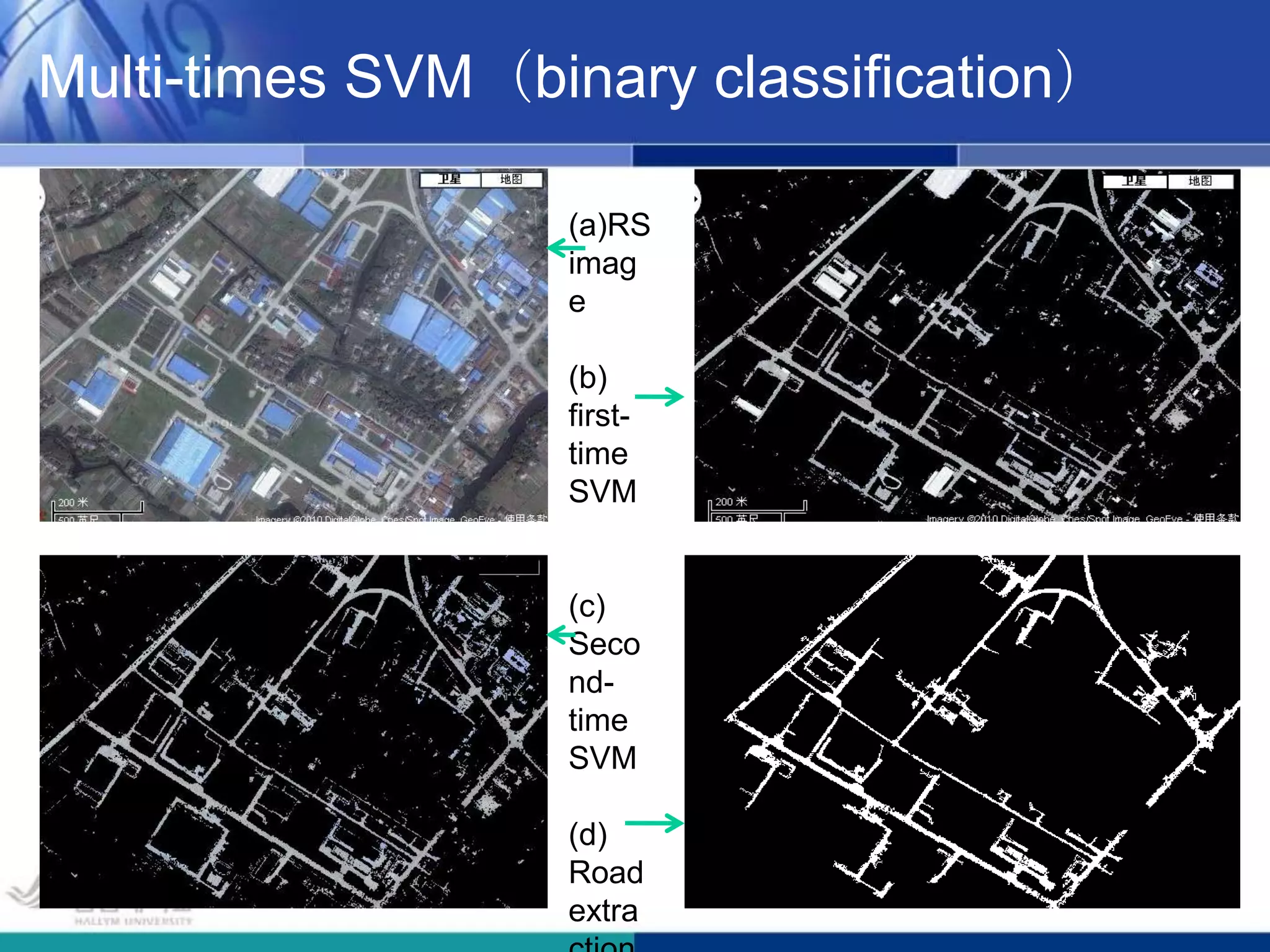
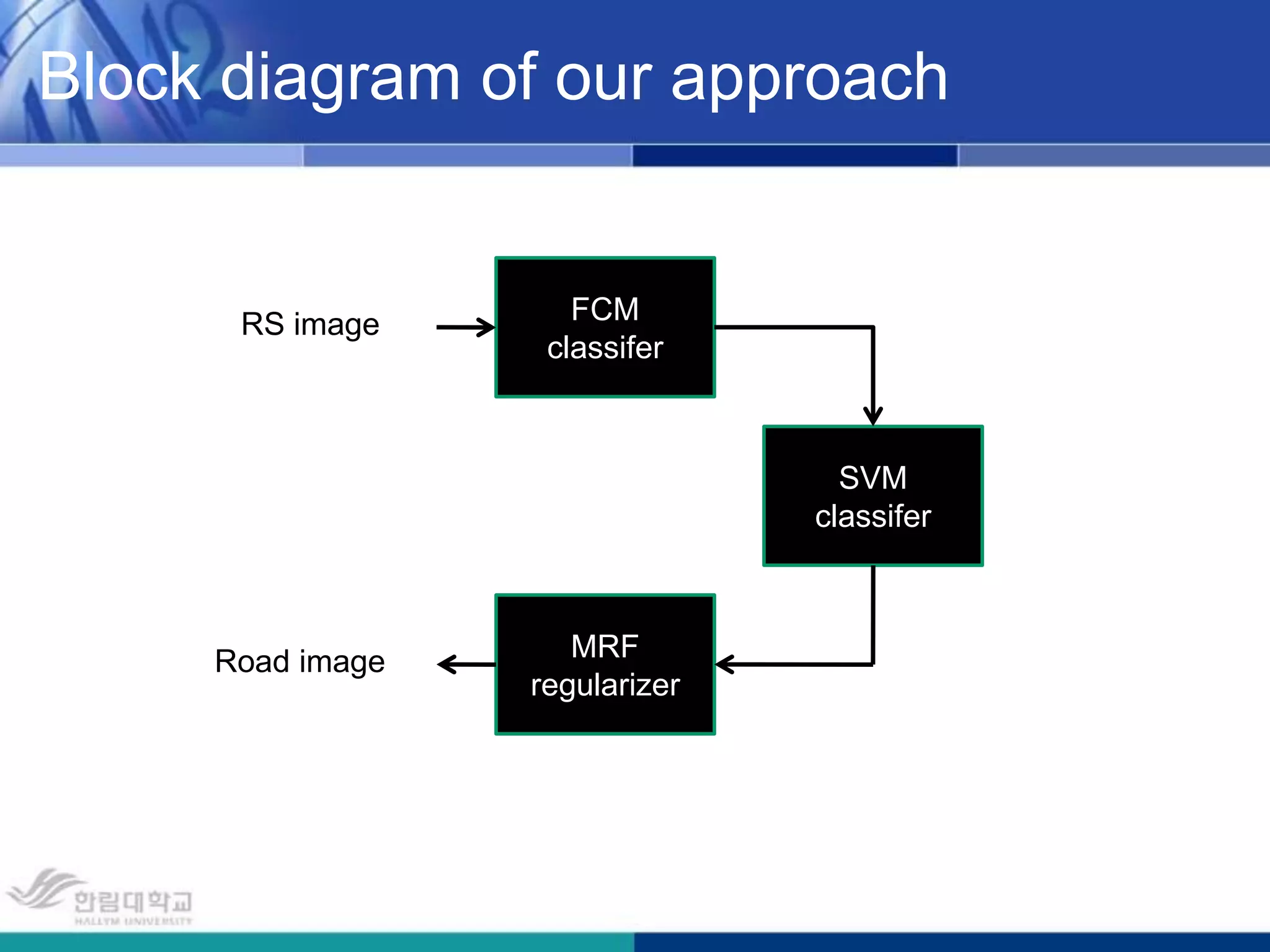
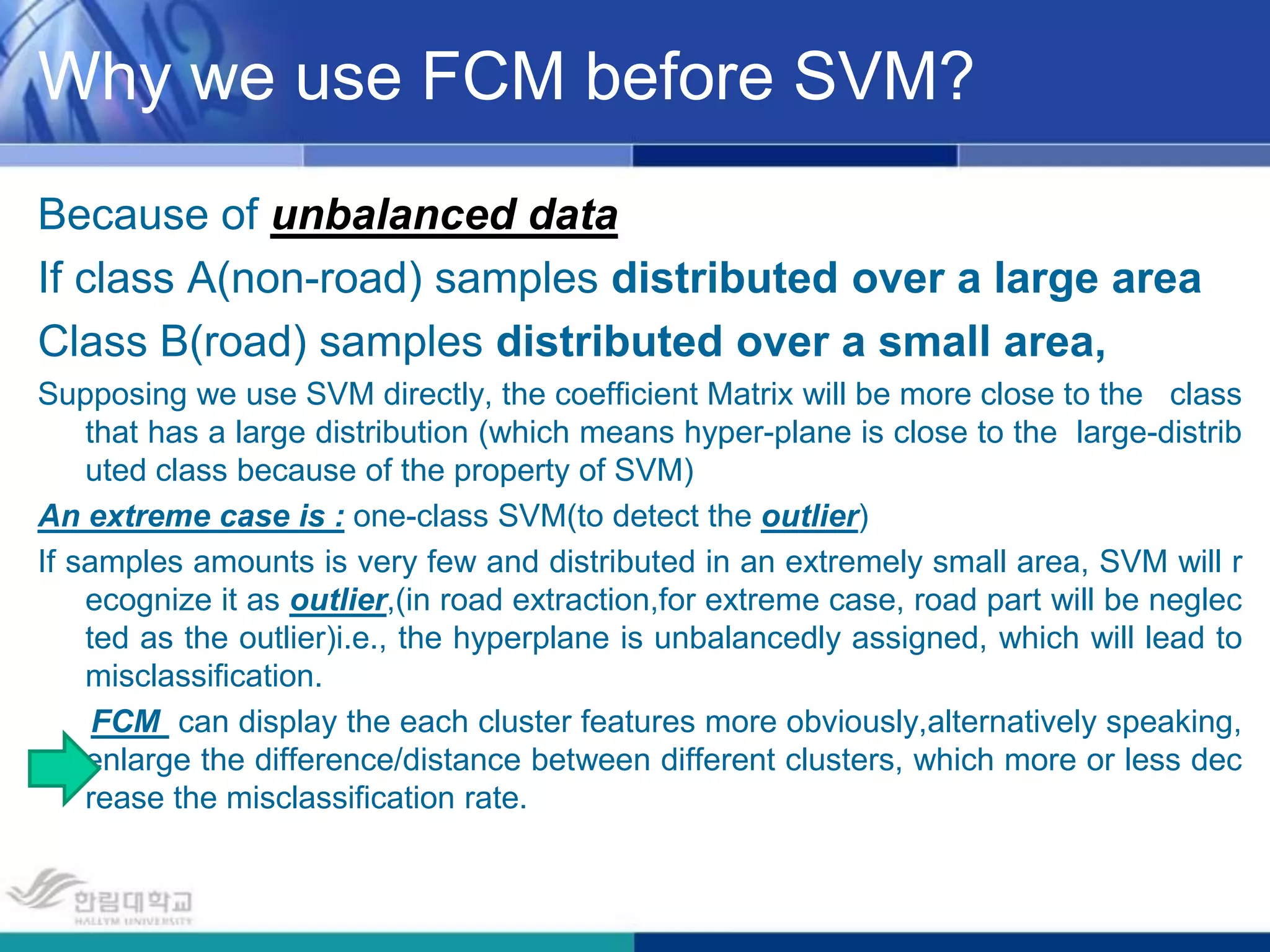
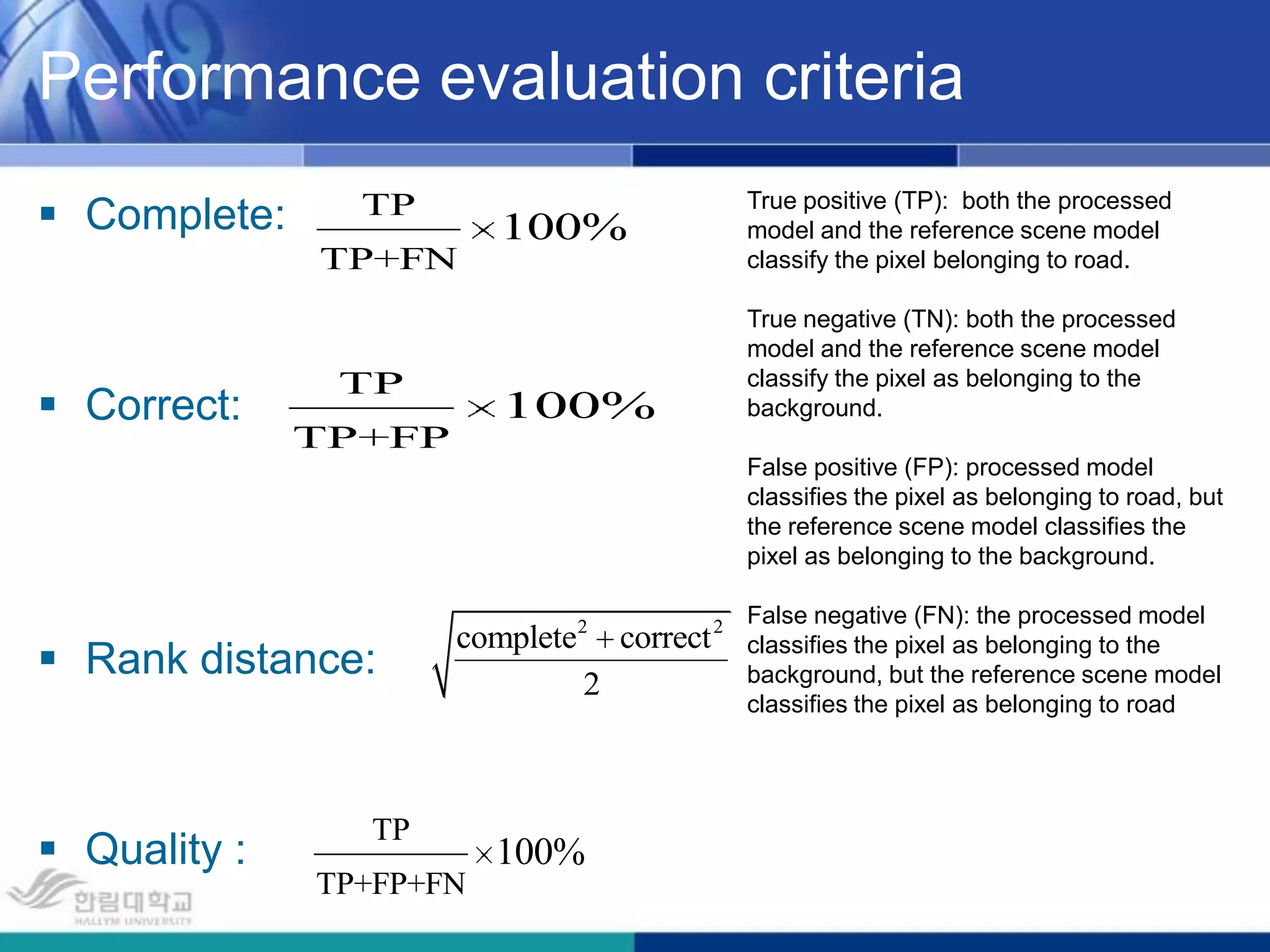
