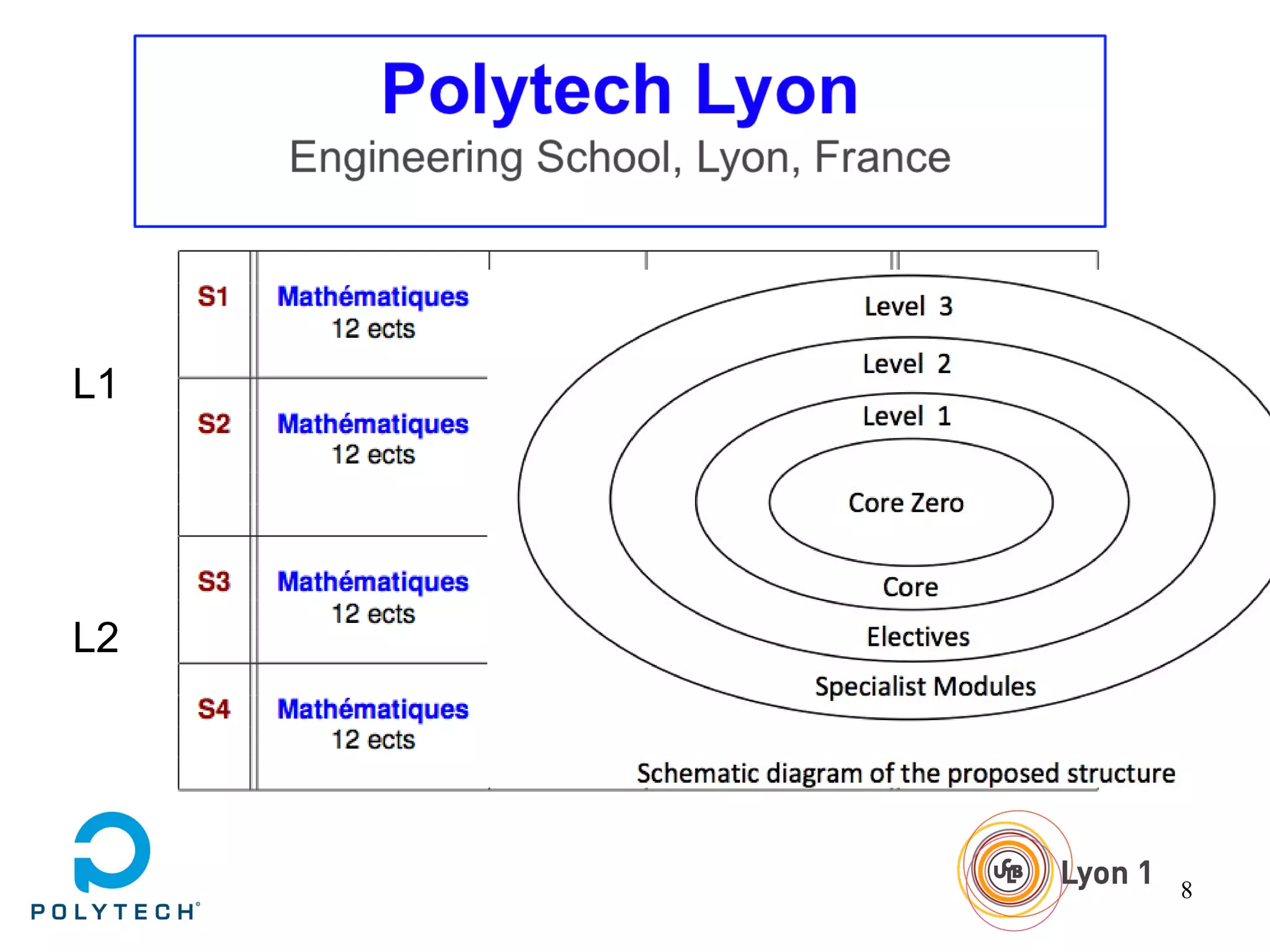
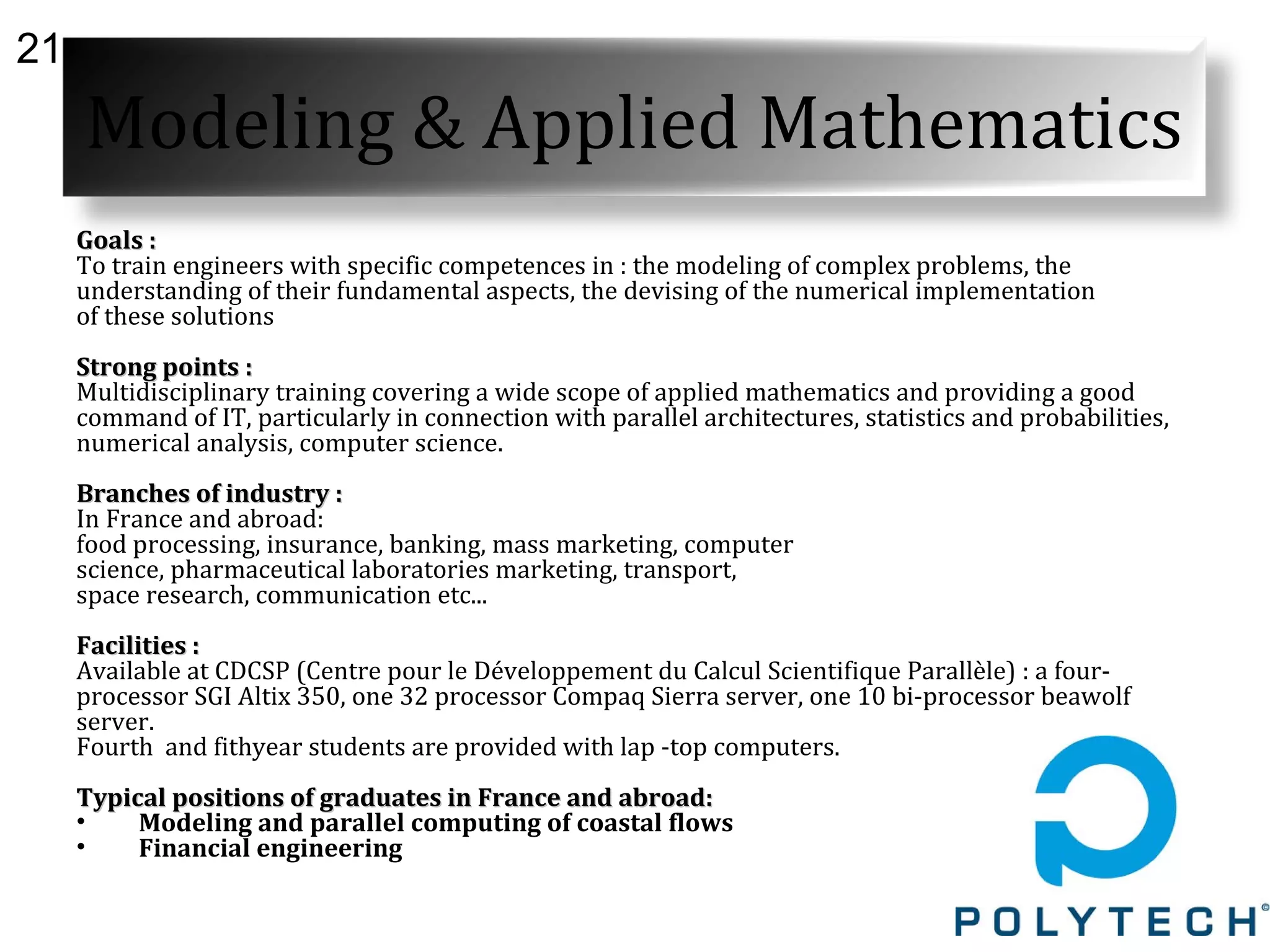
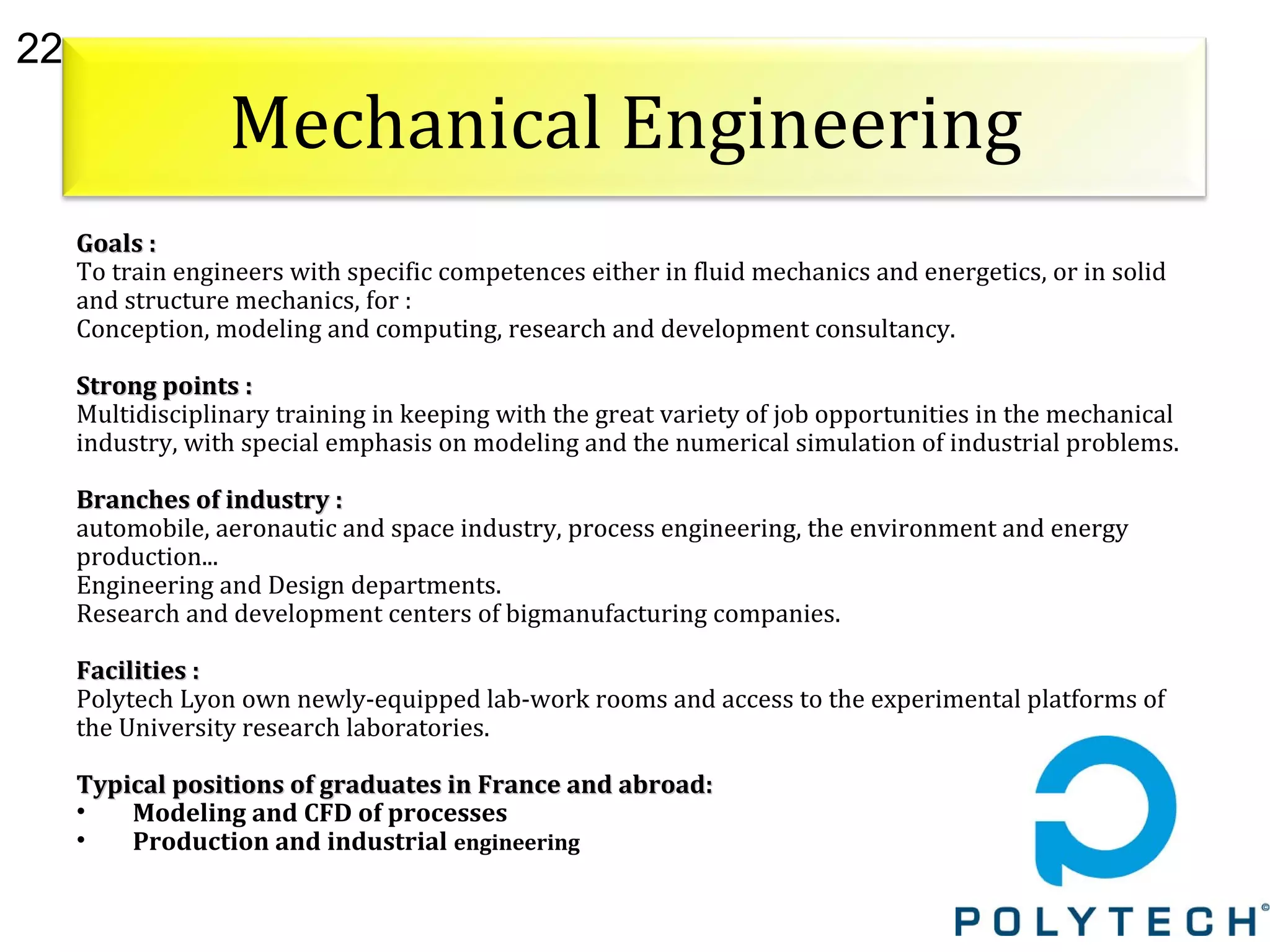
