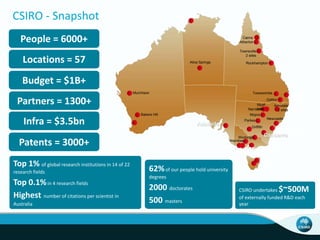
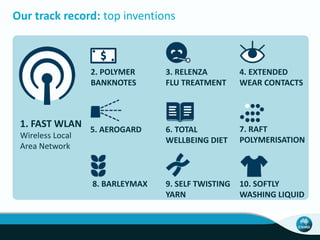
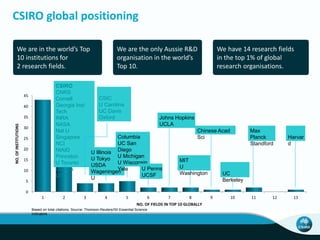
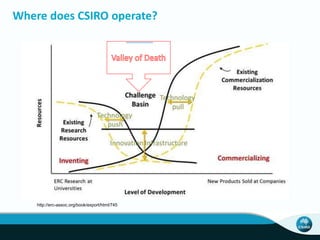
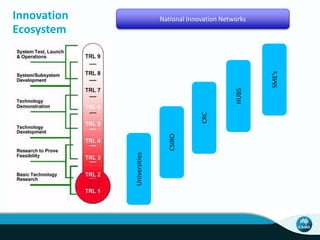
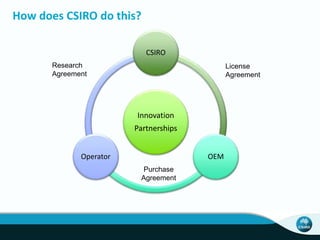
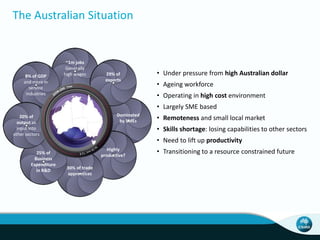
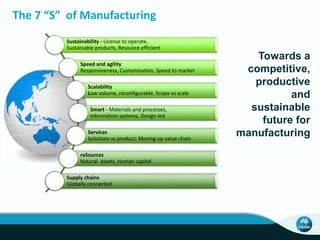
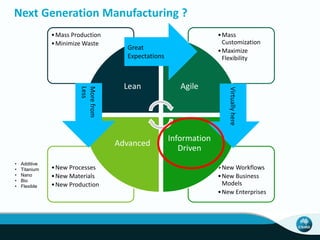
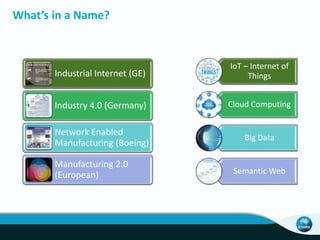
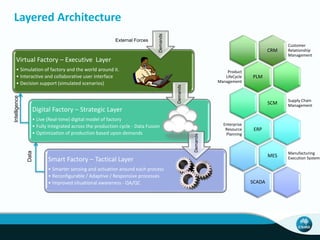
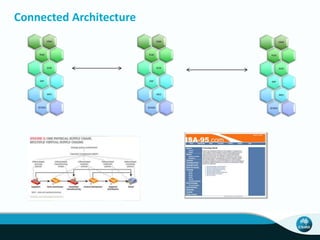
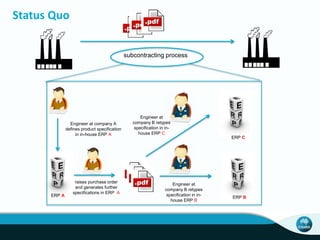
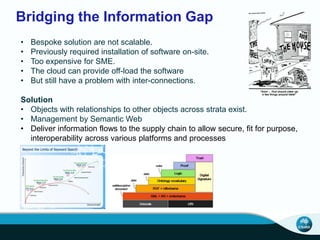
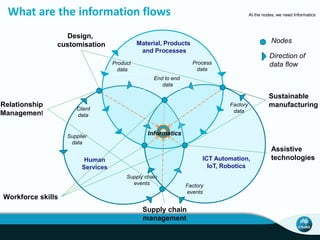
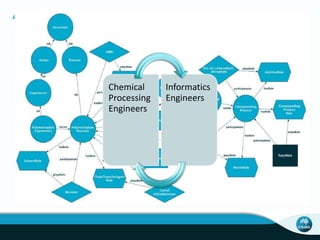
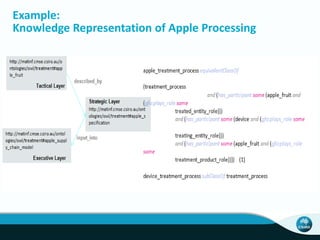
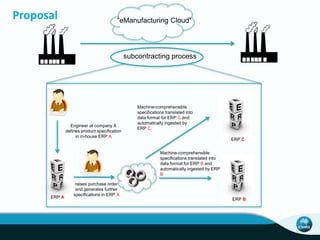
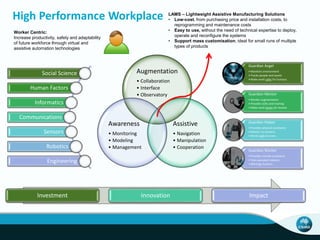
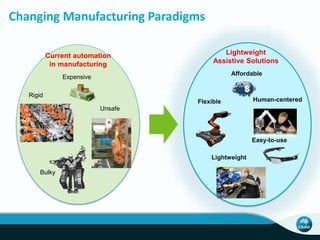
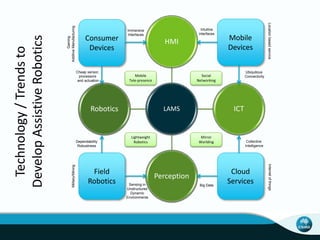
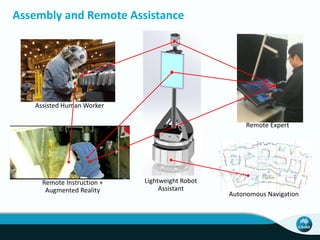
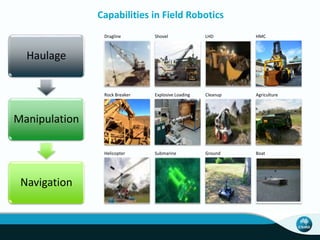
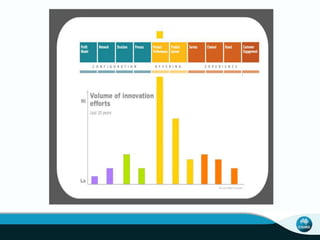
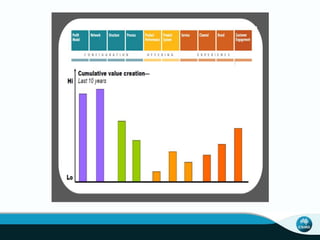
The document outlines CSIRO's role and achievements in future manufacturing, emphasizing its research in autonomous systems, robotics, and innovative technologies. It highlights the importance of adapting the manufacturing sector to emerging opportunities to enhance Australia's economic resilience. CSIRO operates numerous facilities and collaborates with global research institutions to drive advancements in various fields, aiming for a sustainable and productive future in manufacturing.