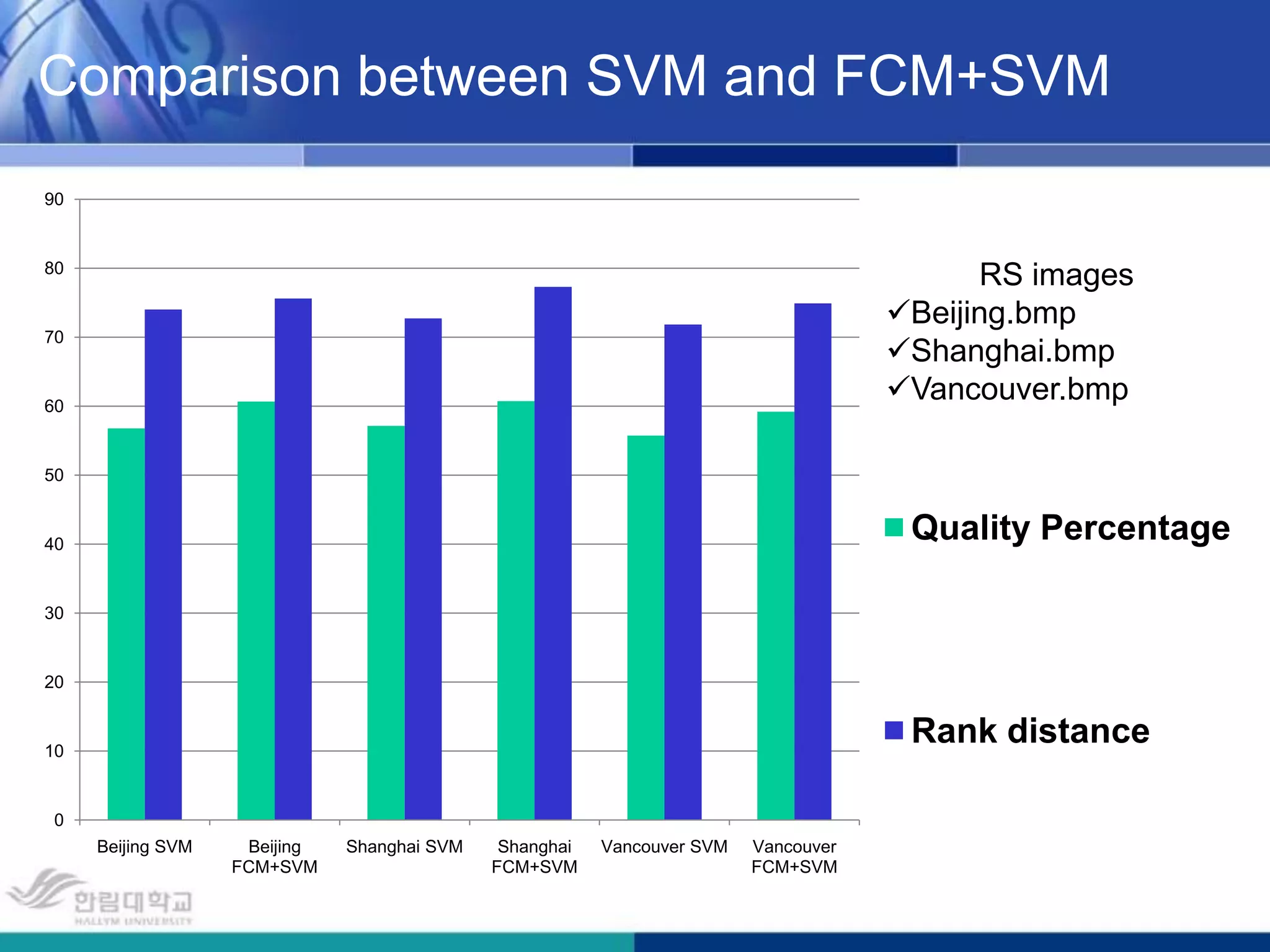
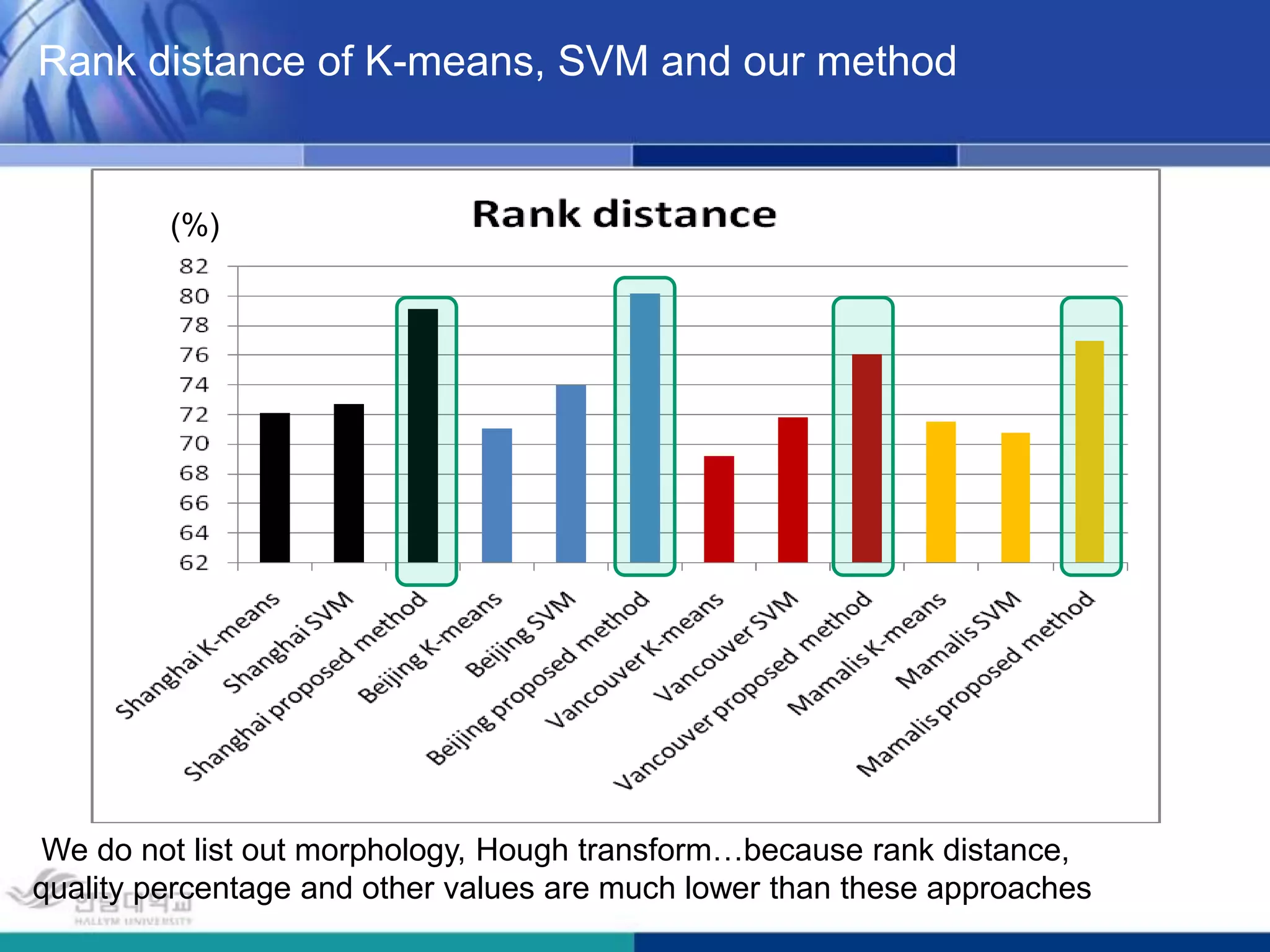
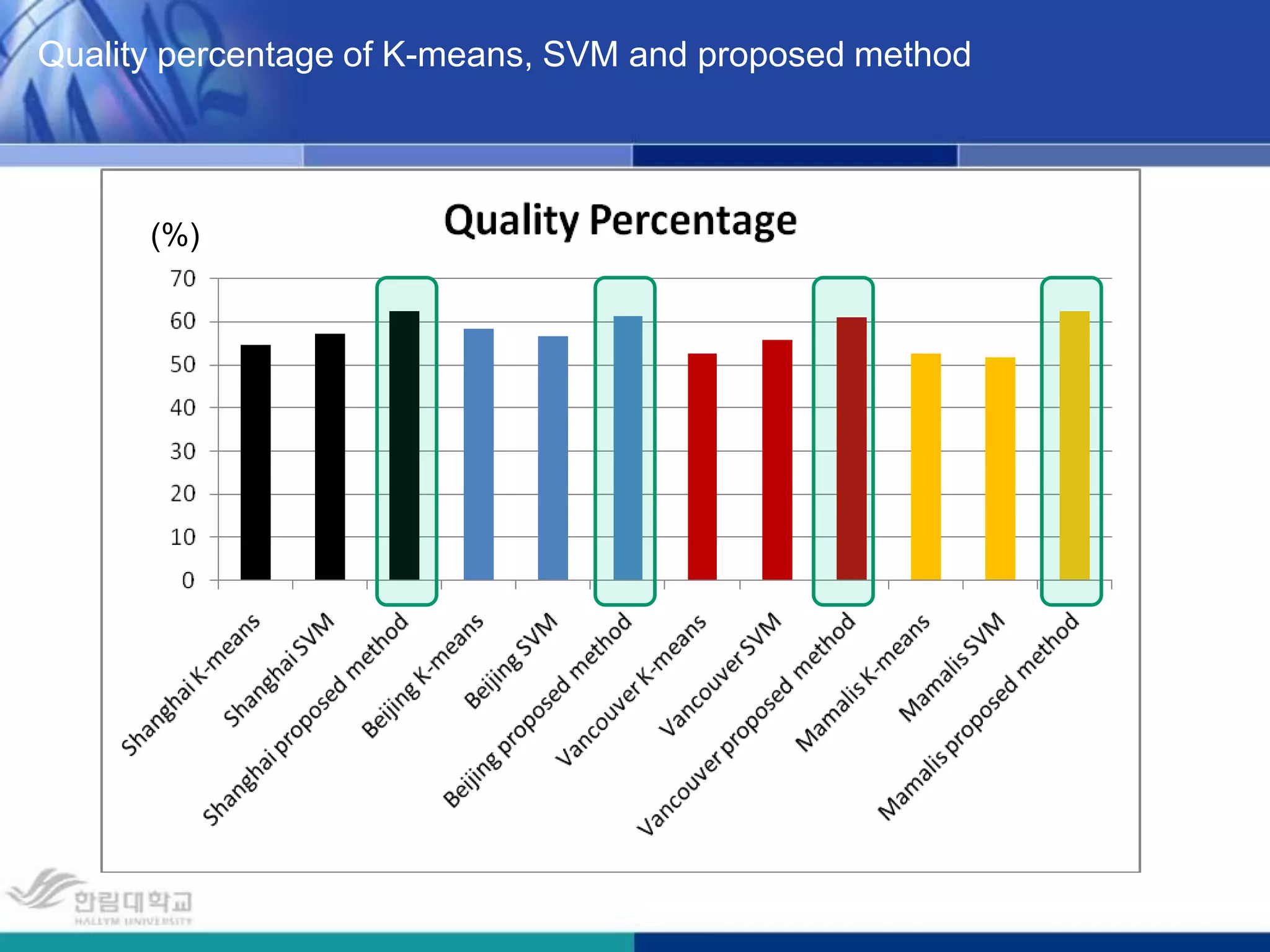
