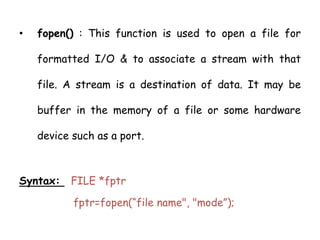
This document discusses file input and output (I/O) in C programming. It defines a file as a connection of bytes stored in secondary storage that can be processed by programs. There are two types of files: text files containing ASCII characters and binary files containing non-ASCII data like images, audio, and video. The document outlines the steps to process a file in C using library functions like fopen() to open a file, fclose() to close it, and fflush() to clear buffers. It also describes various functions for character, string, formatted, and random access I/O.