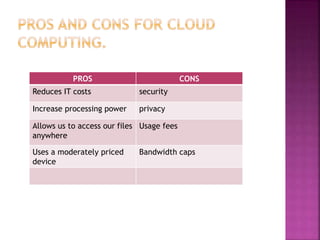
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, defining it as a network-based computing model that utilizes internet resources instead of local infrastructure. It discusses its benefits, such as reduced IT costs and increased accessibility, alongside its primary service models: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Additionally, it highlights factors affecting cloud services, including usage fees and security concerns.