The document discusses a project focused on road extraction from high-resolution satellite imagery using various image processing techniques. It outlines methodologies such as classification-based methods, deep learning, and knowledge-based methods, highlighting their advantages and challenges in accurately detecting road segments. Additional insights into image processing tools, code implementation, and expected outcomes for specific applications are also provided.








![Code Go, change the world
14
Intelligent Systems
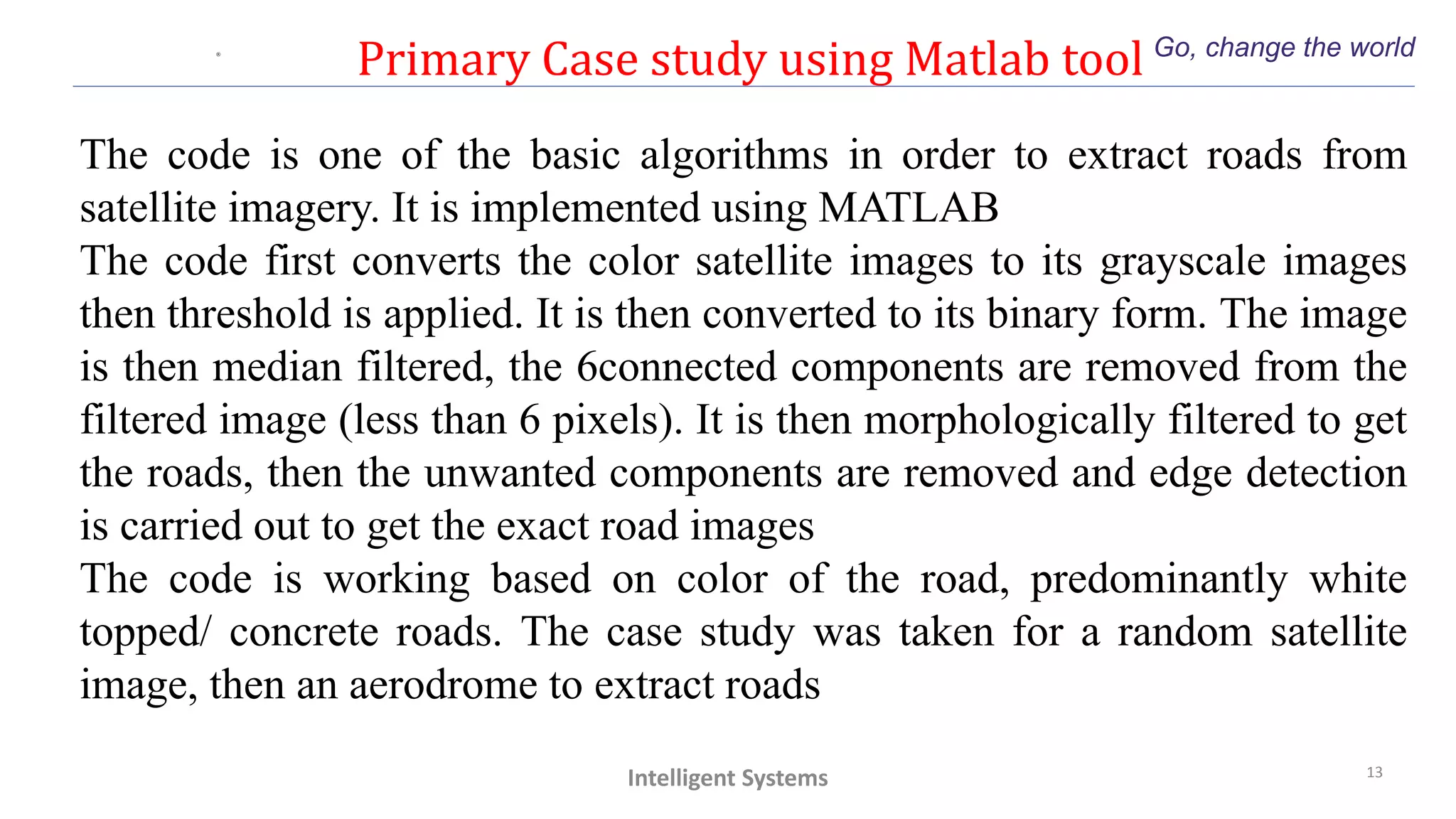
Clc
clear all;
close all;
addpath
'C:UsersJIOCHDesktop'
I=imread('input3.jpg');
figure;
imshow(I);
title('Original image');
%% coversion to grayscale
J=rgb2gray(I);
%whos
figure,imshow(J);
title('grayscale image');
%[a,b]=size(J);
%K = zeros(a,b);
K=imadjust(J,[0.5 0.9],[]);
%P=find(J >= 127.5);
%S=find(J <= 229.5);
%M=intersect(P,S);
%K(M)= J(M);
figure;
imshow(K);
%% threshold grayscale image and
binarize
level = graythresh(K);
I=imbinarize(K,level);
figure;
imshow(I);
title('Binary image after
thresholding');
%% median filtering
B = medfilt2(I);
figure,imshow(B);
title('median filtered image');
%% removal of unwanted
componets less than 6 pixels
im = bwareaopen(B,1200);
%Binary = imfill(im,'holes');
figure,imshow(im);
title('removing connected
components(pixel <6)');
%% morphological filtering
BW = bwmorph(im,'remove');
figure,imshow(BW);
title('morphological filtering');
%% edge detection algorithm
BW1 = edge(BW,'sobel');
figure,imshow(BW1);
title('edge detection(sobel)');
%% overlaying image
H = vision.AlphaBlender;
J = im2single(J);
BW1 = im2single(BW1);
Y = step(H,J,BW1);
figure,imshow(Y)
title('overlay on grayscale image');
%whos
%% final display
figure,imshow(J);
hold on;
contour(BW1,100);
hold off;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/part3-210628101538/75/TRAFFIC-MANAGEMENT-THROUGH-SATELLITE-IMAGING-Part-3-14-2048.jpg)