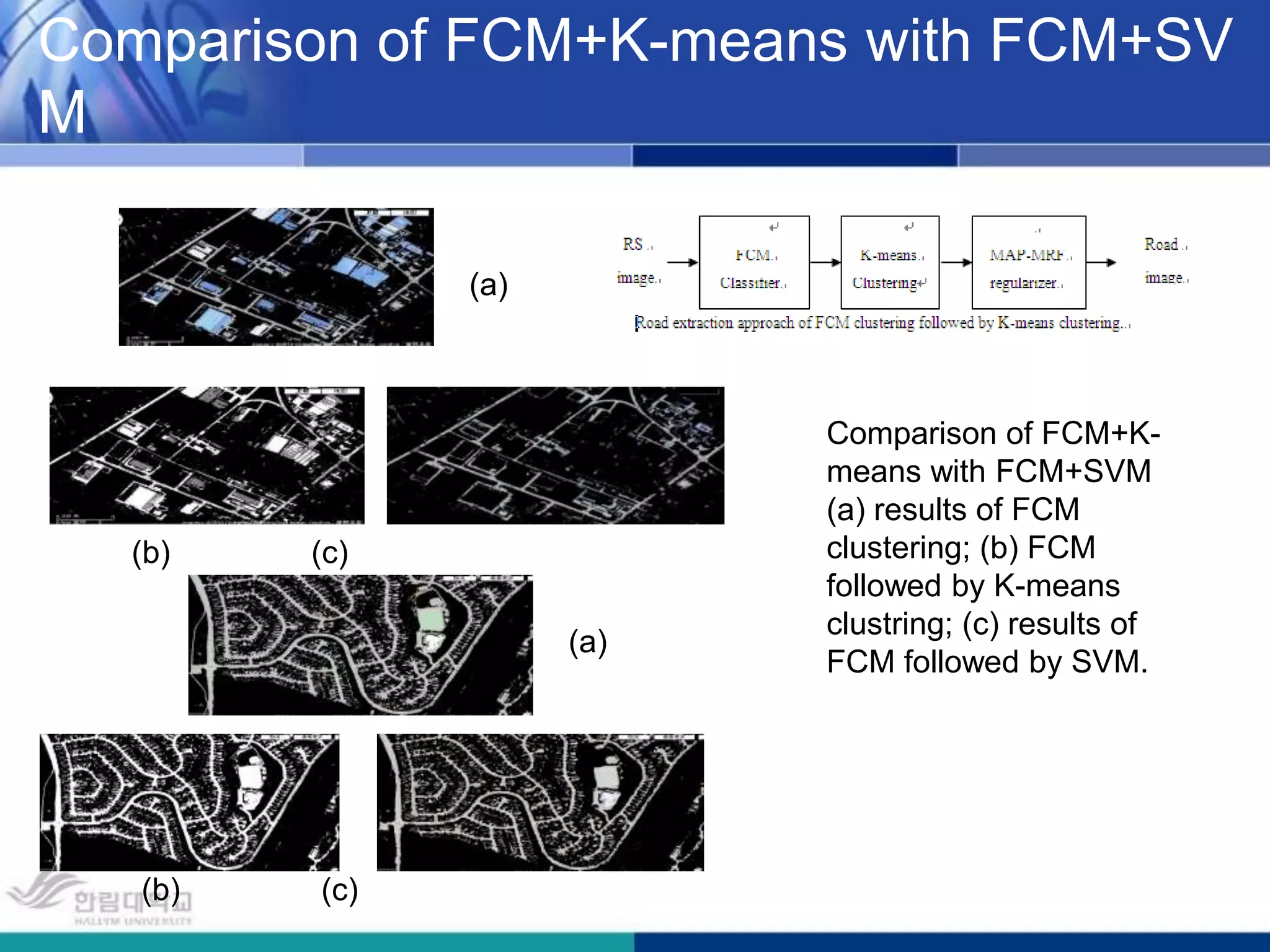
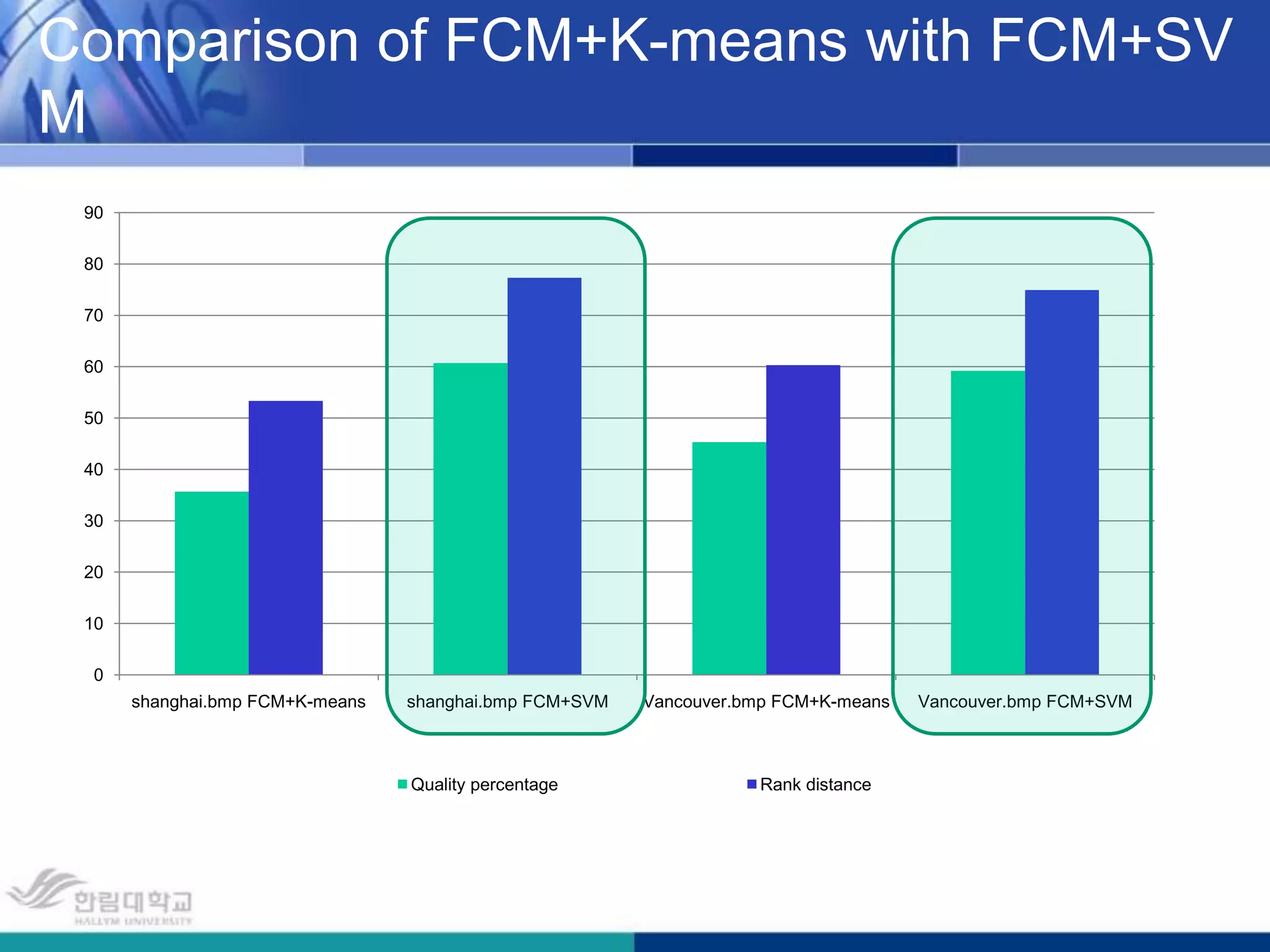
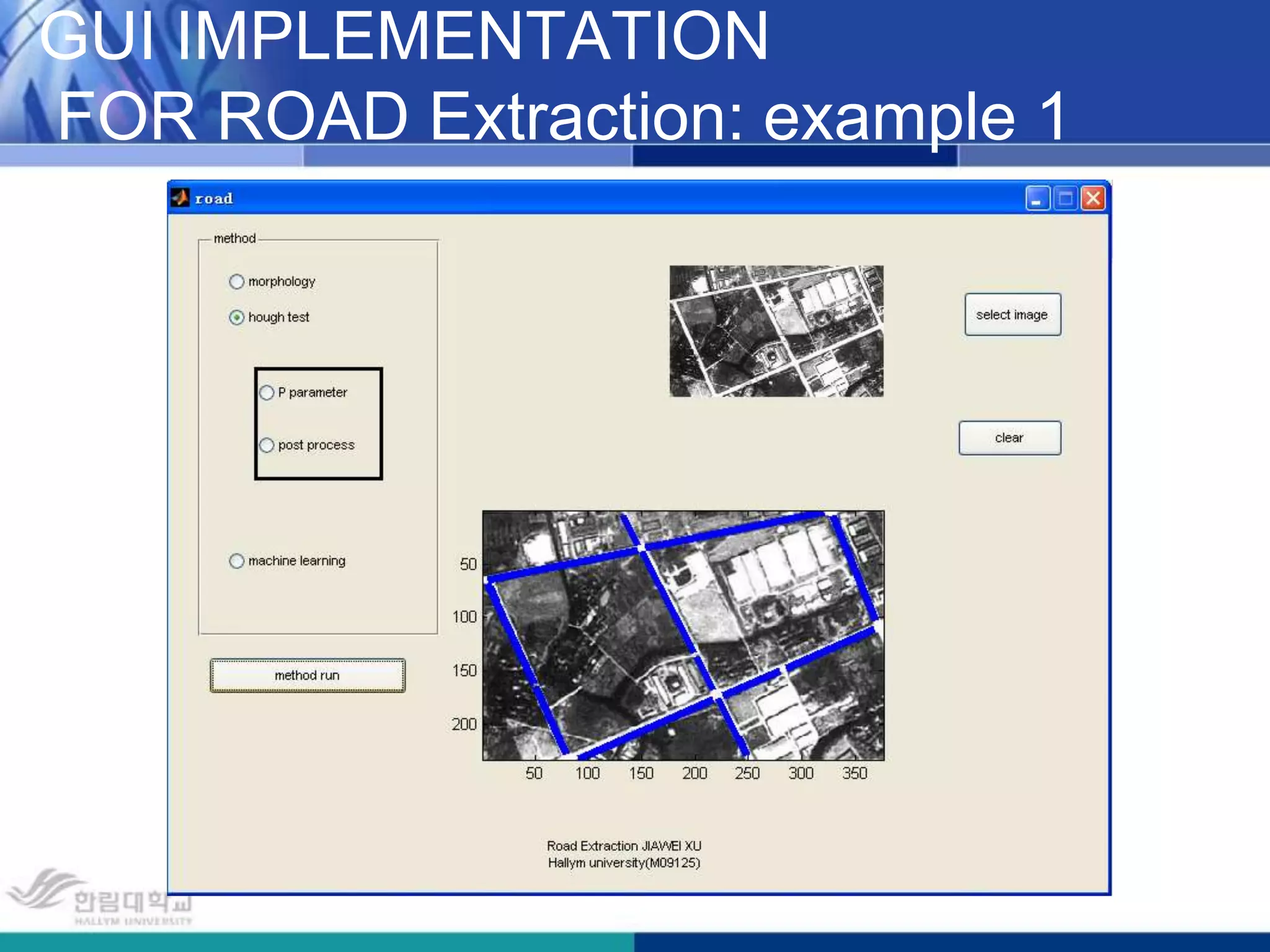
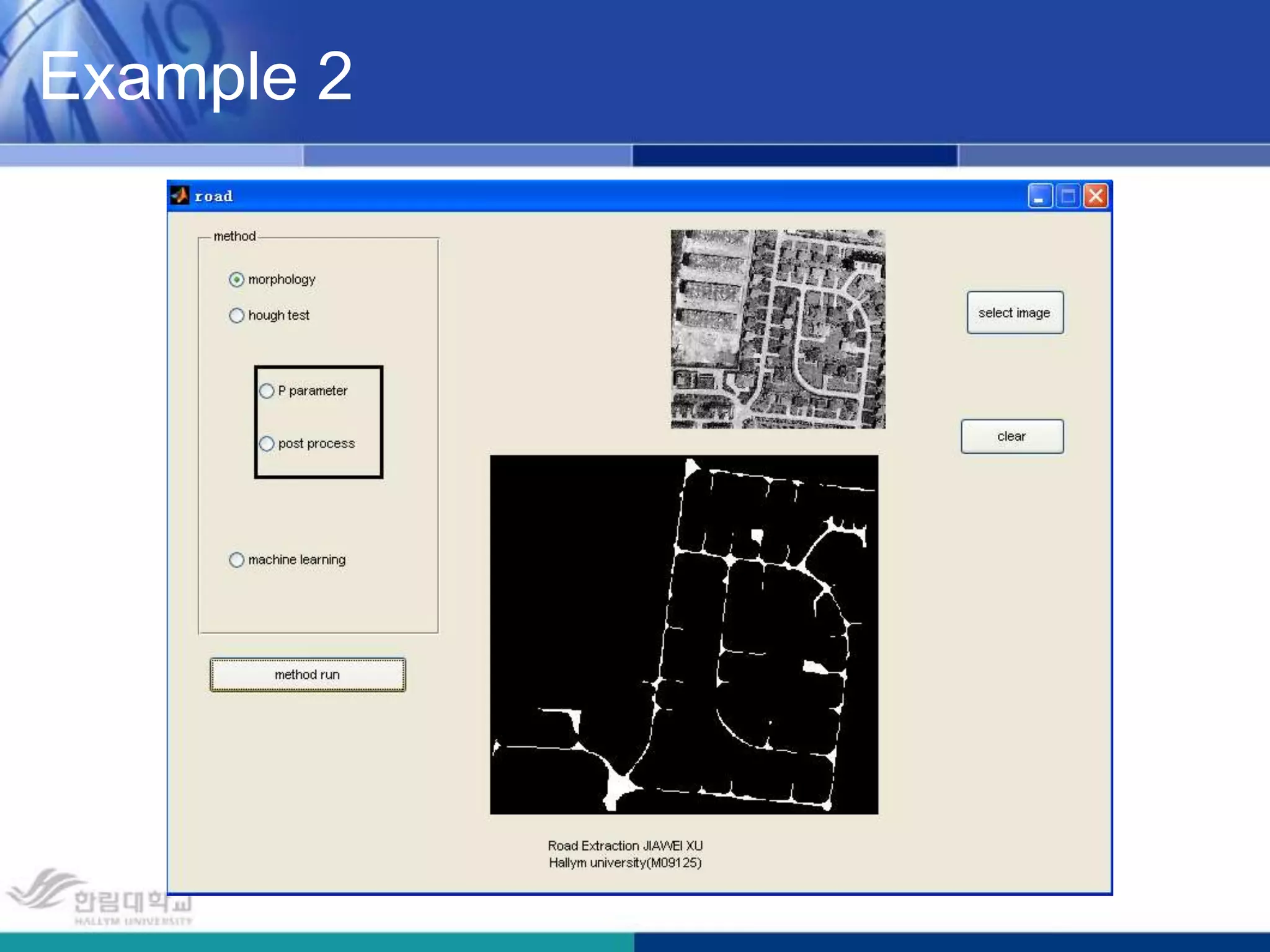
