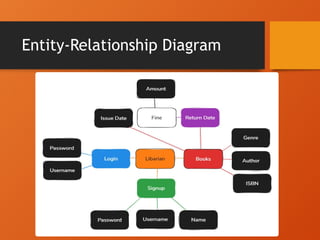
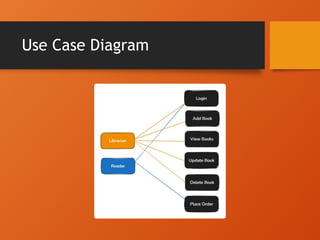
The document outlines the design and implementation of a Library Management System (LMS) using Java and MySQL, focusing on efficient management of books and user information. Key features include user management, book tracking, and an intuitive interface, while addressing various functional and non-functional requirements. It also discusses the system architecture, challenges encountered, and solutions implemented to enhance usability and performance.