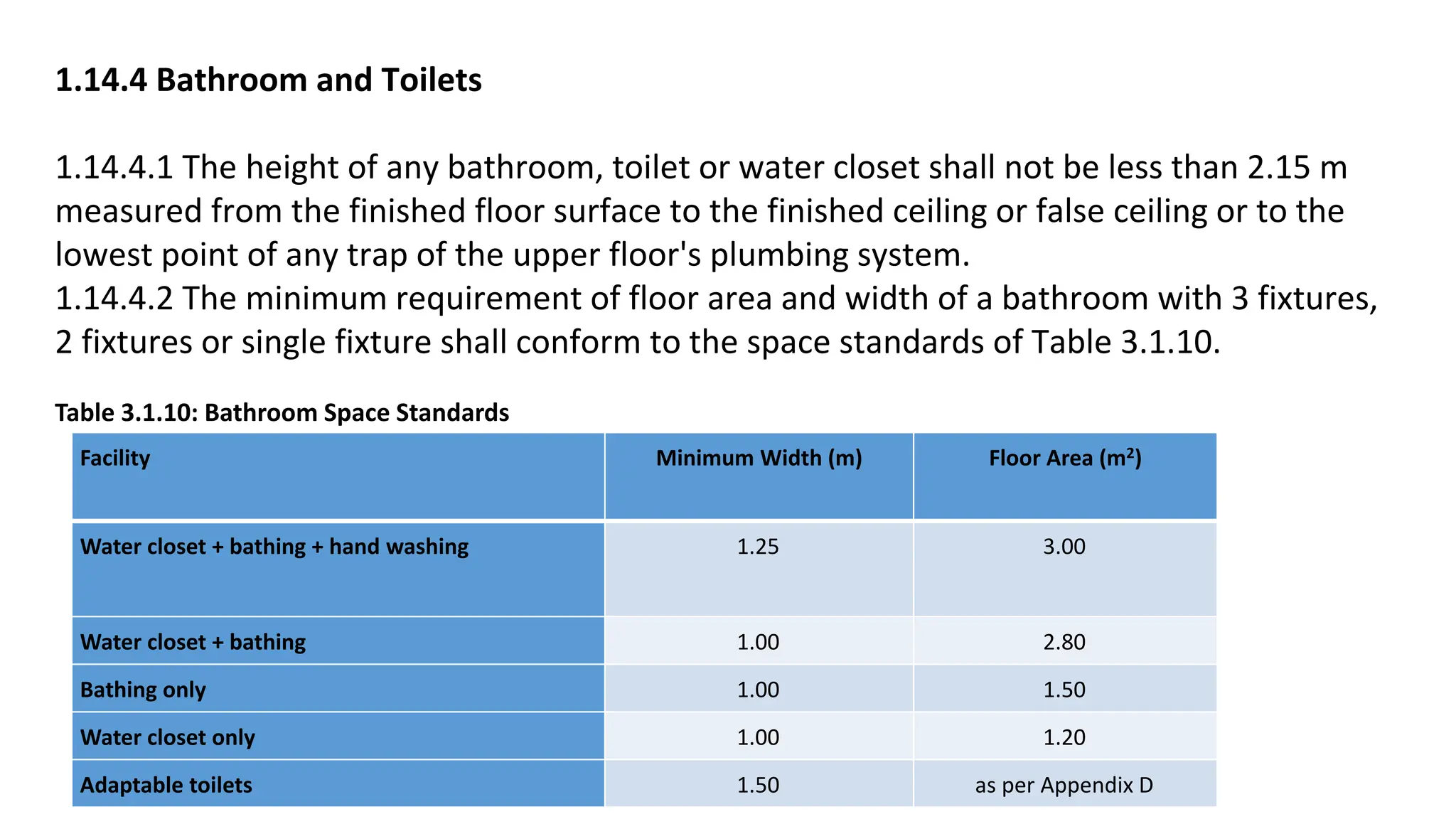
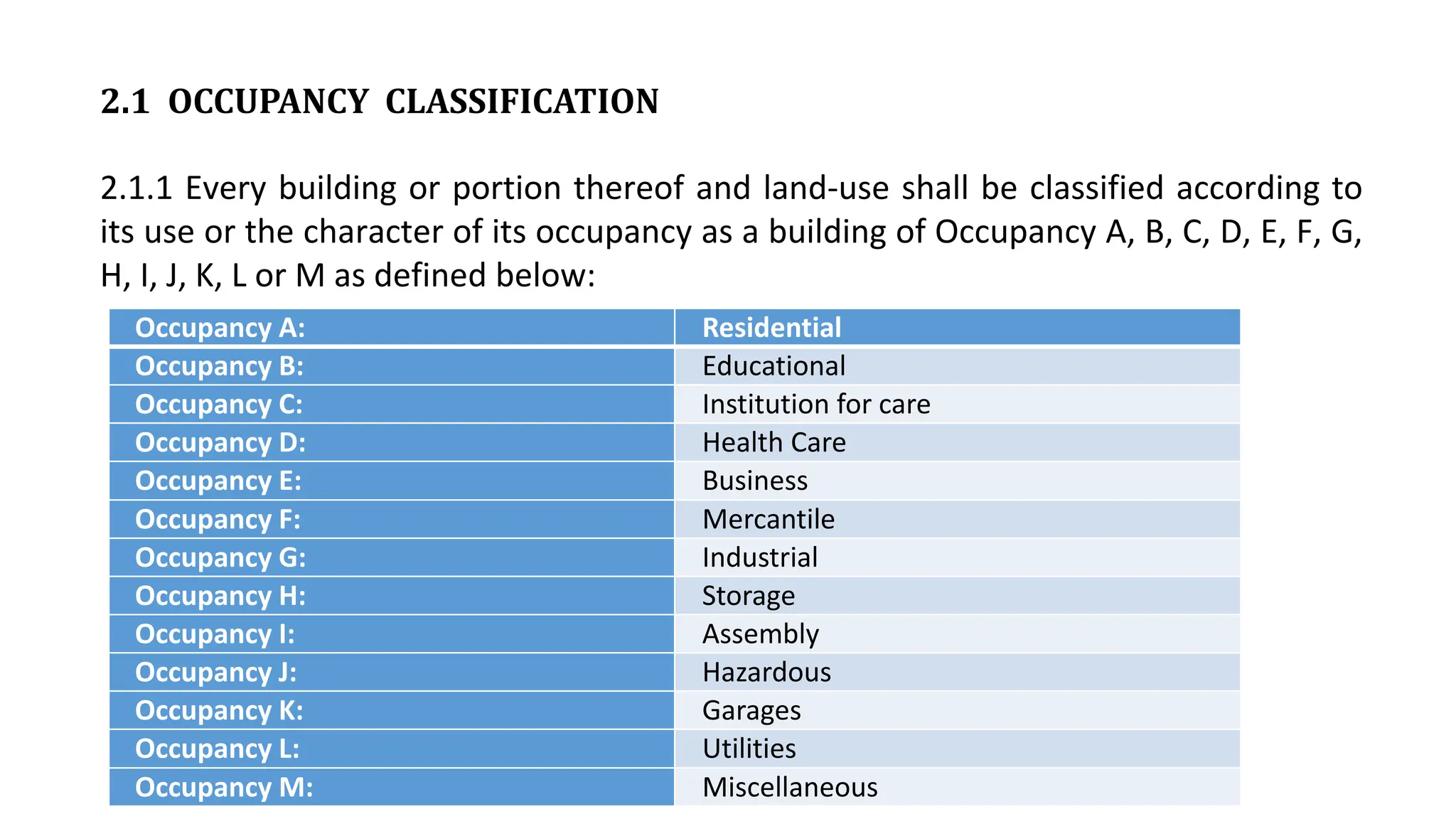
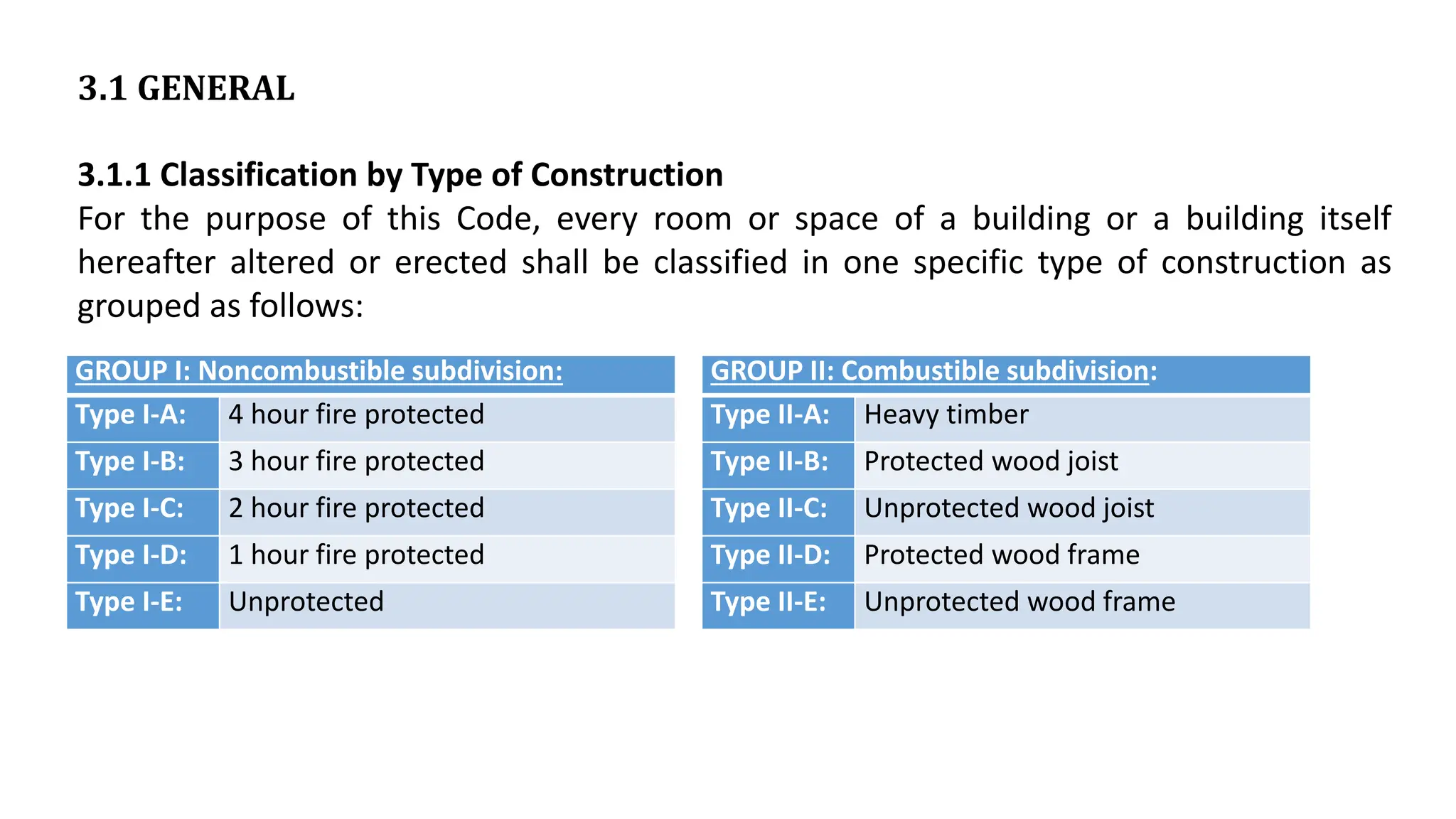
