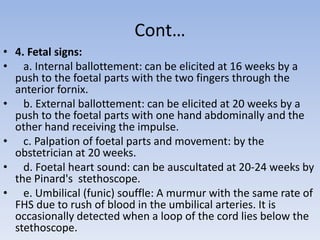
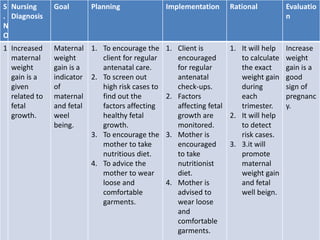
The document discusses pregnancy, including its definition and symptoms across three trimesters, along with trends in midwifery and obstetrics. It highlights changes in birthing practices, the increased emphasis on antenatal care, and the evolution of medical approaches to childbirth. Additionally, it outlines diagnostic methods, common pregnancy-related disorders, and guidelines for nursing care during pregnancy.