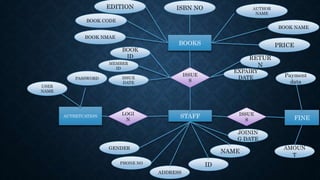
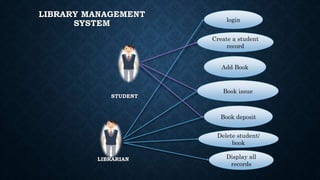
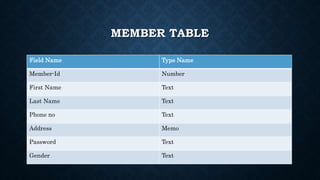
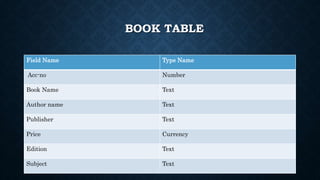
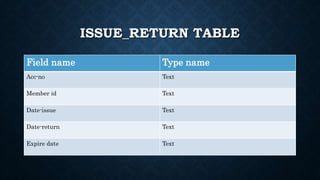
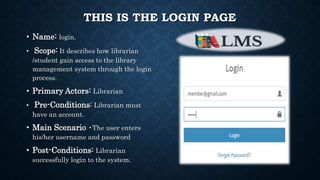
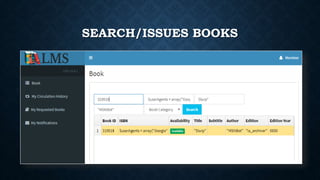
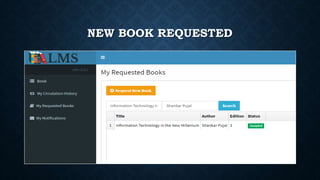
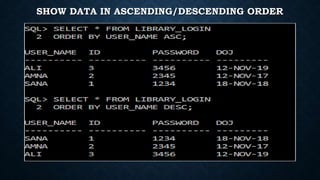
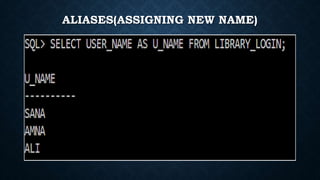
This document outlines the requirements for a library management system. It includes sections on group members, introduction, purpose, functional requirements, non-functional requirements, entity relationship diagram, use case diagram, and proposed modules. The system would allow students and librarians to login, search for books, issue and return books, and request new books. It describes tables for members, books, and book issues/returns. The document provides an overview of the proposed system.