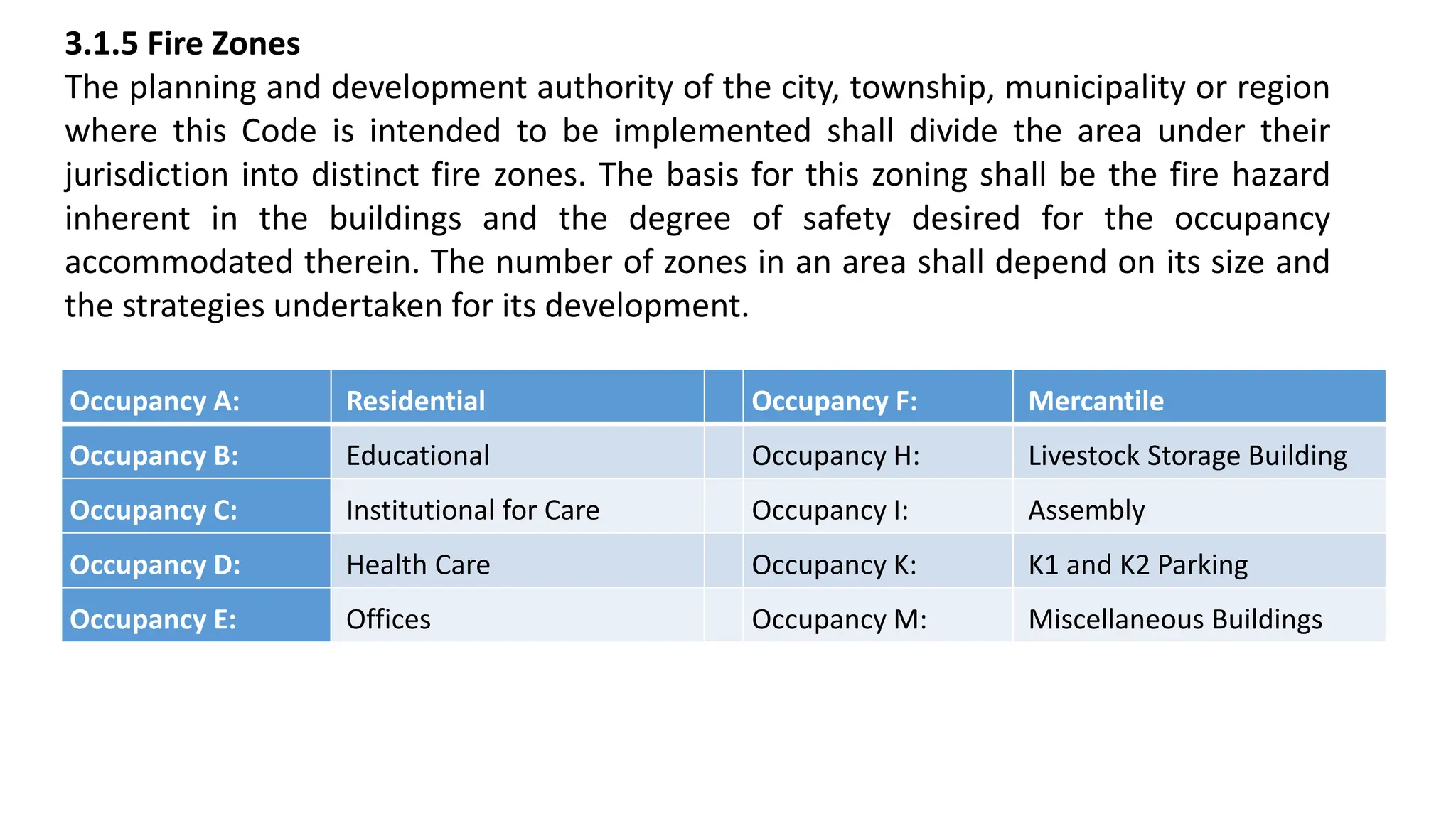
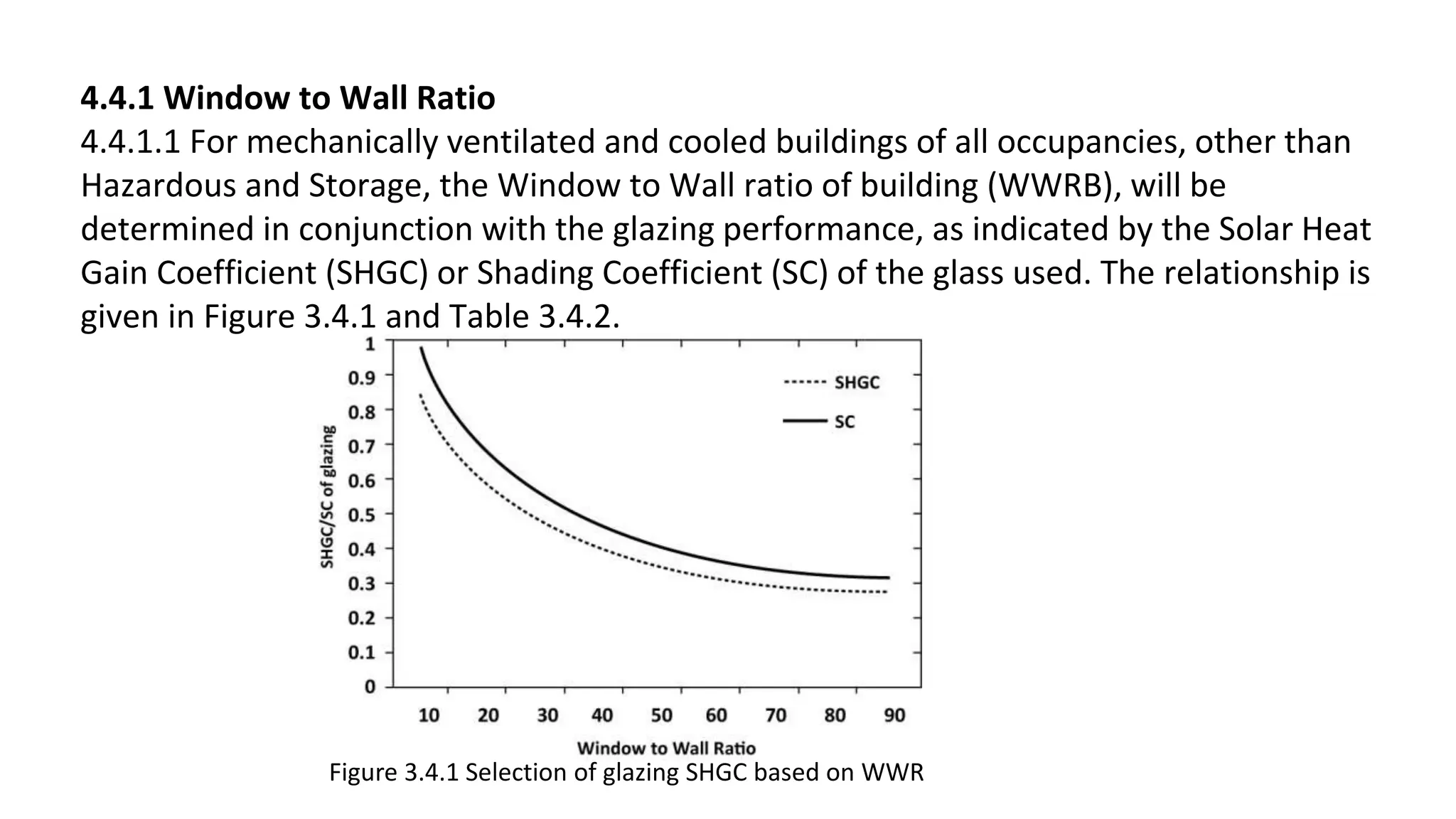
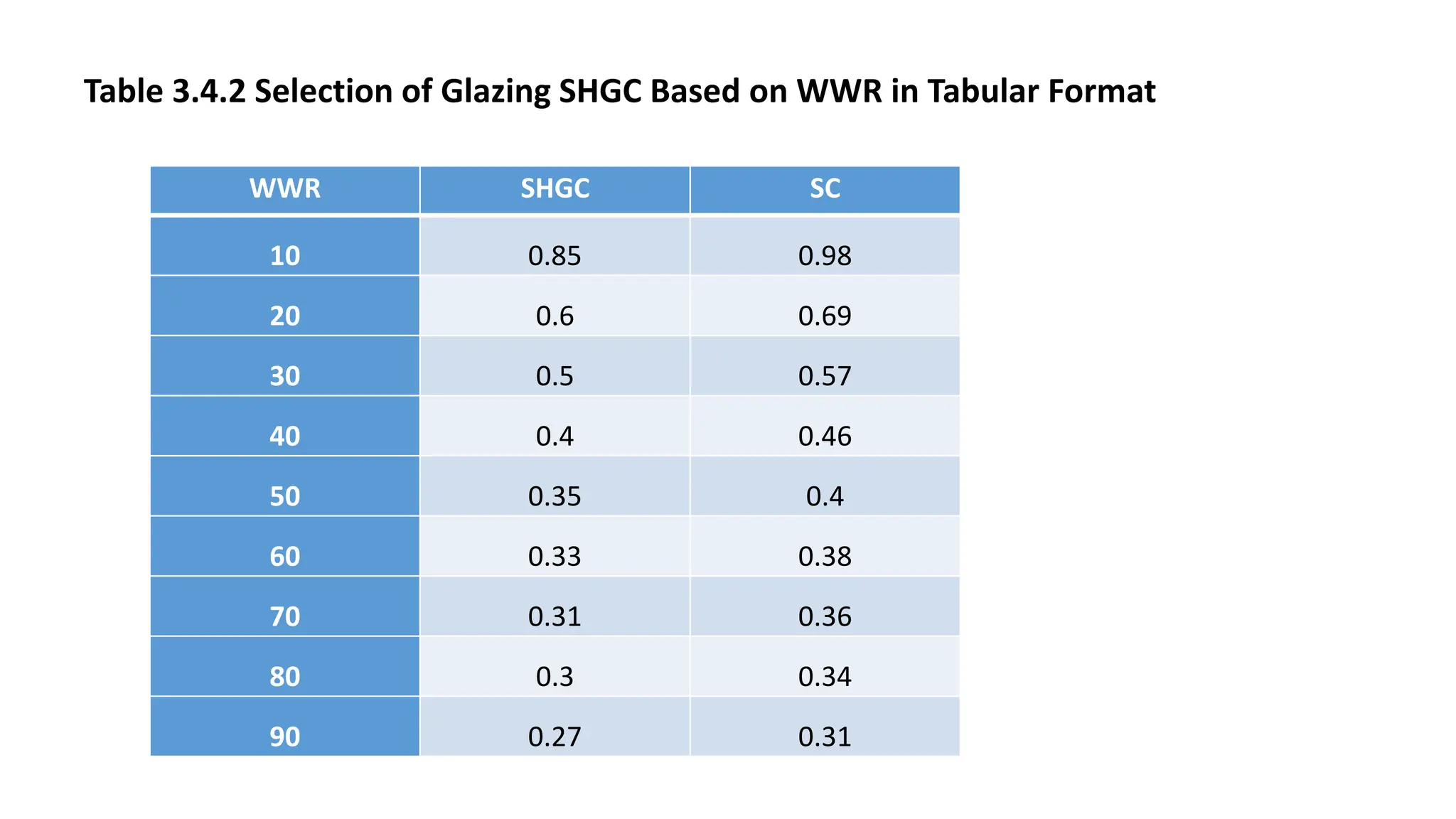
This document outlines the general building requirements and regulations, focusing on classifications based on occupancy and construction type, particularly regarding fire resistance, energy efficiency, and sustainability. It details specifications for plots, including site conditions, drainage, open spaces, and building heights, while also defining terminology related to construction. Additionally, it includes guidelines for building parts, room dimensions, and landscaping, ensuring safety and functionality in various occupancy types.