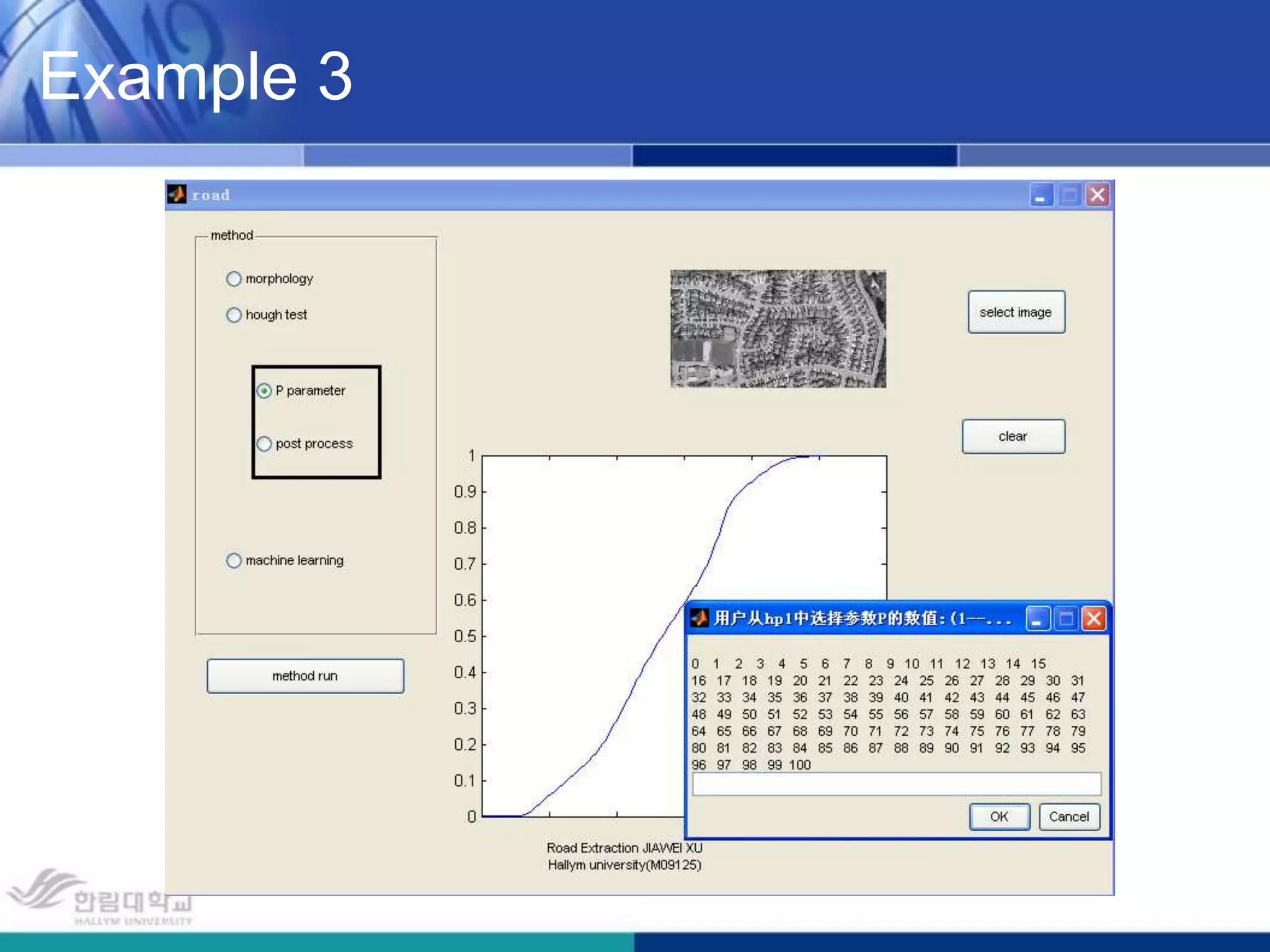
The document presents a novel road extraction method utilizing Support Vector Machine (SVM) classification combined with Fuzzy C-Means (FCM) clustering and Markov Random Field (MRF) regularization. The proposed algorithm demonstrates improved accuracy and robustness in extracting road networks from remote sensing images compared to traditional methods like morphological approaches and Hough transforms. Experimental results indicate a significant enhancement in classification performance, thereby validating the effectiveness of the methodology in diverse image characteristics.





