The document summarizes the purification of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) from chicken muscle. Key steps included:
1. Homogenizing the muscle tissue to disrupt cells and release LDH.
2. Removing debris via centrifugation.
3. Precipitating and concentrating LDH using ammonium sulfate.
4. Dialyzing the sample to remove salt.
5. Purifying LDH using affinity chromatography on a Cibacron blue column.
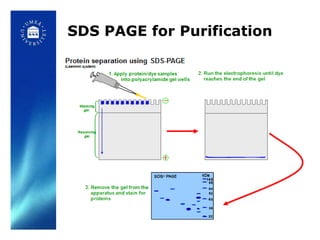
6. Analyzing purity via SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis and activity assays.