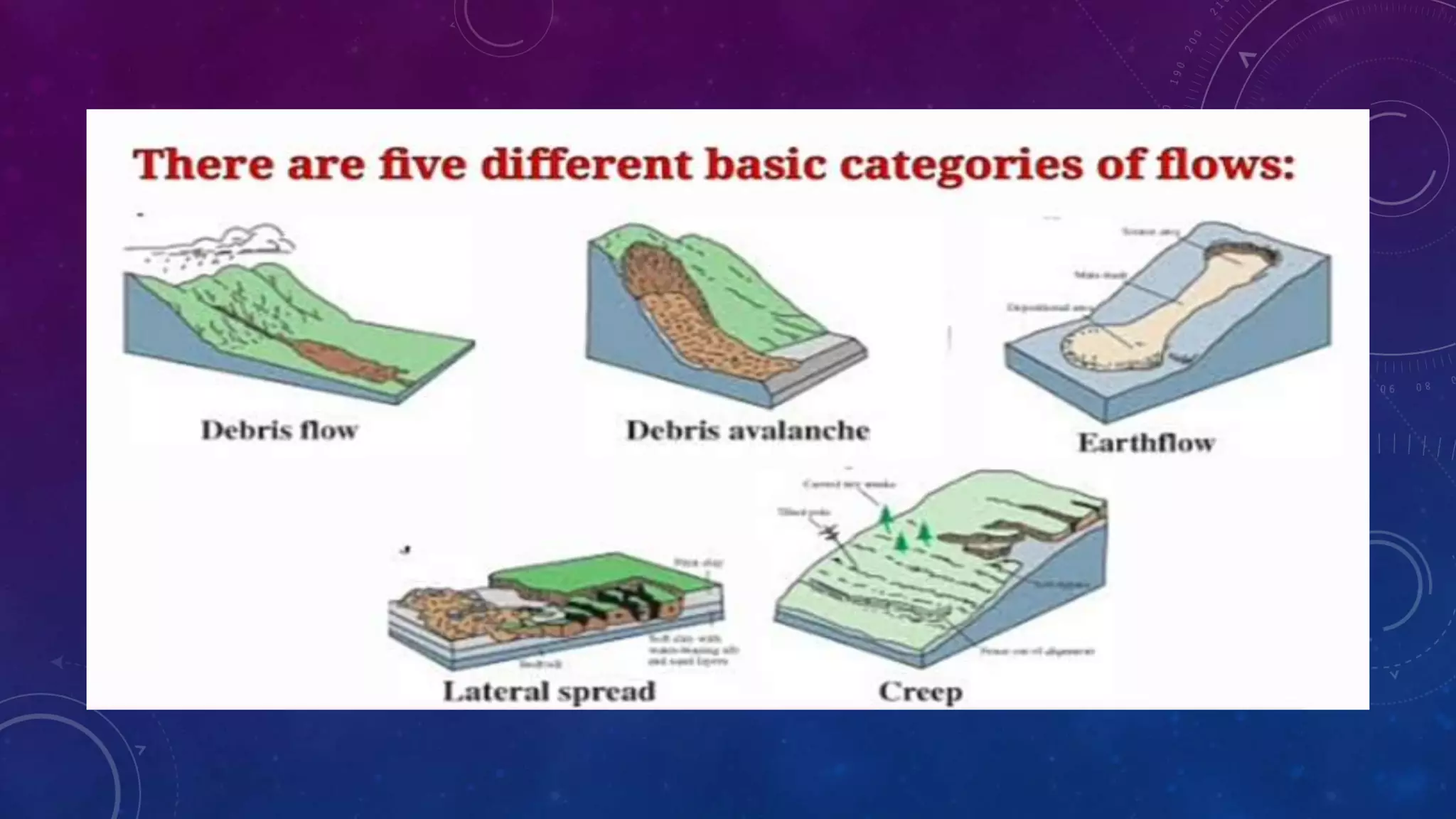
Team Boyles presented on geological hazards. They identified areas prone to hazards from earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and landslides using hazard maps. The team described the different geological hazards including earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and landslides. They explained how hazard maps help identify vulnerable areas and their usefulness for disaster management.