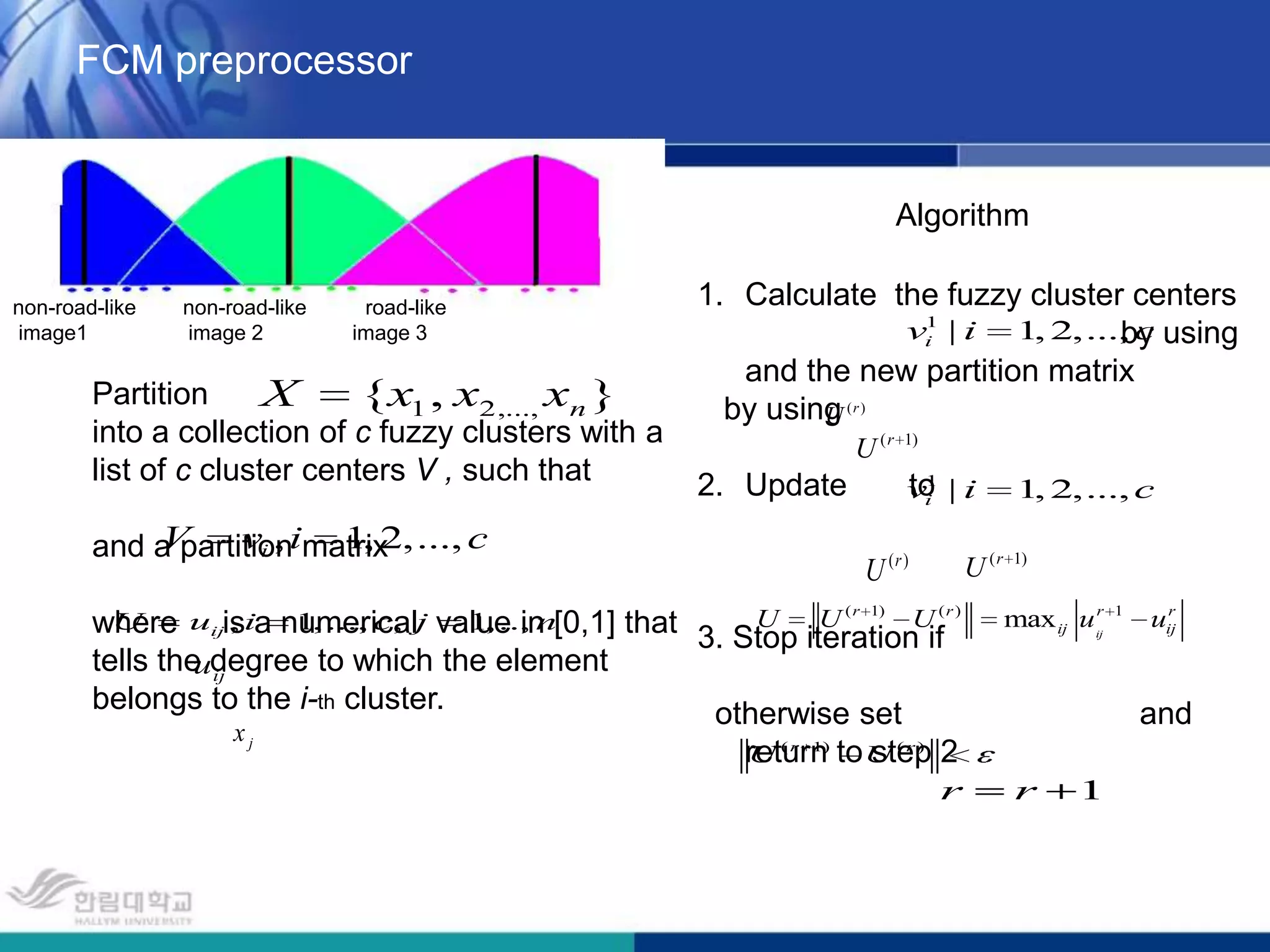

![FCM preprocessorAlgorithmCalculate the fuzzy cluster centers by using and the new partition matrix by usingUpdate to 3. Stop iteration if otherwise set and return to step 2non-road-like non-road-like road-like image1 image 2 image 3Partitioninto a collection of c fuzzy clusters with a list of c cluster centers V , such that and a partition matrixwhere is a numerical value in [0,1] that tells the degree to which the element belongs to the i-th cluster.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationforkoreamultimediainenglish-110327204831-phpapp01/75/Presentation-for-korea-multimedia-in-english-17-2048.jpg)





![References[1] Stefan Hinz, “Automatic extraction of urban road networks from multi-view aerial imagery”, Technische University 2003[2] VladmirVapnik, ”Statistical Learning Theory”, JOHN WILELY & SONS, Inc.1998[3] Curt H.Davis, “An integrated system for automatic road mapping from high-resolution multi-spectral satellite imagery by information fusion”, Elsevier Inc. 2004 [4] Yairmoshe, “GUI with Matlab” Department of Electronic Engineering, Columbia University , May 2004.[5] http://maps.google.com/[6] Yang Li, “A new validity function for fuzzy clustering”, School of mathematical sciences, Beijing normal university, 2005[6] Xu Yong and Shaoguang Zhou, “Markov random field for road extraction applications in remote sensing images”, Department of Surveying and Mapping Engineering, Hohai University, 2008[7] David M.McKeown ,“Performance evaluation for automatic feature extraction ”, Computer Science Department, Carnegie Mellon University 2000[8] Patrick Perez, “Markov random fields and images”, Campus Beauileu, 1999[9] Drs. Trani and Rahka, “MATLAB Graphic user interfaces(GUI) computer applications in civil engineering ”, Spring, 2000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationforkoreamultimediainenglish-110327204831-phpapp01/75/Presentation-for-korea-multimedia-in-english-39-2048.jpg)