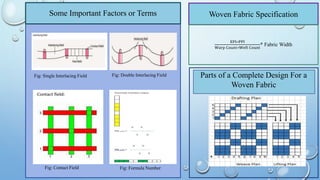
The presentation provided an introduction to fabric structure and design, focusing on plain weave as the most basic weave structure. Key aspects of plain weave were defined, including the interlacing of warp and weft threads at right angles. Variations of plain weave such as rib weave and matt weave were also described, highlighting differences in their structural properties and production methods.