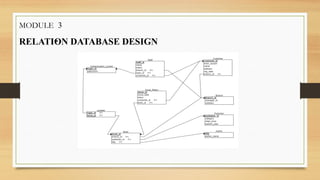
The document presents a comprehensive overview of a proposed Library Management System (LMS) designed to streamline the management of library records and user interactions. It includes requirement analysis, e-r diagram representations, relational database design, and discusses the future of LMS integration with modern technologies like AI and cloud computing to enhance user experience. The project aims to ensure that libraries remain relevant in the digital age by improving data security, resource management, and user engagement.