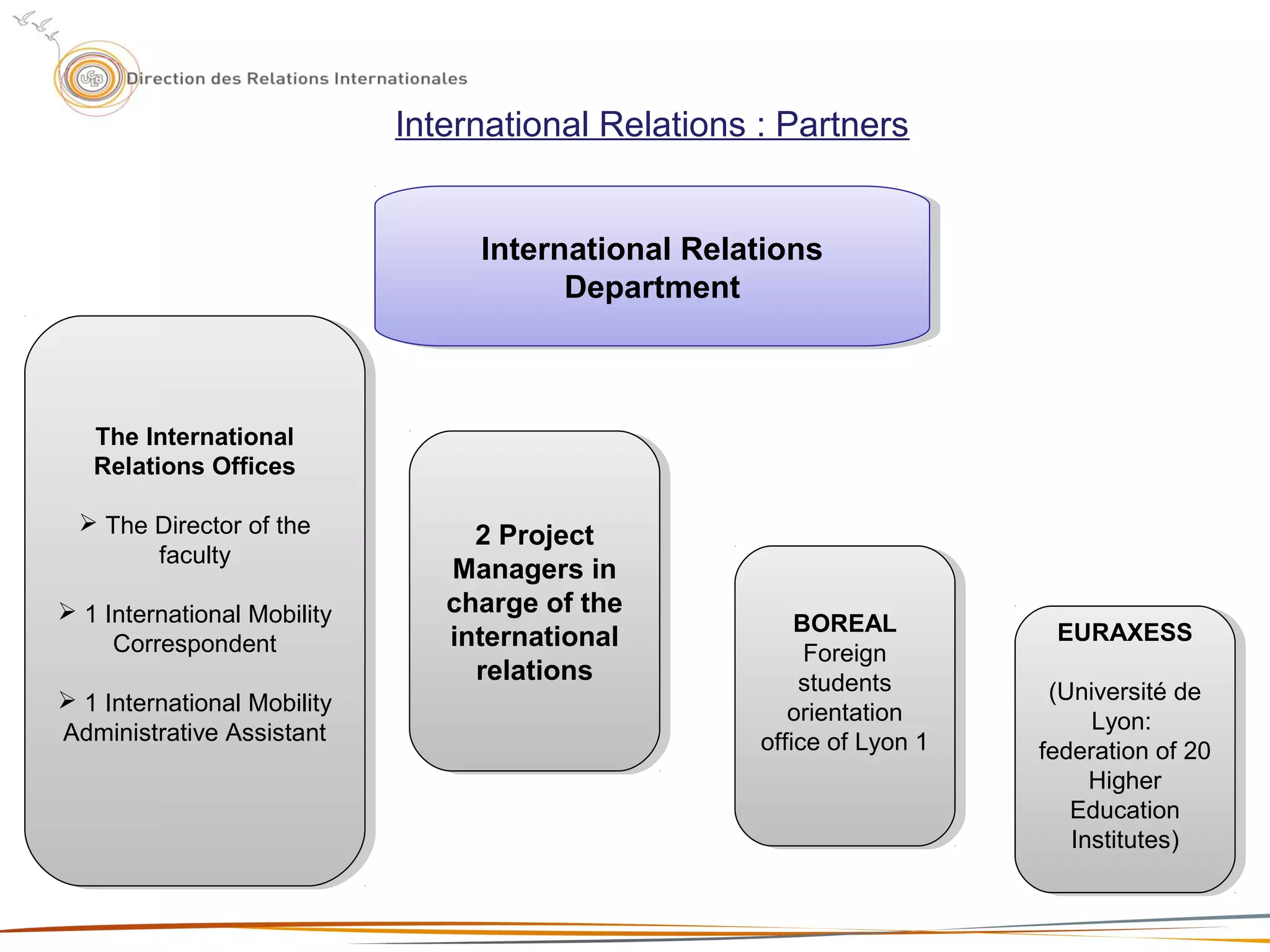
The document provides information about the Claude Bernard University Lyon 1, including:
- It has 39,000 students across more than 300 degree programs.
- It is highly active internationally with many partnerships globally.
- It seeks to develop partnerships in both developed and developing countries.