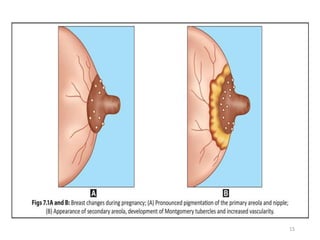
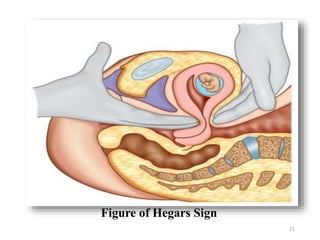
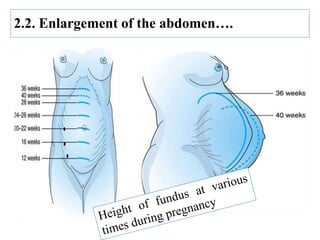
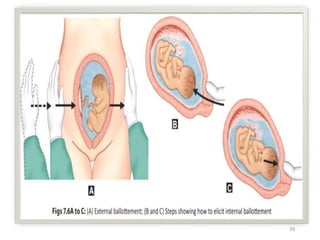
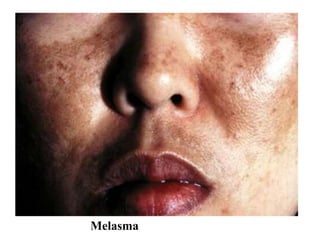
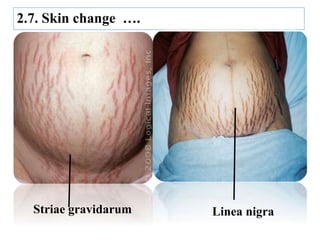
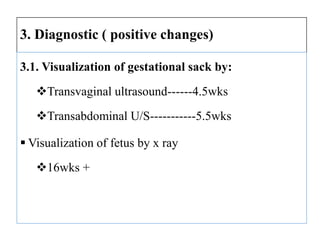
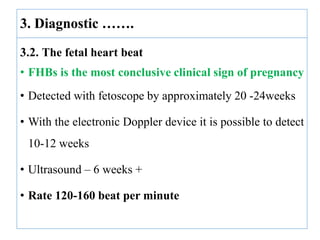
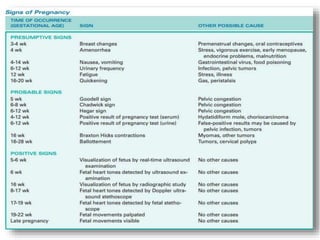
The document describes the diagnosis of pregnancy through various signs and symptoms. It distinguishes between possible/presumptive signs (based on a woman's subjective reports), probable signs (combining subjective and objective findings), and positive signs (conclusive proof of pregnancy). Possible signs include missed period, morning sickness, breast changes, frequent urination, and quickening. Probable signs involve pelvic exam findings, abdominal enlargement, and ballottement. Positive signs are fetal heart tones, palpation of the fetus, ultrasound examination, and fetal movement. Diagnosis progresses from possible to probable to positive as the pregnancy advances.