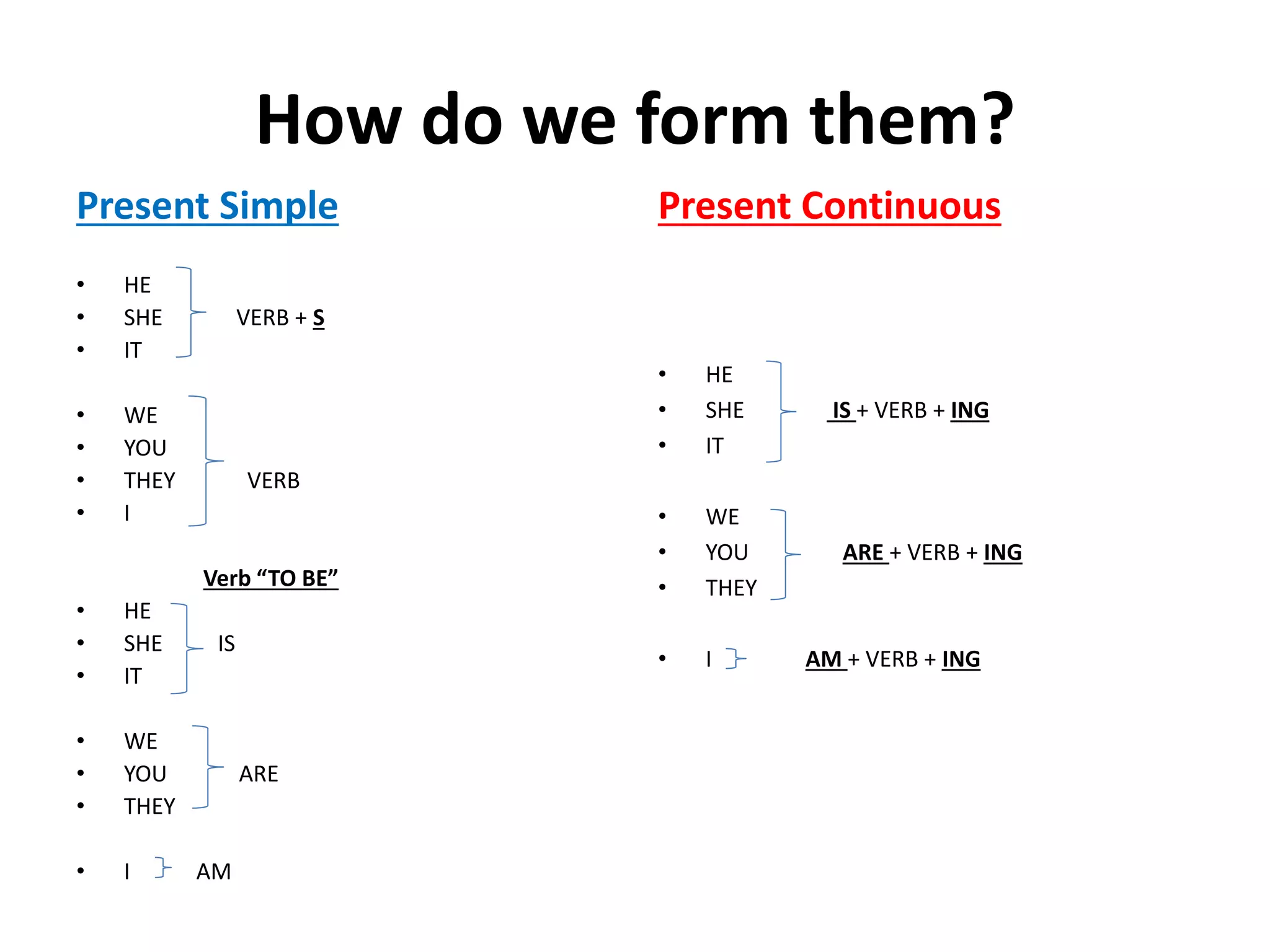
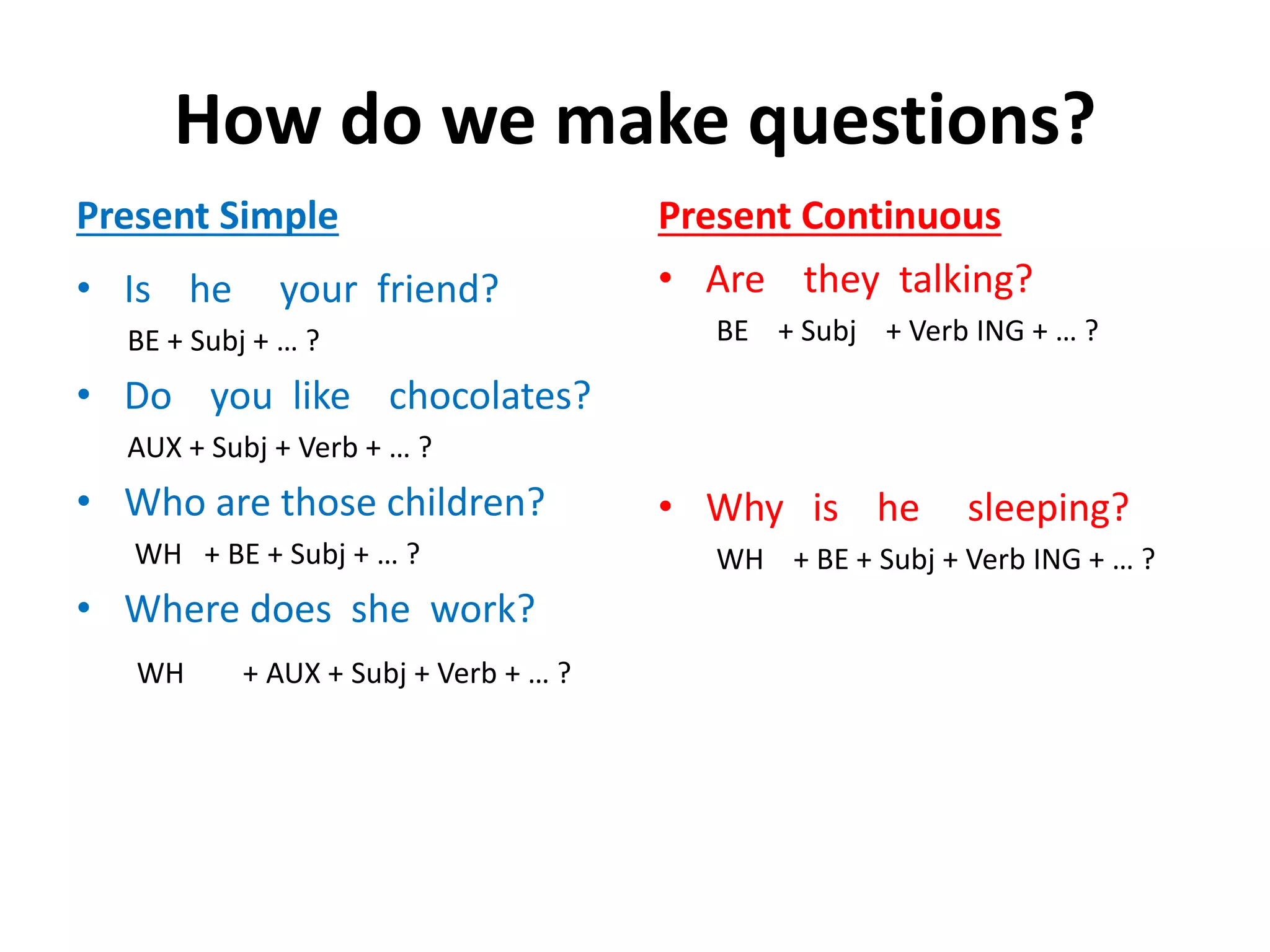
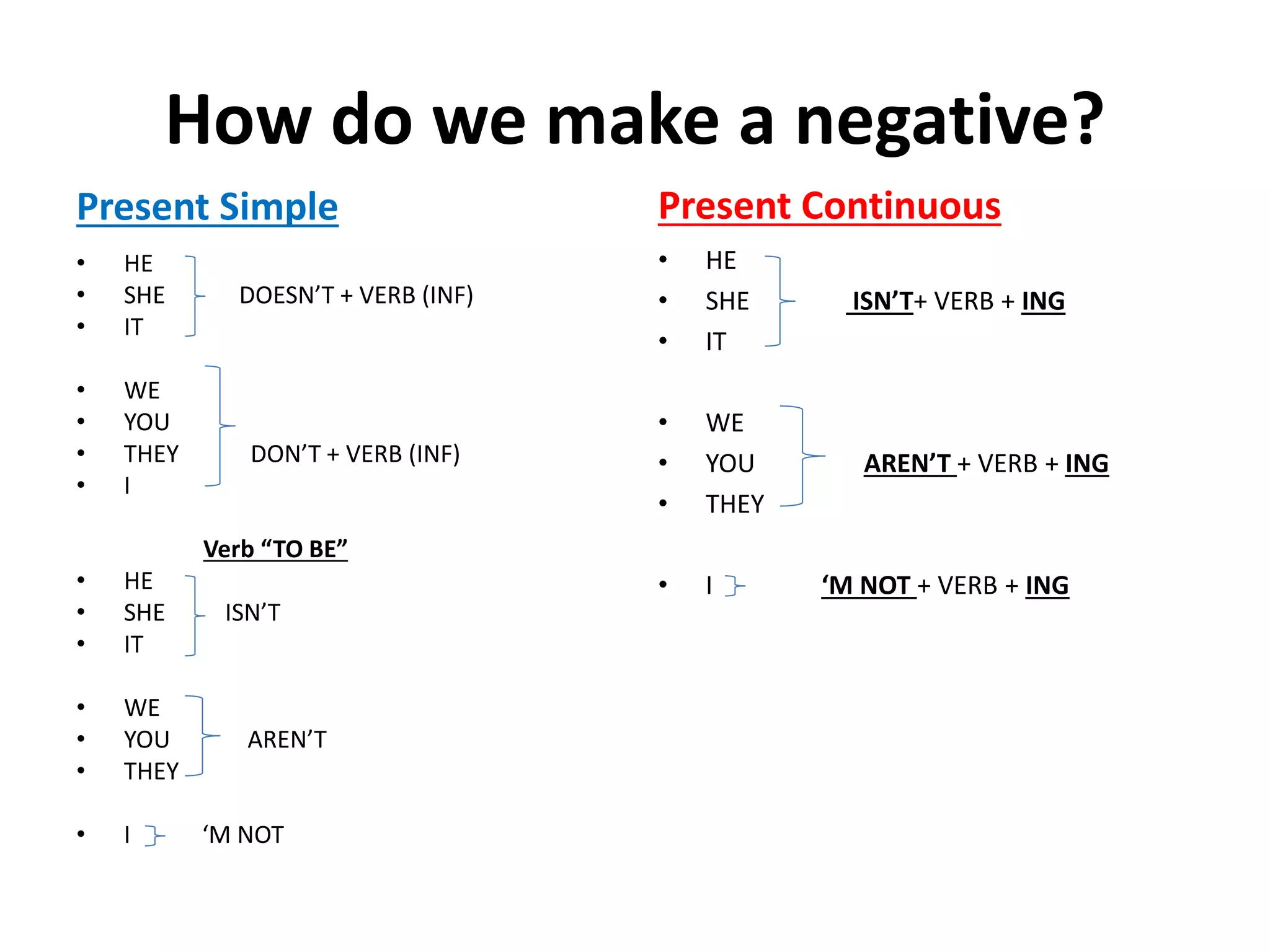
This document provides information on the proper use of the present simple and present continuous tenses in English. It explains how to form, question, and negate sentences using these tenses. It also discusses when each tense should be used, such as for permanent situations versus temporary actions. Finally, it covers the use of adverbs of frequency and state verbs with these tenses.