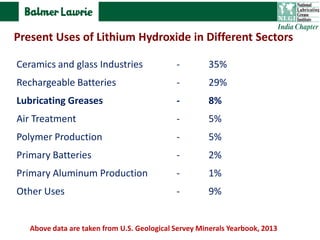
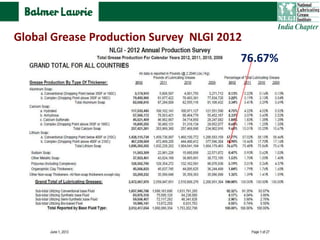
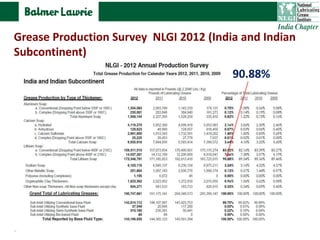
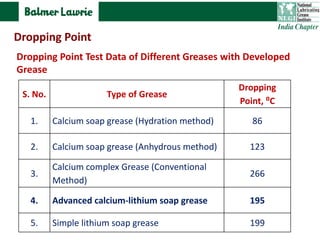
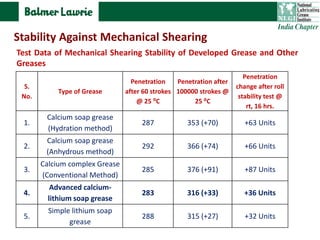
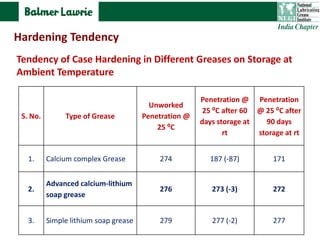
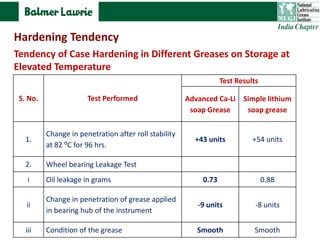
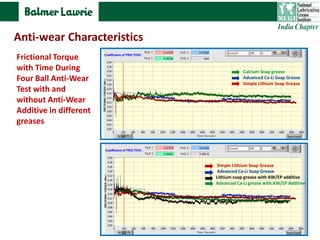
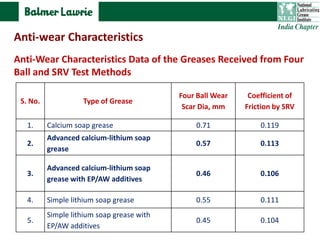
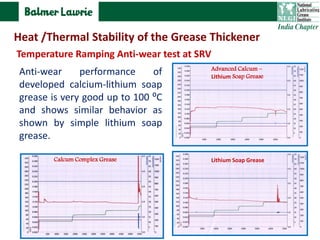
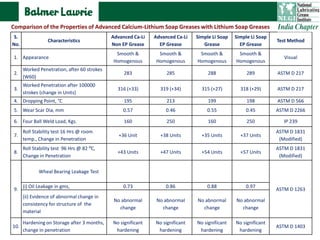
The document describes research into developing an advanced calcium-lithium soap grease using minimal lithium hydroxide. Researchers aimed to create a grease with properties similar to lithium soap greases which have high heat resistance and shear stability. The developed grease was found to have a dropping point, mechanical stability, and wear resistance comparable to lithium soap greases. It also showed much less tendency to harden than conventional calcium greases. The grease can potentially help address the increasing demand and costs of lithium hydroxide from batteries and other uses.