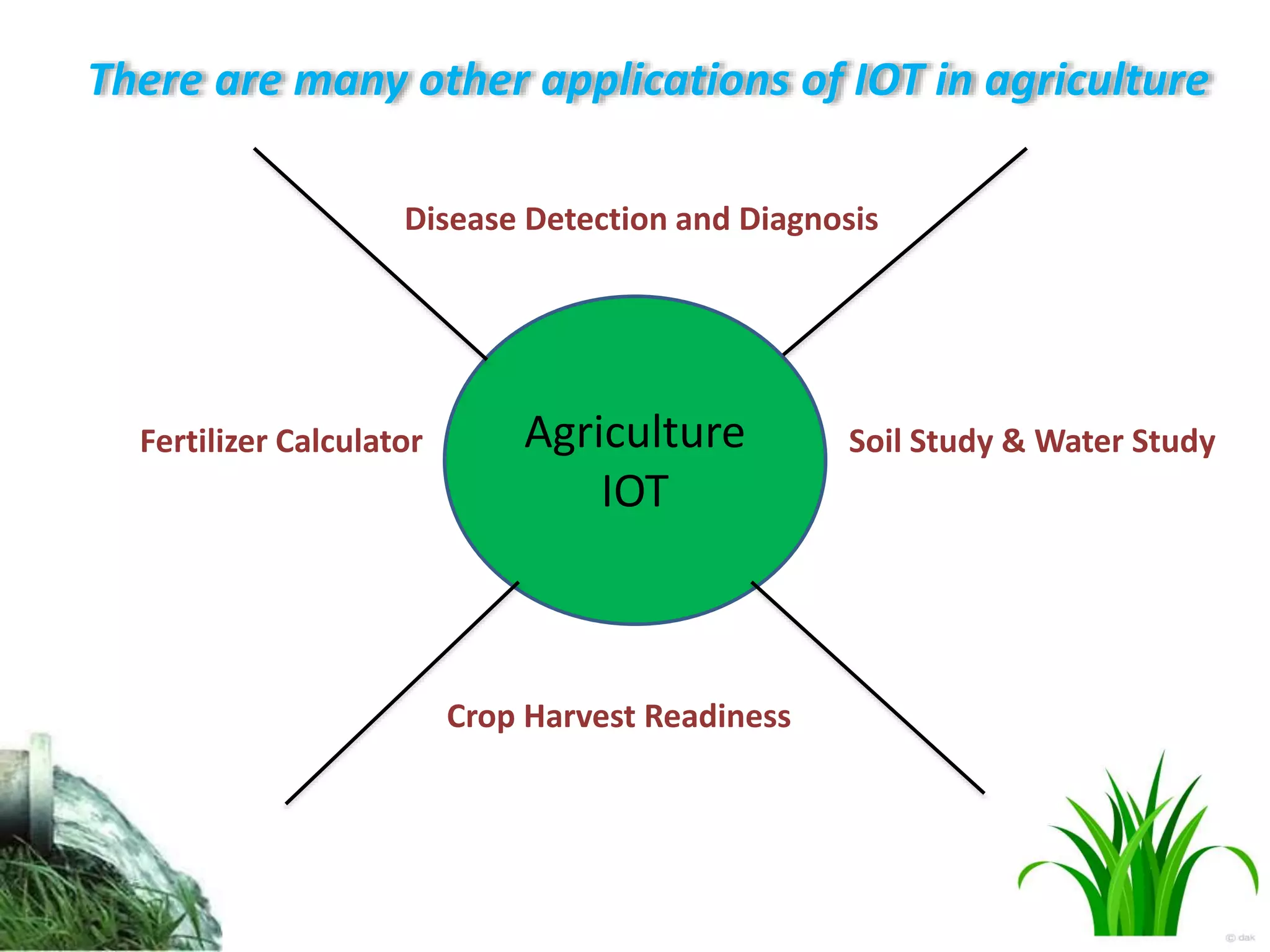
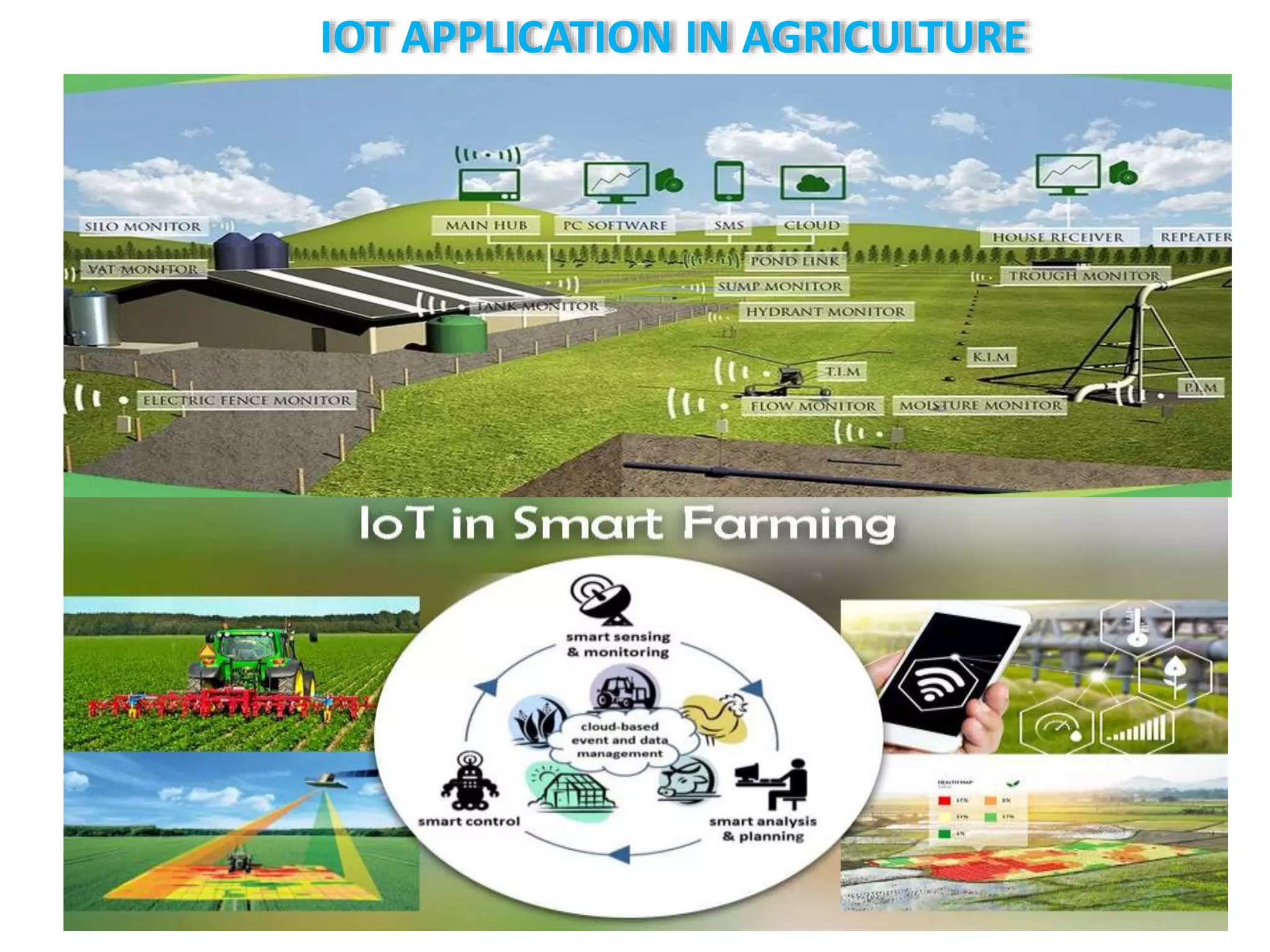
The document discusses the Internet of Things (IoT) and its applications in agriculture, highlighting its rapid growth and benefits, such as improved water conservation and enhanced crop management through smart sensors and drones. It outlines various IoT applications, including precision farming, livestock monitoring, and smart greenhouses, while also noting challenges like costs and technology comprehension in rural areas. Overall, it concludes that IoT can significantly improve agricultural productivity and sustainability.