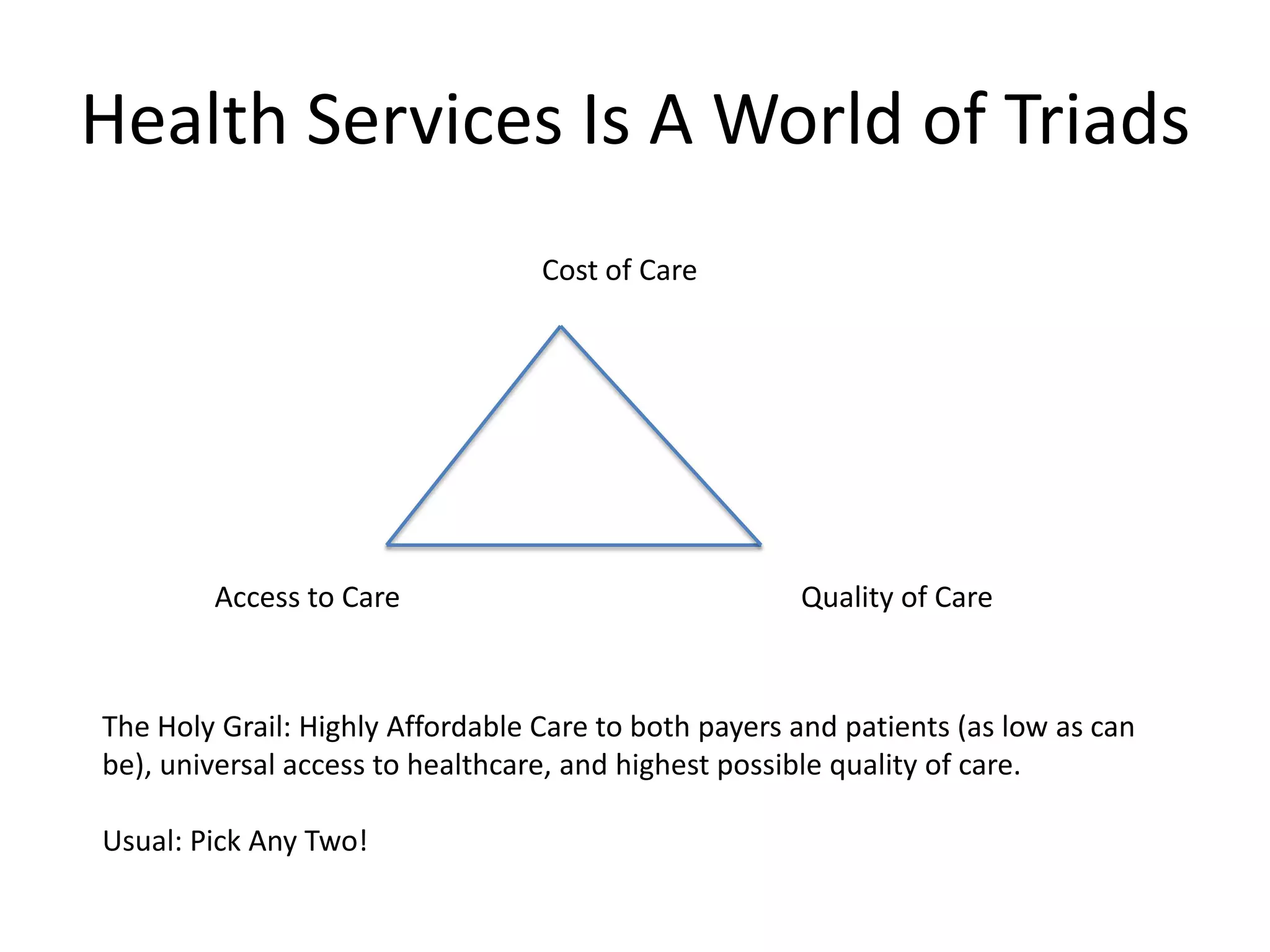
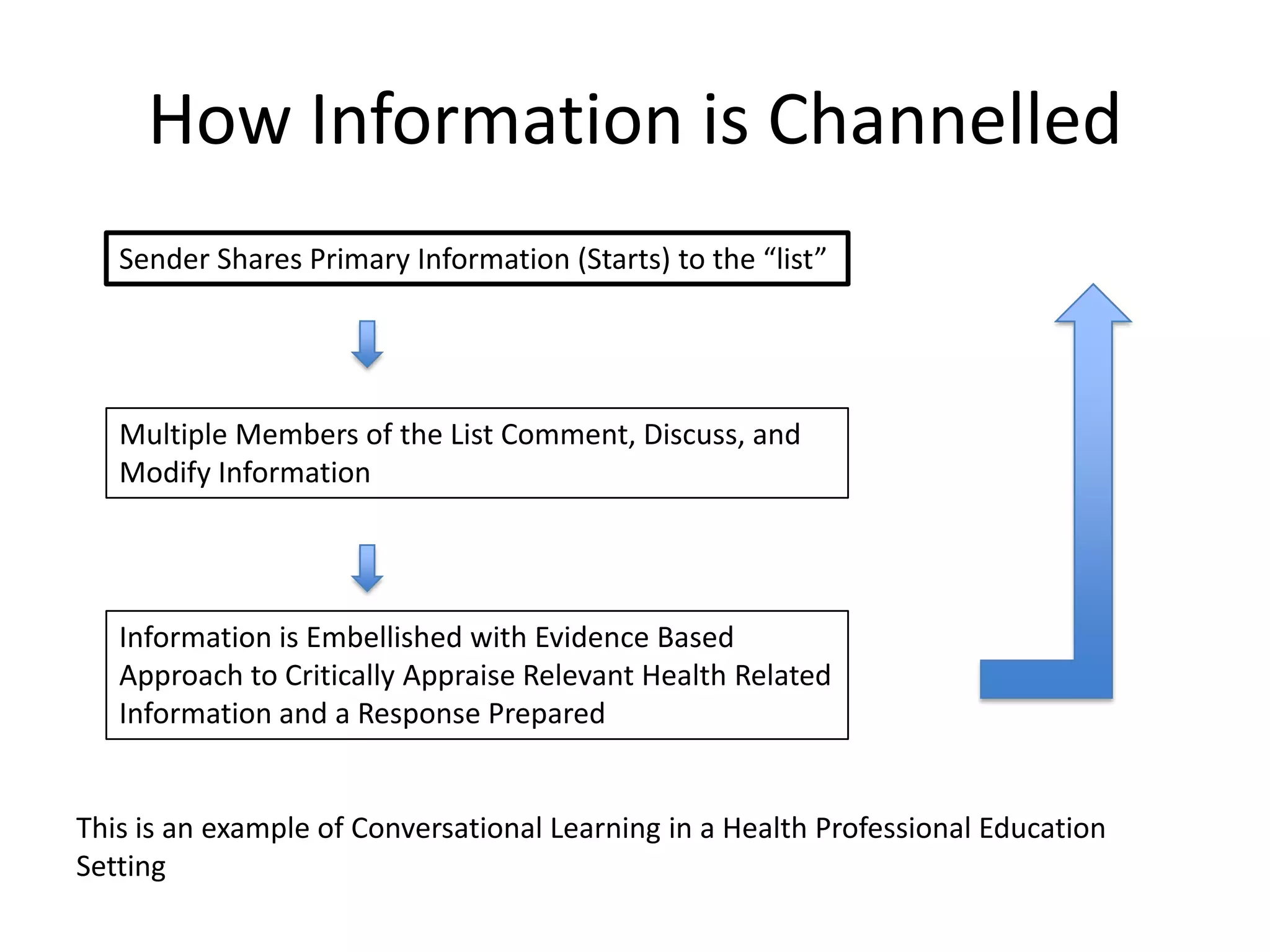
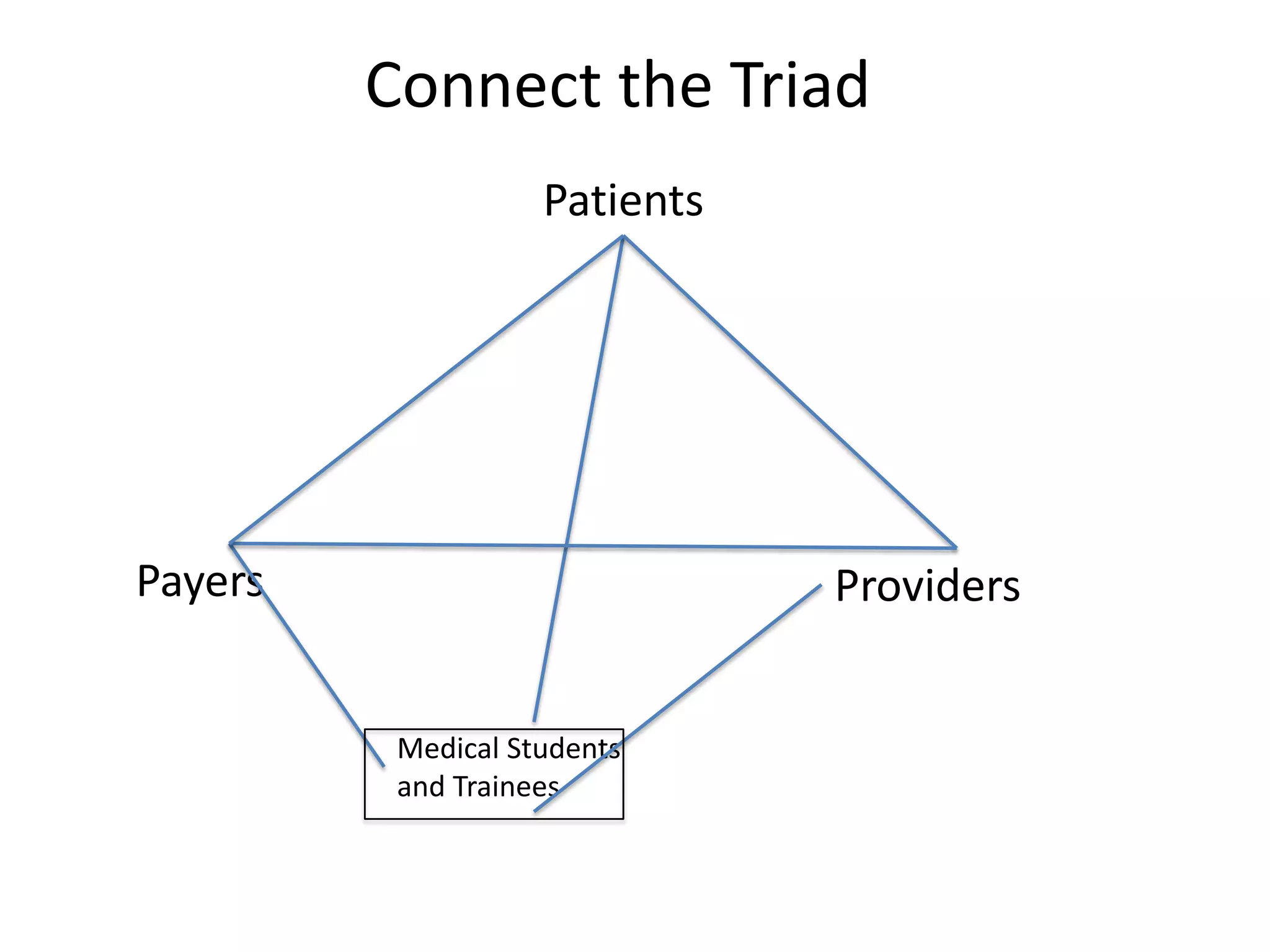
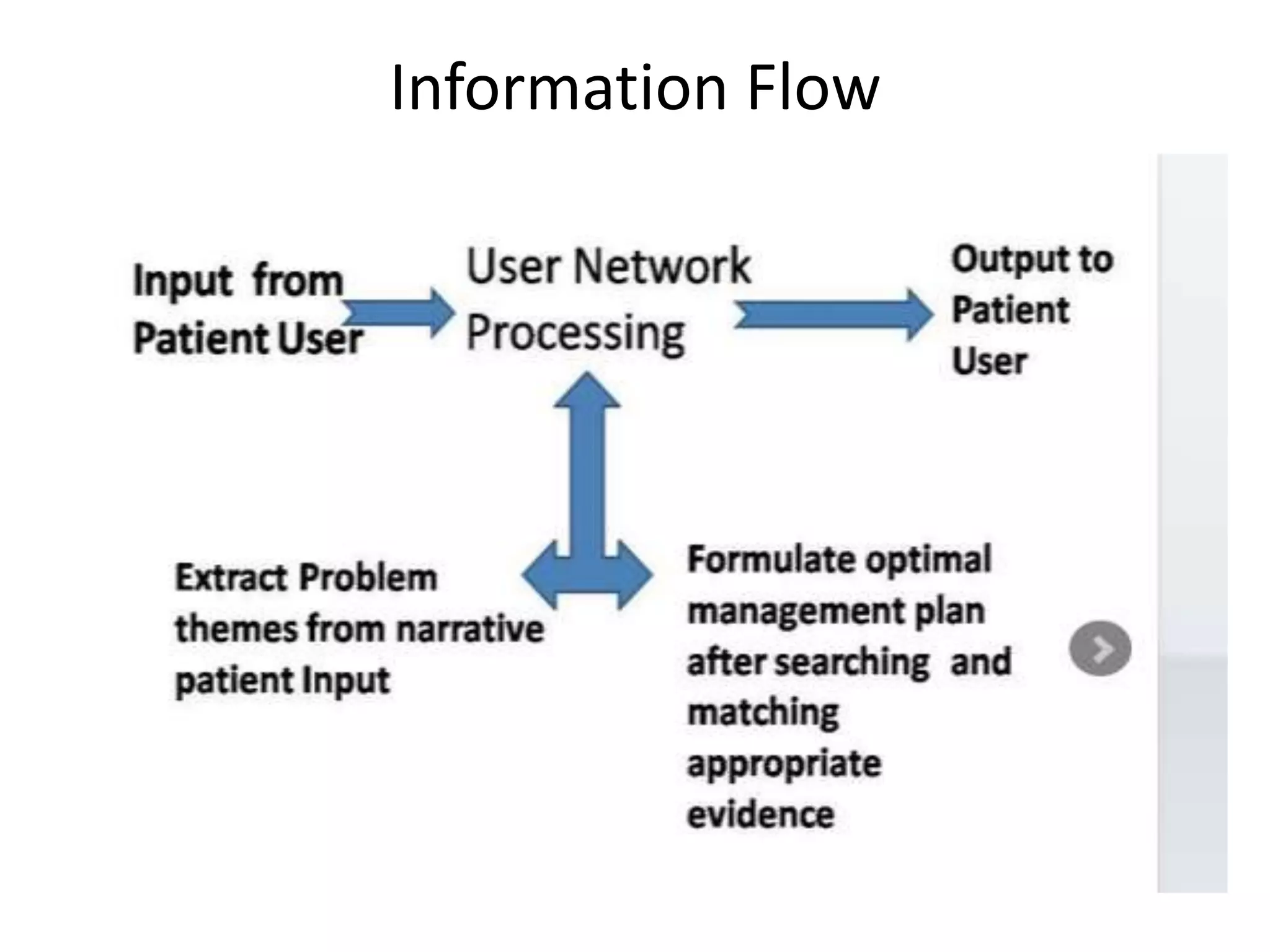
The document discusses the need for improved access to evidence-based health information, highlighting the challenges faced by patients and healthcare providers, particularly in developing countries. It emphasizes the role of students in connecting various stakeholders and fostering a system of conversational learning that enhances community engagement in healthcare. The text proposes creating a collaborative platform that brings together students, experts, and patients to address healthcare access and quality through telehealth and other innovative solutions.