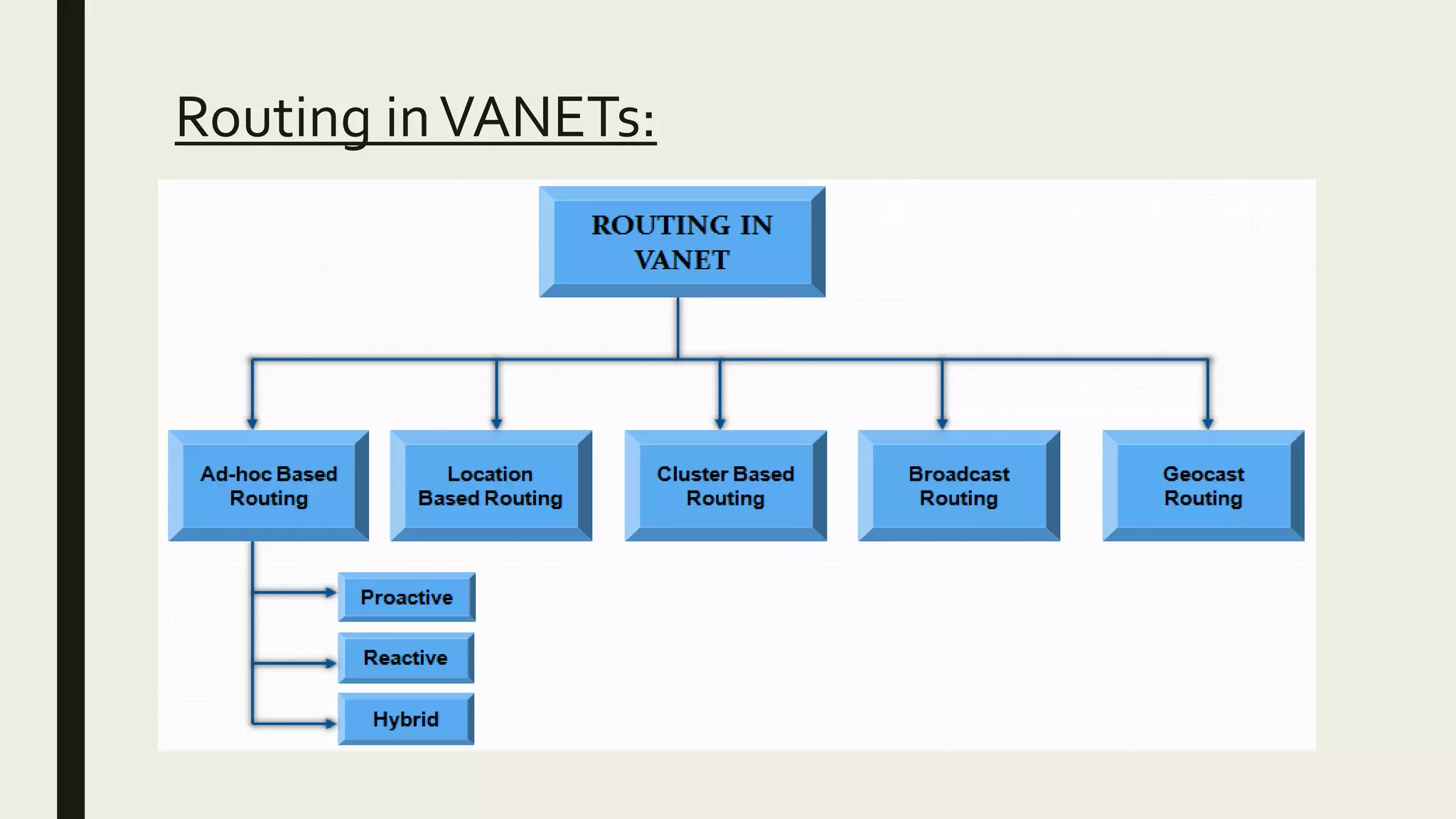
VANET (Vehicular Ad-hoc Network) technology allows vehicles to communicate with each other (V2V) and with nearby road infrastructure (V2I) to increase road safety. The goal is to avoid over 60% of accidents through early warnings. Vehicles broadcast safety and event messages within a 1000m range at speeds up to 120kph. Challenges include developing effective routing, security, broadcasting, and quality of service standards for the fast moving and unbounded network. Current uses provide navigation, emergency response, theft assistance and alert services through telematics features.