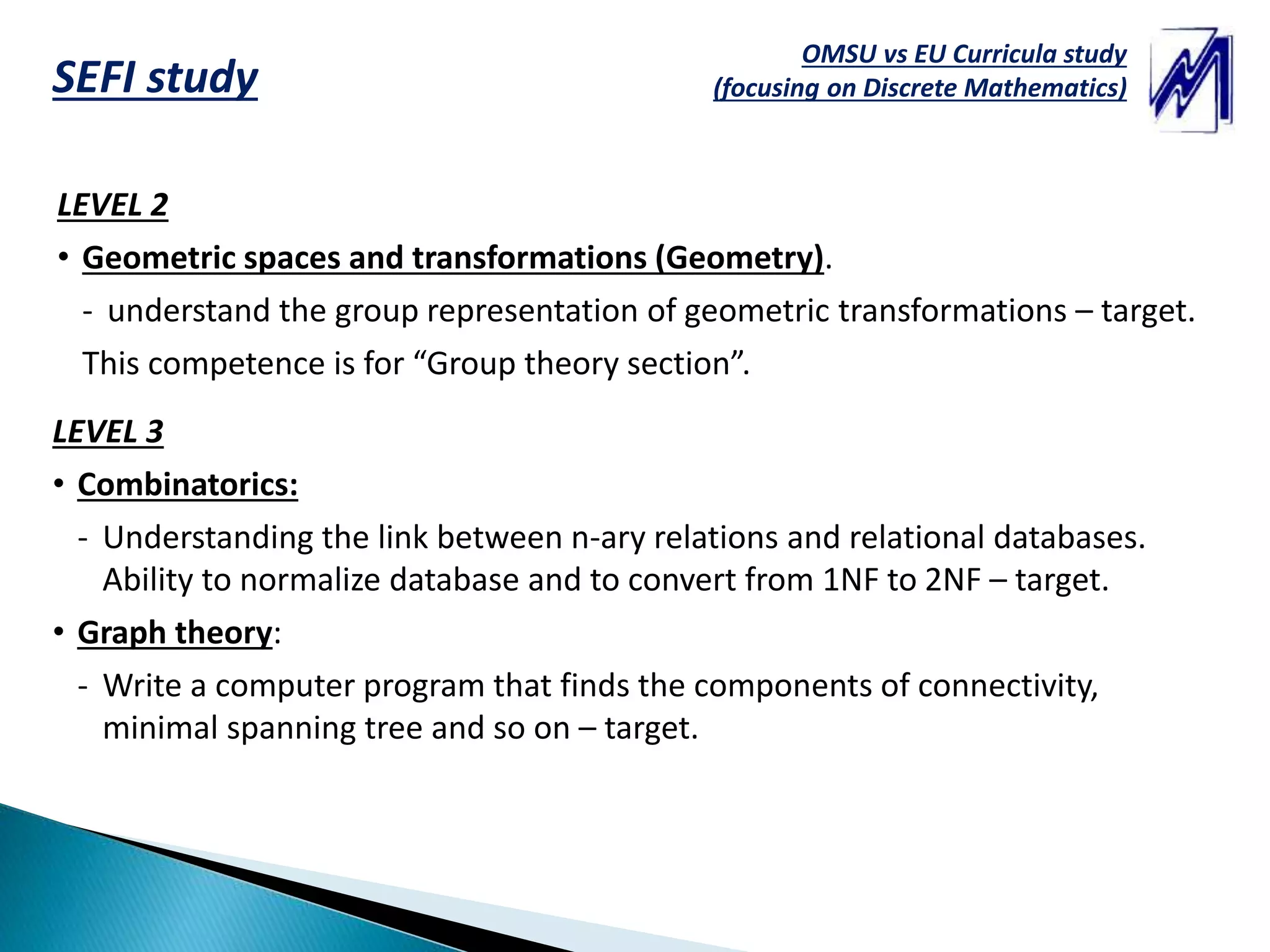
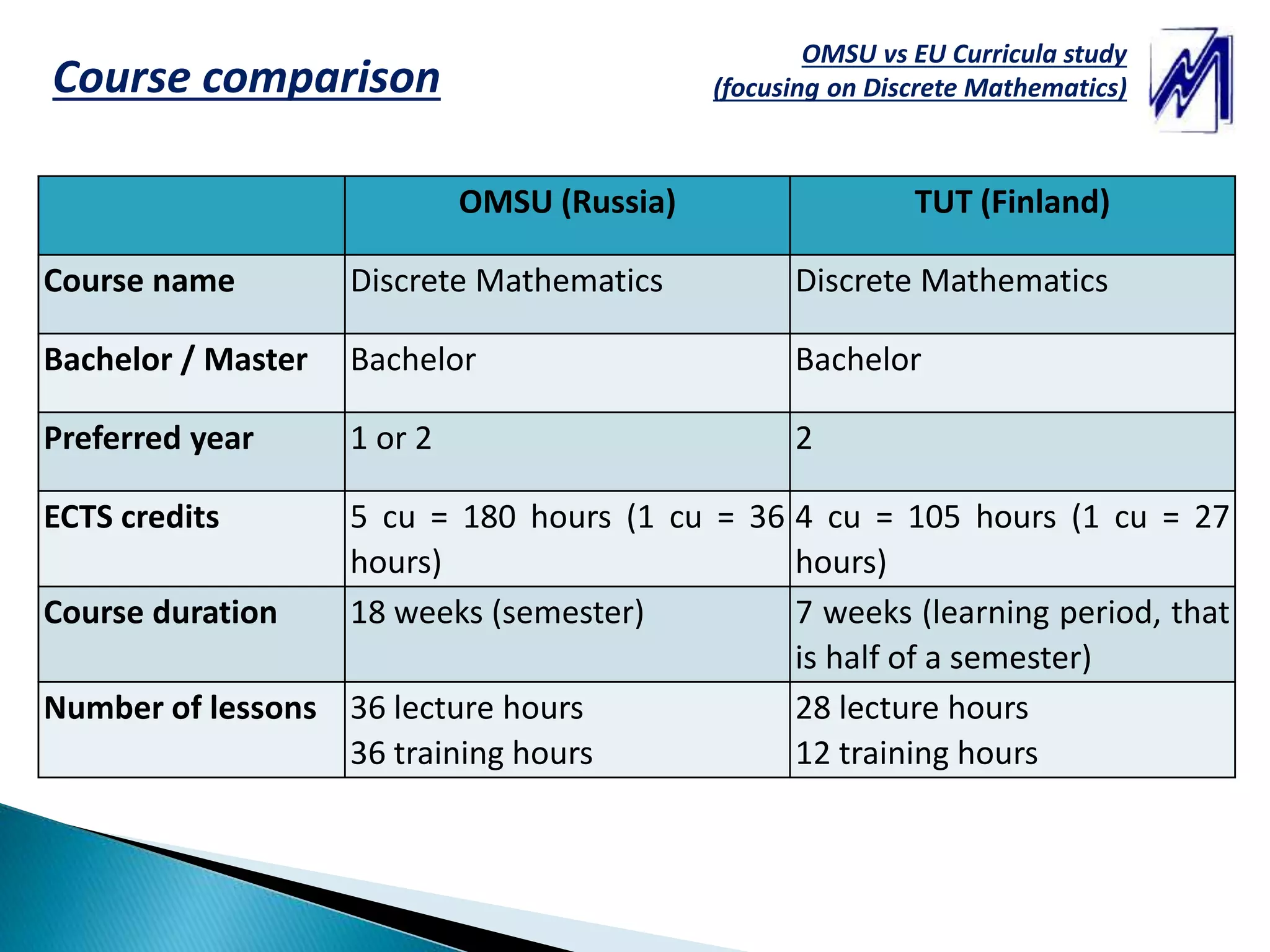
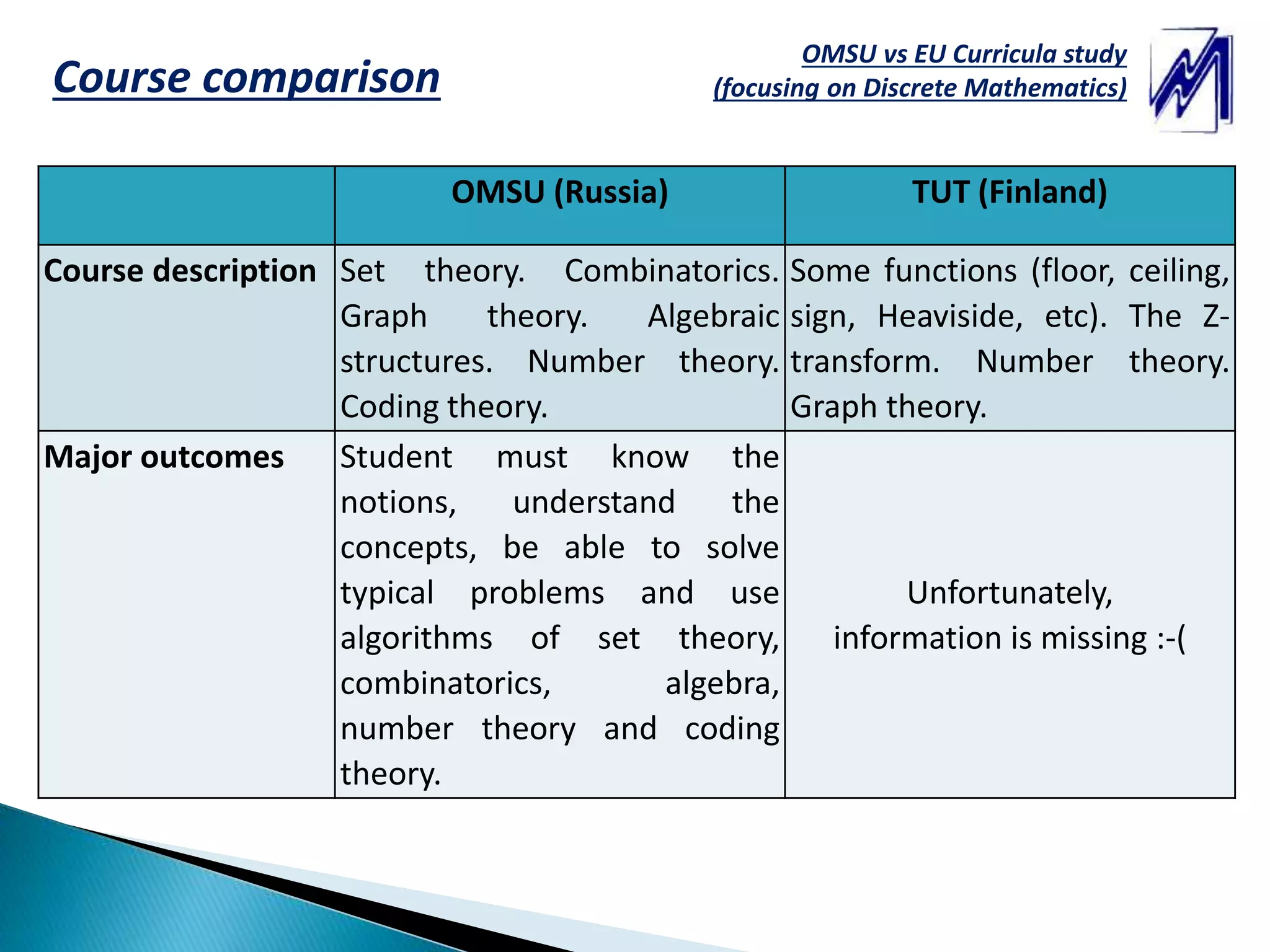
This document compares the Discrete Mathematics curricula and courses between OMSU (National Research Ogarev Mordovia State University) in Russia and TUT (Tampere University of Technology) in Finland. It analyzes the competencies, topics, and learning outcomes covered in the Discrete Mathematics courses based on three levels of difficulty. Overall, the OMSU course covers more topics like set theory, combinatorics, algebraic structures, and coding theory over a longer duration, while the TUT course focuses more on number theory over a shorter period. The document proposes increasing engineering applications and using an online learning system to help modernize the Discrete Mathematics courses.