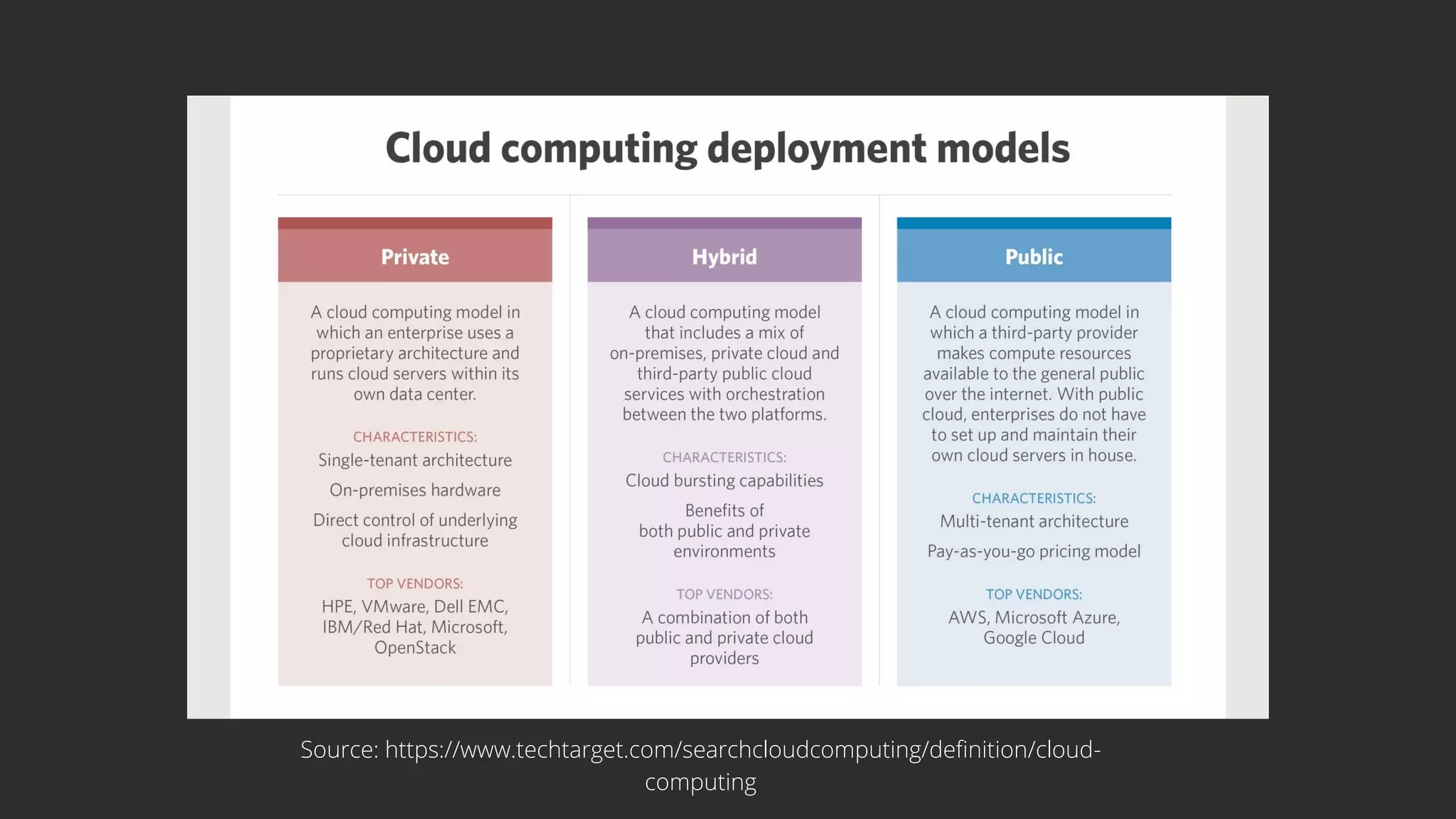
This document discusses cloud computing, including its definition, how it works, and different types. Cloud computing delivers hosted services over the internet and enables access to data and applications from remote servers. The main types of cloud computing are infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). IaaS provides virtual servers and storage, PaaS hosts development tools, and SaaS delivers software applications via the internet. The document also covers characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of cloud computing.