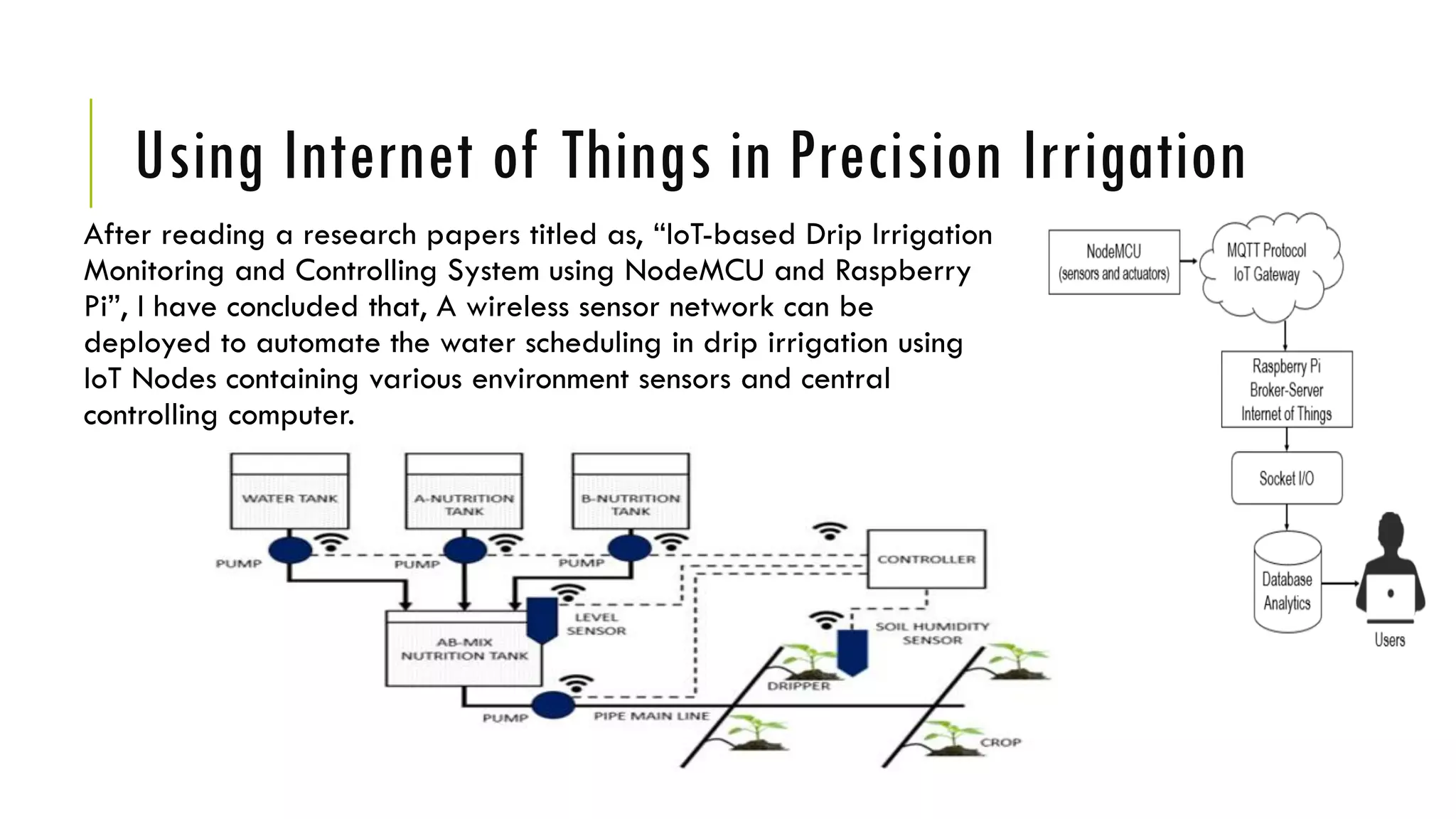
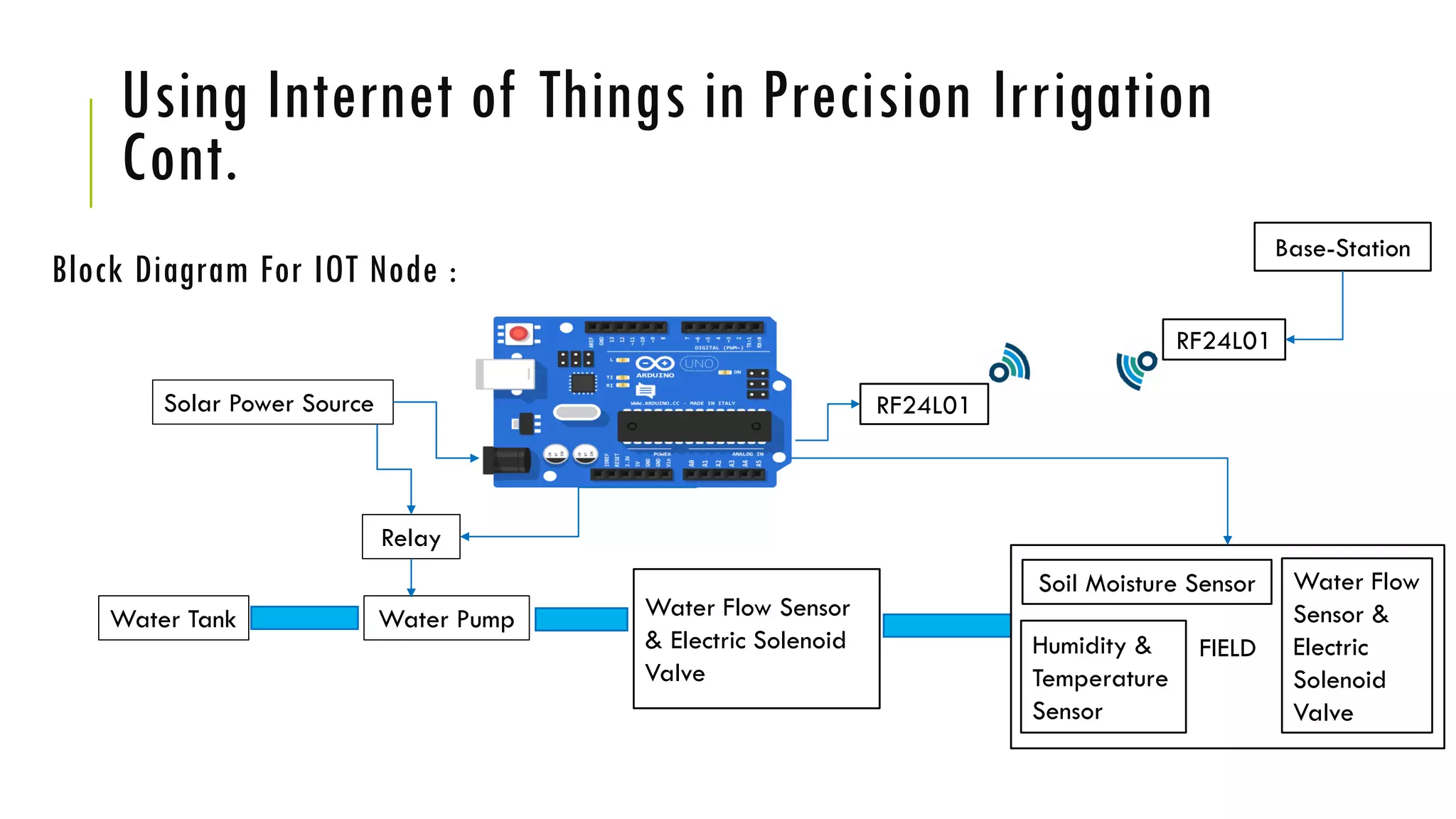
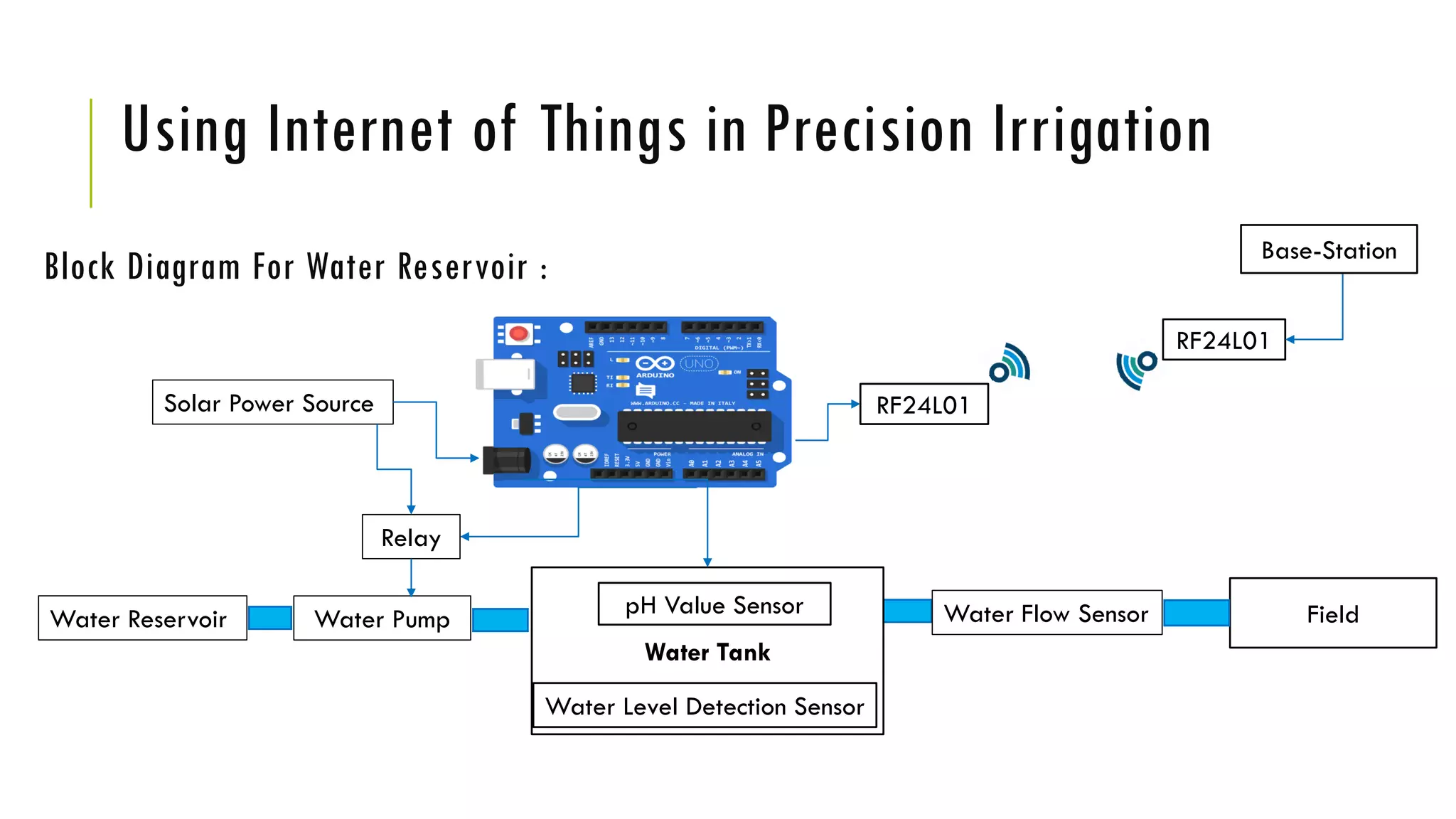
The document discusses precision irrigation, which provides the right amount of water to crops at the right time and place, primarily using drip irrigation systems. It highlights the advantages of drip irrigation, such as significant water savings, uniform water distribution, and suitability for various crops and soil types. Additionally, it explores the integration of machine learning and IoT technologies in precision irrigation, emphasizing their role in optimizing irrigation scheduling through data analysis and automation.